Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 10 Photosynthesis Mastering AP Biology
front 1 Which of the following sequences correctly represents the flow of electrons during photosynthesis? A. H2O > NADPH > Calvin Cycle B. NADPH > Chlorophyll > Calvin Cycle C. NADPH > Electron transport chain > O2 D. NADPH > O2 > CO2 E. H20 > Photosystem 1 > Photosystem 2 | back 1 A. H2O > NADPH > Calvin cycle |
front 2 Photosynthesis is a redox reaction. This means that H2O is _____ during the light reactions and CO2 is _____ during the Calvin cycle. A. Oxidized ... Reduced B. Reduced ... Reduced C. Consumed ... Consumed D. Consumed ... Reduced E. Reduced ... Oxidized | back 2 A. Oxidized ... Reduced |
front 3 What is the basic role of CO2 in photosynthesis? A. CO2 is fixed or incorporated into organic molecules. B. CO2 is taken in by plants as a form of inverse respiration, in which carbon dioxide is “breathed in” and oxygen is “breathed out.” C. CO2 is a source of electrons in the formation of organic molecules. | back 3 A. CO2 is fixed or incorporated into organic molecules. |
front 4 Which of the following is a product of the light reactions of photosynthesis? A. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate B. High-energy photons C. Oxygen, ATP, and NADPH D. NADP+ and RuBP E. Water and CO2 | back 4 C. Oxygen, ATP, and NADPH |
front 5 Photosystem 1 Photosystem 2 Photosystem 1 & 2 Reduction of NADP+ Reduction of primary electron acceptor Oxidation of electron transport chain between two photosystems Reduction of electron transport chain between the two photosystems Light absorption Oxidation of water | back 5 Photosystem 1 Oxidization of water Reduction of electron transport chain between the two photosystems P2 Reduction of NADP+ Oxidation of electron transport chain between two photosystems P1&2 Reduction of primary electron acceptor Light absorption |
front 6 Electron transport step l Energy input required
| back 6 Electron transport step l Energy input required
|
front 7 Diagram of H+ movement | back 7
|
front 8 When light strikes chlorophyll molecules, they lose electrons, which are ultimately replaced by _____. A. Oxidizing glucose B. Fixing carbon C. Splitting water D. Breaking down ATP E. Removing them from NADPH | back 8 C. Splitting water |
front 9 C4 plants occur more commonly in desert conditions because _____. A. They store carbon by incorporating CO2 into organic acids that are later catabolized B. They produce water as a product of their photosynthetic pathways C. The stomata open at night and close in the day D. They can fix carbon at the lower CO2 concentrations that develop when the stomata are closed E. They produce carbon dioxide internally via photorespiration | back 9 D. They can fix carbon at the lower CO2 concentrations that develop when the stomata are closed |
front 10 Carbon fixation involves the addition of carbon dioxide to _____. A. Rubisco B. G3P C. NADPH D. RuBP E. 3-PGA | back 10 D. RuBP |
front 11 After 3-PGA is phosphorylated, it is reduced by _____. A. CO2 B. NADPH C. ATP D. ADP E. NADP+ | back 11 B. NADPH |
front 12 How many carbon dioxide molecules must be added to RuBP to make a single molecule of glucose? A. 6 B. 2 C. 10 D. 4 E. 8 | back 12 A. 6 |
front 13 In the Calvin cycle, how many ATP molecules are required to regenerate RuBP from five G3P molecules? A. 1 B. 3 C. 2 D. 4 E. 5 | back 13 B. 3 |
front 14 Which term describes ATP production resulting from the capture of light energy by chlorophyll? A. Substrate-level phosphorylation B. Photophosphorylation C. Dephosphorylation D. Oxidative phosphorylation | back 14 B. Photophosphorylation |
front 15 True or false? The chemiosmotic hypothesis states that the synthesis of ATP generates a proton gradient that leads to electron flow through an electron transport chain. True False | back 15 False |
front 16 According to the chemiosmotic hypothesis, what provides the energy that directly drives ATP synthesis? A. Temperature gradient B. Osmotic gradient C. Electrons D. Proton gradient | back 16 D. Proton gradient |
front 17 Which of the following particles can pass through the ATP synthase channel? A. ATP B. ADP C. Inorganic phosphate D. Protons | back 17 D. Protons |
front 18 True or false? The region of ATP synthase that catalyzes the production of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate spans the chloroplast membrane. True False | back 18 False |
front 19 Chloroplast membrane vesicles are equilibrated in a simple solution of pH 5. The solution is then adjusted to pH 8. Which of the following conclusions can be drawn from these experimental conditions? A. ATP will be produced because the proton gradient favors proton movement through the ATP synthase channels. B. ATP will not be produced because there is no ADP and inorganic phosphate in the solution. C. The change in the solution's pH results in a gradient across the chloroplast membranes such that there is a lower concentration of protons inside the vesicles and a higher concentration outside. D. Protons will not diffuse toward the outside of the vesicles. | back 19 B. ATP will not be produced because there is no ADP and inorganic phosphate in the solution. |
front 20 _____ has a longer wavelength than _____. A. Yellow ... red B. Red ... green C. Violet ... blue D. Green ... yellow E. Blue ... green | back 20 B. Red ... green |
front 21 The overall function of the Calvin cycle is _____. A. Making sugar B. Producing carbon dioxide C. Capturing sunlight D. Splitting water E. Oxidizing glucose | back 21 A. Making sugar |
front 22 In mechanism, photophosphorylation is most similar to A. Reduction of NADP+. B. Carbon fixation. C. The Calvin cycle. D. Oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration. E. Substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis. | back 22 D. Oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration. |
front 23 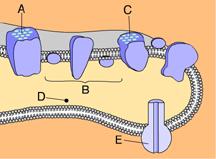 Which of these phosphorylates ADP to make ATP? a. A b. D c. E d. C e. B | back 23 C. E |
front 24 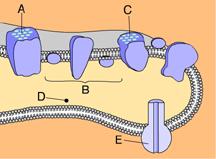 _____ releases energy that is used to pump hydrogen ions from the stroma into the thylakoid compartment. A. E B. C C. B D. D E. A | back 24 C. B |
front 25 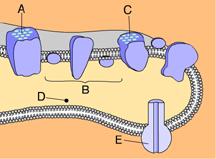 _____ splits water into 1/2 O2, H+, and e- . A. B B. C C. A D. E E. D | back 25 C. A |
front 26 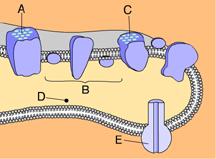 Energized electrons from ____ enter an electron transport chain and are then used to reduce NADP+. A. B B. E C. A D. C E. D | back 26 D. C |
front 27 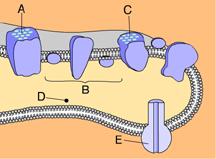 Chlorophyll can be found in _____. A. B and C B. A and C C. A and B D. B and D E. B and E | back 27 B. A and C |
front 28 Which of these equations best summarizes photosynthesis? A. C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 12 H2O B. H2O → 2 H+ + 1/2 O2 + 2e- C. 6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 D. 6 CO2 + 6 O2 → C6H12O6 + 6 H2O E. C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy | back 28 C. 6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 |
front 29 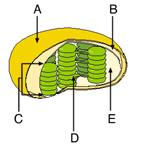 Where does the Calvin cycle occur? A. C B. E C. D D. B E. A | back 29 B. E |
front 30 The light reactions of photosynthesis use _____ and produce _____. A. Water ... NADPH B. NADPH ... oxygen C. Carbon dioxide ... oxygen D. NADPH ... NADP+ E. Carbon dioxide ... sugar | back 30 A. Water ... NADPH |
front 31 Select the correct molecule that is the main product of the Calvin cycle. A. G3P B. NADPH C. Glucose | back 31 A. G3P |
front 32 In C3 plants the conservation of water promotes _____. A. A shift to C4 photosynthesis B. The light reactions C. The opening of stomata D. Photosynthesis E. Photorespiration | back 32 E. Photorespiration |
front 33 In C4 and CAM plants carbon dioxide is fixed in the _____ of mesophyll cells. A. Grana B. Thylakoids C. Cytoplasm D. Stomata E. Stroma | back 33 C. Cytoplasm |
front 34 C4 plants differ from C3 and CAM plants in that C4 plants _____. A. Use malic acid to transfer carbon dioxide to the Calvin cycle B. Transfer fixed carbon dioxide to cells in which the Calvin cycle occurs C. Are better adapted to wet conditions D. Open their stomata only at night E. Use PEP carboxylase to fix carbon dioxide | back 34 B. Transfer fixed carbon dioxide to cells in which the Calvin cycle occurs |
front 35 How is photosynthesis similar in C4 plants and CAM plants? A. In both cases, rubisco is not used to fix carbon initially. B. Both types of plants make sugar without the Calvin cycle. C. In both cases, only photosystem I is used. D. Both types of plants make most of their sugar in the dark. E. In both cases, thylakoids are not involved in photosynthesis. | back 35 A. In both cases, rubisco is not used to fix carbon initially. |