Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Ch 14 - Mendel and the Gene Idea
front 1 How could the botanist best determine whether the genotype of the green-pod plant is homozygous or heterozygous? | back 1 Cross the green-pod plant with a yellow-pod plant. |
front 2 Suppose that the botanist carried out the test cross described in Parts A and B and determined that the original green-pod plant was heterozygous (Gg). Which of Mendel’s findings does her test cross illustrate? | back 2 law of segregation |
front 3 During which part of meiosis (meiosis I or meiosis II) do the two alleles of a gene separate? During which phase does the separation occur? | back 3 meiosis I, anaphase |
front 4 What is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals? | back 4 All of the gametes from a homozygote carry the same version of the gene while those of a heterozygote will differ. |
front 5 When constructing a Punnett square, the symbols on the outside of the boxes represent _______, while those inside the boxes represent _______. | back 5 gametes, progeny |
front 6 True or false? The same phenotype can be produced by more than one genotype. | back 6 True |
front 7 A tall, purple-flowered pea plant (TtPp) is allowed to self-pollinate. (The recessive alleles code for short plants and white flowers.) The phenotypic ratio of the resulting offspring is 9:3:3:1. What is the genotype of the plant whose phenotype appeared once out of every 16 offspring (the "1" in the 9:3:3:1 ratio)? | back 7 ttpp |
front 8 A dominant phenotype is indeed expressed if the individual is homozygous dominant for that trait, but the dominant phenotype is also expressed if the individual is heterozygous for the trait. In fact, heterozygous expression is the definition of dominant. | back 8 true |
front 9 If an organism with the genotype AaBb produces gametes, what proportion of the gametes would be Bb? | back 9 none |
front 10 Two mice are heterozygous for albinism (Aa) . The dominant allele (A) codes for normal pigmentation, and the recessive allele (a) codes for no pigmentation. What percentage of their offspring would have an albino phenotype? | back 10 25
|
front 11 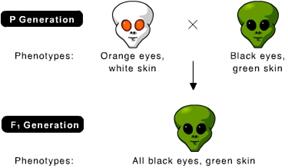 What is the genotype of the parent with orange eyes and white skin? (Note: orange eyes are recessive.) | back 11 bbgg
|
front 12 Black eyes are dominant to orange eyes, and green skin is dominant to white skin. Sam, a MendAlien with black eyes and green skin, has a parent with orange eyes and white skin. Carole is a MendAlien with orange eyes and white skin. If Sam and Carole were to mate, the predicted phenotypic ratio of their offspring would be _____. | back 12 1 black eyes, green skin : 1 black eyes, white skin : 1 orange eyes, green skin : 1 orange eyes, white skin
|
front 13 In order to determine the genotype of a MendAlien with black eyes and green skin, you would cross this individual with a(n) _____ individual. | back 13 bbgg |
front 14 A cross between an individual with orange eyes and green skin and an individual with black eyes and white skin is an example of a _____ cross. | back 14 dihybrid |
front 15 A phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 in the offspring of a cross indicates that _____. | back 15 both parents are heterozygous for both genes |
front 16 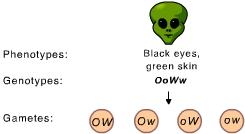 The observed distribution of alleles into gametes is an illustration of _____. | back 16 Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment |
front 17 An individual heterozygous for eye color, skin color, and number of eyes mates with an individual who is homozygous recessive for all three characters; what would be the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? [Hint: B = black eyes, b = orange eyes; G = green skin, g = white skin; C = two eyes, c = one eye] | back 17 1 black eyes, green skin, two eyes : 1 black eyes, green skin, one eye : 1 black eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 black eyes, white skin, one eye : 1 orange eyes, green skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, green skin, one eye : 1 orange eyes, white skin, two eyes : 1 orange eyes, white skin, one eye |
front 18 A BbGg x bbgg cross yields a phenotypic ratio of approximately 5 black eyes, green skin : 5 orange eyes, white skin : 1 black eyes, white skin : 1 orange eyes, green skin. Which of the following best explains these results? | back 18 Mendel's law of independent assortment is being violated. |
front 19 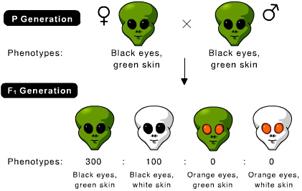 In the following cross the genotype of the female parent is BbGg. What is the genotype of the male parent? [Hint: B = black eyes, b = orange eyes, G = green skin, g = white skin] | back 19 BBGg |
front 20 In a situation in which genes assort independently, what is the ratio of the gametes produced by an AaBB individual? | back 20 1 AB : 1 aB |
front 21 What process is responsible for the independent assortment of alleles? | back 21 Meiosis |
front 22 How do cells acquire homologous chromosome pairs that carry the alleles that are independently assorted? | back 22 Fusion of gametes
|
front 23 Which of the following statements most accurately describes the process of independent assortment? | back 23 Alleles of different genes segregate from one another in a random manner. |
front 24 The principle of independent assortment is best illustrated by events that take place during metaphase I, during which nonhomologous chromosomes segregate independently of each other. | back 24 this is correct |
front 25 How many genetically unique types of gametes could be produced by an individual with the genotype RrYY? | back 25 Two |
front 26 Which of the following parental genotypes would yield a 1:1:1:1 phenotypic ratio in the offspring? | back 26 AaBb, aabb |
front 27 In his breeding experiments, Mendel first crossed true-breeding plants to produce a second generation, which were then allowed to self-pollinate to generate the offspring. How do we name these three generations? | back 27 P ... F1 ... F2
|
front 28 Which of the following is true about a plant with the genotype AABbcc? | back 28 It is homozygous at two loci.
|
front 29 What is an allele? | back 29 alternative version of a gene |
front 30 Mendel's second law of independent assortment has its basis in which of the following events of meiosis I? | back 30 alignment of tetrads at the equator |
front 31 Mendel worked _____. | back 31 in a monastery
|
front 32 Consider pea plants with the genotypes GgTt and ggtt . These plants can each produce how many type(s) of gametes? | back 32 four ... one |
front 33 Two organisms with genotype AaBbCcDdEE mate. These loci are all independent. What fraction of the offspring will have the same genotype as the parents? | back 33 1/16 |
front 34 Two true-breeding stocks of pea plants are crossed. One parent has red, axial flowers and the other has white, terminal flowers; all F1 individuals have red, axial flowers. The genes for flower color and location assort independently.
| back 34 3/16 |
front 35 Labrador retrievers are black, brown, or yellow. In a cross of a black female with a brown male, results can be either all black puppies, 1/2 black to 1/2 brown puppies, or 3/4 black to 1/4 yellow puppies.
| back 35 Epistasis is involved. |
front 36 Drosophila (fruit flies) usually have long wings (+) but mutations in two different genes can result in bent wings (bt) or vestigial wings (vg).
| back 36 3/16 |