Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Biology 191 Final Review - Midterm Exam I
front 1 The fundamental unit of life is: | back 1 The cell |
front 2 The order of events in scientific inquiry are: | back 2 Observations => Predictions => Test Predictions by Experiment => New Observations |
front 3 The change of populations of organisms over many generations is: | back 3 Evolution |
front 4 The ultimate source of energy in the biosphere is: | back 4 Solar Fusion |
front 5 What is the right hierarchical order for biological organization? | back 5 Biosphere > Ecosystem > Community > Species > Individual |
front 6 How many elements are essential for life? | back 6 25 |
front 7 Most of the volume of an atom is made up of: | back 7 Empty Space |
front 8 An atom is generally the most chemically stable when: | back 8 Its entire valence shell is filled. |
front 9 A bond between Bromine (electronegativity: 2.96) and Titanium (electronegativity: 1.54) would be expected to be: | back 9 A Polar Covalent Bond |
front 10 The attraction between the negatively-charged atom on one water molecule and a positively-charged atom on another is a: | back 10 Hydrogen Bond |
front 11 Why is helium (a noble gas) chemically unreactive? | back 11 A solitary helium atom already has its valence shell filled with electrons. |
front 12 What determines what kind of element an atom is? | back 12 The number of protons in the nucleus. |
front 13 A water molecule can have how many hydrogen bonds with adjacent water molecules? | back 13 4 |
front 14 Ionic solids like salts readily dissolve in water because water forms: | back 14 Hydration shells around each ion. |
front 15 Why does evaporating sweat cool us off? | back 15 The hydrogen bonds in water take a lot of energy to break, water has a high heat of vaporization, the evaporating water molecules carry away thermal energy from the liquid, and evaporation absorbs thermal energy while condensation releases it.
|
front 16 A food calorie is defined as: | back 16 The energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 L of water by 1 degree Celsius. |
front 17 When water freezes, the hydrogen bonds between adjacent water molecules: | back 17 Get locked into place, pushing the water molecules further apart. |
front 18 Nonpolar substances prefer to associate with other nonpolar substances and are: | back 18 Hydrophobic |
front 19 The concentration of Hydroxide(OH-) in a solution with a pH of 3 is: | back 19 10^-11 M |
front 20 A solution with a pH of 3 is: | back 20 Acidic |
front 21 What is produced when HCl and NaOH are combined? | back 21 Water, salt, and heat.
|
front 22 Stanley Miller put simple compounds like carbon dioxide, ammonia, hydrogen gas, and water in a closed system, then subjected it to electricity. What did he find? | back 22 He found that simple organic molecules could be formed. |
front 23 This functional group can absorb a H+ ion from water and become positively charged: | back 23 Amino Group |
front 24 This functional group can release a H+ ion into water and become negatively charged: | back 24 Carboxyl Group |
front 25 This functional group is found in alcohols: | back 25 Hydroxyl Group |
front 26 This functional group forms disulfide bridges: | back 26 Sulfhydryl Group |
front 27 This functional group only has carbon-hydrogen bonds: | back 27 Methyl Group |
front 28 Two molecules with the same chemical formula, but different ways of connecting their atoms, are called: | back 28 Isomers |
front 29 Which kind of covalent bond allows the bonded atoms to stably pivot around the bond: | back 29 Single bond |
front 30 The formula for a phosphate functional group is: | back 30 OPO3^2- |
front 31 What is the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fat? | back 31 A saturated fat has no double bonds, while an unsaturated fat has at least one or more. |
front 32 Enantiomers are molecules that: | back 32 Are identical except that they are mirror images of each other. |
front 33 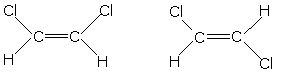 Which of these molecules is a cis configuration? | back 33 The one on the left. |
front 34  What functional group is not a part of this molecule? | back 34 Sulfhydryl Group |
front 35  The above molecule is a monomer that could be used to form a: | back 35 Polypeptide |
front 36  The formula of the side (R) group of the above monomer is: | back 36 -CH2OH |
front 37  Suppose the above monomer were being added to a growing polymer. Which side of the central carbon would have the bond connecting to the polymer? | back 37 The right (Amino terminal) |
front 38 The connections between two sugar monomers in a polysaccharide are called: | back 38 Glycosidic Linkages |
front 39 This polysaccharide is made up of alternating alpha-glucose and beta-glucose molecules: | back 39 Cellulose |
front 40 A fat molecule is made up of: | back 40 One glycerol molecule and three fatty acid molecules. |
front 41 This part of the phospholipids are contacting each other in the middle of a phospholipid bilayer: | back 41 Hydrophobic Tails |
front 42 Lipid molecules consisting of four fused carbon rings are called: | back 42 Steroids |
front 43 This type of protein structure includes alpha helices and beta sheets: | back 43 Secondary Structure |
front 44 The side chain of lysine is -CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-NH2. Lysine is what class of amino acids? | back 44 Basic |
front 45 When you fry an egg white and it changes from clear to solid... | back 45 ...the proteins in the egg are denaturing. |
front 46 This nitrogenous base is only found in DNA and not in RNA | back 46 Thymine |
front 47 Which DNA sequence would correctly pair with the sequence 5'-C-A-T-G-A-G-3'? | back 47 5'-C-T-C-A-T-G-3' |
front 48 This type of cell structure is found in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes: | back 48 Membrane Bound Organelle |
front 49 This organelle is where most biosynthesis occurs in your cells: | back 49 Endoplasmic Reticulum |
front 50 The space contained inside the inner membrane of a mitochondria is called: | back 50 The mitochondrial matrix |
front 51 The cellular compartment used for storage of water or other compounds is: | back 51 Vacuole |
front 52 Which of these is not found in chloroplasts: thylakoids, chlorophyll, DNA molecules, cristae, grana? | back 52 Cristae |
front 53 Which compartment connected to the extracellular matrix is embedded in the plasma membrane? | back 53 Integrin |
front 54 Which cytoskeletal protein does myosin interact with to make muscle fibers contract? | back 54 Actin |
front 55 Which cytoskeletal protein is in the core of motile cilia and flagella? | back 55 Tubulin |
front 56 True or false: Plant cells have both mitochondria and chloroplasts. | back 56 True |
front 57 The ___ is the microtubule organizing center, and contains the ___. | back 57 Centrosome...Centrioles |
front 58 To transport materials and vesicles within the cell, the cytoskeleton is "walked along by: | back 58 Motor Proteins |
front 59 Which of the following enables tissues of cells to form fluid-impermeable sheets? | back 59 Tight Junctions |
front 60 In plants, plasmodesmata are equivalent to what structure in animal cells? | back 60 Gap Junctions |