Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 18- Regulation of Gene Expression
front 1 Which of the following statements best defines the term operon? | back 1 An operon is a region of DNA that codes for a series of functionally related genes under the control of the same promoter. |
front 2 What molecule binds to promoters in bacteria and transcribes the coding regions of the genes? | back 2 RNA polymerase |
front 3 What is allosteric regulation? | back 3 In allosteric regulation, a small molecule binds to a large protein and causes it to change its shape and activity. |
front 4 Under which conditions are the lac structural genes expressed most efficiently? | back 4 No glucose, high lactose |
front 5 What happens to the expression of the lacI gene if lactose is not available in the cell? | back 5 There is no change—the lacI gene is constitutively expressed. |
front 6 What is the function of the lacZ gene? | back 6 This gene encodes an enzyme, b-galactosidase, which cleaves lactose into glucose and galactose. |
front 7 Which of the following enzymes converts ATP to cAMP? | back 7 Adenylyl cyclase |
front 8 True or false? The mechanism by which glucose inhibits expression of the lac structural genes is known as catabolite stimulation, whereas the mechanism by which lactose stimulates expression of the lac structural genes is known as allosteric regulation. | back 8 False
|
front 9 The operon model of the regulation of gene expression in bacteria was proposed by _____. | back 9 Jacob and Monod |
front 10 Which of these is NOT a component of the lac operon? | back 10 regulatory gene only |
front 11 Regulatory proteins bind to _____. | back 11 the operator |
front 12 In the presence of a regulatory protein the lac operon is _____. | back 12 not transcribed
|
front 13 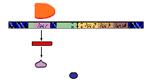 In this animation the blue sphere represents _____. | back 13 lactose
|
front 14 In this animation the orange object represents _____. | back 14 RNA polymerase |
front 15 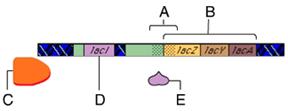 Which of these is a regulatory gene? | back 15 D |
front 16 Why is the lac operon said to be an inducible operon? | back 16 When allolactose is present, it induces the inactivation of the lac repressor. |
front 17 Which statements about the modification of chromatin structure in eukaryotes are true? | back 17 Some forms of chromatin modification can be passed on to future generations of cells.
|
front 18 Which statements about the regulation of transcription initiation in these genes are true? | back 18 The fantasin gene will be transcribed at a high level when activators specific for control elements A, B, and C are present in the cell.
|
front 19 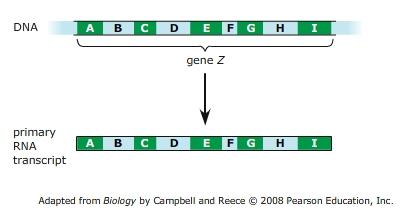 Which of the following choices represent mRNA molecules that could be produced from the primary RNA transcript by alternative RNA splicing? (In each choice, the yellow part on the left represents the 5' cap, and the yellow part on the right represents the poly-A tail.) | back 19  ACEI
|
front 20 _____ bind(s) to DNA enhancer regions. | back 20 Activators |
front 21 What is the event that IMMEDIATELY follows the last event of this animation? | back 21 binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter |
front 22 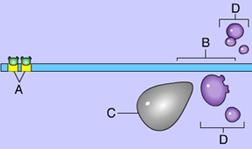 Which of these indicates an enhancer region? | back 22 A
|
front 23 Which of these directly bind(s) to the promoter? | back 23 C and D
|
front 24 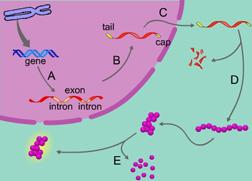 The process of transcription is indicated by the letter _____. | back 24 A
|
front 25 The letter E is indicating a process of gene expression that involves _____. | back 25 protein breakdown |
front 26 RNA processing is indicated by the letter _____. | back 26 B
|
front 27 Which of the following processes is NOT indicated by the label A, B, C, D, or E? | back 27 DNA unpacking
|
front 28 Enzyme complexes that break down protein are called _____. | back 28 proteasomes |
front 29 The nuclear membrane's role in the regulation of gene expression involves _____. | back 29 regulating the transport of mRNA to the cytoplasm |
front 30 What is the function of a spliceosome? | back 30 RNA processing |
front 31 Protein-phosphorylating enzymes' role in the regulation of gene expression involves _____. | back 31 protein activation
|
front 32 DNA methylation is a mechanism used by eukaryotes to do what? | back 32 inactivate genes |
front 33 In humans, the hormone testosterone enters cells and binds to specific proteins, which in turn bind to specific sites on the cells' DNA. These proteins probably act to do what? | back 33 help RNA polymerase transcribe certain genes |
front 34 It is possible for a cell to make proteins that last for months; hemoglobin in red blood cells is a good example. However, many proteins are not this long-lasting; they may be degraded in days, hours, or even minutes. What is the advantage of short-lived proteins? | back 34 Short-lived proteins enable the cells to control their activities precisely and efficiently. |
front 35 miRNAs can control gene expression by what action? | back 35 binding to mRNAs and degrading them or blocking their translation |
front 36 Which of the following would be most likely to lead to cancer? | back 36 amplification of a proto-oncogene and inactivation of a tumor-suppressor gene |
front 37 All your cells contain proto-oncogenes, which can change into cancer-causing genes. Why do cells possess such potential time bombs? | back 37 Proto-oncogenes are necessary for the normal control of cell growth and division. |
front 38 If a particular operon encodes enzymes for making an essential amino acid and is regulated like the trp operon, then | back 38 the amino acid acts as a corepressor. |
front 39 Muscle cells differ from nerve cells mainly because they | back 39 express different genes. |
front 40 Which of the following is an example of post-transcriptional control of gene expression? | back 40 the removal of introns and alternative splicing of exons |
front 41 What would occur if the repressor of an inducible operon were mutated so it could not bind the operator? | back 41 continuous transcription of the operon's genes |
front 42 Within a cell, the amount of protein made using a given mRNA molecule depends partly on | back 42 the rate at which the mRNA is degraded. |
front 43 Proto-oncogenes can change into oncogenes that cause cancer. Which of the following best explains the presence of these potential time bombs in eukaryotic cells? | back 43 Proto-oncogenes normally help regulate cell division. |
front 44 Which statement(s) about inducible operons is/are correct? | back 44 In an inducible operon, the repressor is synthesized in an active form.
|
front 45 Which statement(s) about repressible operons is/are correct? | back 45 Repressible enzymes generally function in anabolic pathways.
|
front 46 Which of the following best describes siRNA? | back 46 a short double-stranded RNA, one of whose strands can complement and inactivate a sequence of mRNA |