Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 11- Cell Communication
front 1 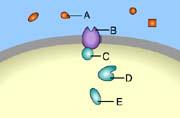 Which of these is a receptor molecule? | back 1 B |
front 2 A signal transduction pathway is initiated when a _____ binds to a receptor. | back 2 signal molecule |
front 3 Which of these is a signal molecule? | back 3 A |
front 4 A signal molecule is also known as a(n) _____. | back 4 Ligand |
front 5 Which of these is the second of the three stages of cell signaling? | back 5 transduction |
front 6 Which of the following provides molecular evidence that signal transduction pathways evolved early in the history of life? | back 6 The molecular details of cell signaling are quite similar in organisms whose last common ancestor was a billion years ago. |
front 7 Which of the following is a substance that acts at a long distance from the site at which it is secreted? | back 7 hormone |
front 8 What is most likely to happen to an animal's target cells that lack receptors for local regulators? | back 8 They might not be able to multiply in response to growth factors from nearby cells. |
front 9 In the formation of biofilms, such as those forming on unbrushed teeth, cell signaling serves which function? | back 9 aggregation of bacteria that can cause cavities |
front 10 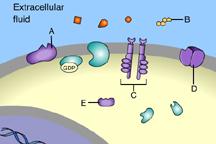 which one of these is NOT a membrane receptor? | back 10 E |
front 11 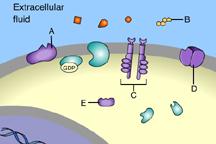 Which of these is a G-protein-linked receptor? | back 11 A |
front 12 Which of these is a receptor tyrosine kinase? | back 12 C |
front 13 Which of these is an ion-channel receptor? | back 13 D |
front 14 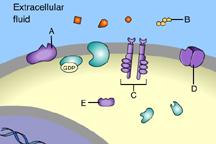 The binding of signal molecules to _____ results in the phosphorylation of tyrosines. | back 14 C |
front 15 Which of these receptor molecules would allow Na+ to flow into the cell? | back 15 D |
front 16 Which of these extracellular signal molecules could diffuse through a plasma membrane and bind to an intracellular receptor? | back 16 estrogen |
front 17 A(n) _____ is an example of a signal molecule that can bind to an intracellular receptor and thereby cause a gene to be turned on or off. | back 17 steroid |
front 18 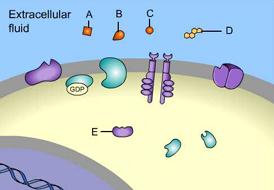 _____ is a signal molecule that binds to an intracellular receptor | back 18 D |
front 19 Thyroid hormones bind to _____ receptors. | back 19 intracellular |
front 20 To what does the term "ligand" refer in cell biology? | back 20 any small molecule that can bind in a specific manner to a larger one |
front 21 Dioxin, produced as a by-product of various industrial chemical processes, is suspected of contributing to the development of cancer and birth defects in animals and humans. It apparently acts by entering cells by simple diffusion and binding to proteins in the cytoplasm, then altering the pattern of gene expression. Which of the following are likely to be the cytoplasmic proteins to which dioxin binds? | back 21 transcription factors |
front 22 What is the function of tyrosine-kinase receptors? | back 22 enzymatic phosphorylation of tyrosine in the receptor protein |
front 23 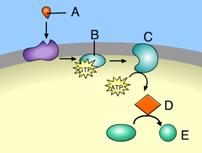 Which of these acts as a second messenger? | back 23 D |
front 24 Which of the following are among the most common second messengers? | back 24 calcium ion and cAMP |
front 25 Which of the following sequences is correct? | back 25 binding of a growth factor to its receptor → phosphorylation cascade → activation of transcription factor → transcription
|
front 26 Which of the following could account for the different cellular responses to histamine? Select all that apply. | back 26 the cell type in which the histamine receptor is located
|
front 27 Which of these is a logical signal transduction pathway? | back 27 A G-protein-linked receptor activates G protein, which activates phospholipase C, which cleaves a membrane lipid to form IP3, which binds to a calcium channel on the ER, which opens to release calcium ions into the cytoplasm, which bind to an intracellular enzyme that carries out a response. |
front 28 What is apoptosis? | back 28 controlled cell suicide |
front 29 Phosphorylation cascades involving a series of protein kinases are useful for cellular signal transduction because | back 29 they amplify the original signal manyfold. |
front 30 Binding of a signaling molecule to which type of receptor leads directly to a change in the distribution of ions on opposite sides of the membrane? | back 30 ligand-gated ion channel |
front 31 The activation of receptor tyrosine kinases is characterized by | back 31 dimerization and phosphorylation. |
front 32 Lipid-soluble signaling molecules, such as testosterone, cross the membranes of all cells but affect only target cells because | back 32 intracellular receptors are present only in target cells. |
front 33 Consider this pathway: epinephrine →\rightarrow G protein-coupled receptor →\rightarrow G protein →\rightarrow adenylyl cyclase →\rightarrow cAMP. Identify the second messenger. | back 33 cAMP |
front 34 Apoptosis involves all but which of the following? | back 34 lysis of the cell
|
front 35 Which observation suggested to Sutherland the involvement of a second messenger in epinephrine's effect on liver cells? | back 35 Glycogen breakdown was observed only when epinephrine was administered to intact cells. |
front 36 Protein phosphorylation is commonly involved with all of the following except | back 36 activation of G protein-coupled receptors. |
front 37 What are the functions of signal transduction pathways? | back 37 Signal transduction pathways amplify the effect of a signal molecule.
|
front 38 Which statement correctly distinguishes the roles of protein kinases and protein phosphatases in signal transduction pathways? | back 38 Protein kinases activate enzymes by phosphorylating or adding phosphate groups to them. Protein phosphatases dephosphorylate or remove phosphate groups from enzymes, including protein kinases. |
front 39 Select the statement that correctly distinguishes between relay proteins and second messengers in signal transduction pathways. | back 39 Signal transduction pathways are multistep pathways that include relay proteins and small, nonprotein, water-soluble molecules or ions called second messengers. |
front 40 Cyclic GMP, or cGMP, acts as a signaling molecule whose effects include relaxation of smooth muscle cells in artery walls. In the penis, this signaling pathway and the resulting dilation of blood vessels leads to an erection. Select the correct statement about the effect of Viagra on this signaling pathway. | back 40 Viagra inhibits the hydrolysis of cGMP to GMP. |
front 41 The cholera bacterium Vibrio cholerae produces an enzyme toxin that chemically modifies a G protein involved in regulating salt and water secretion in intestinal cells. Stuck in its active form, the modified G protein stimulates the production of a high concentration of cAMP, which causes the intestinal cells to secrete large amounts of salts into the intestines, with water following by osmosis. An infected person quickly develops profuse diarrhea and if left untreated can soon die from the loss of water and salts. What is the basic effect of the cholera toxin? | back 41 The basic effect of the cholera toxin is signal amplification. |
front 42 Which of the following is true of steroid receptors? | back 42 The receptor may be inside the nucleus of a target cell. |
front 43 Why are there often so many steps between the original signal event and the cell's response? | back 43 Each step in a cascade produces a large number of activated products, causing signal amplification as the cascade progresses. |
front 44 Why can a signaling molecule cause different responses in different cells? | back 44 The transduction process is unique to each cell type; to respond to a signal, different cells require only a similar membrane receptor. |
front 45 Transcription factors _____. | back 45 Control gene expression |