Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 5 Doppler Prinicples - Review
front 1 Which of the following are parts of the circulatory system?
| back 1 A) Heart
|
front 2 The _____ are the tiniest vessels in te circulatory system. | back 2 Capillaries
|
front 3 In which of the following can Doppler ultrasound detect flow?
| back 3 A) the heart
|
front 4 To flow is to move in a _____. | back 4 stream
|
front 5 The characteristic of a fluid that offers resistance to flow is called _____.
| back 5 B) viscosity
|
front 6 Poise is a unit of _____. | back 6 viscosity
|
front 7 Pressure is _____ per unit area. | back 7 force
|
front 8 Pressure is _____.
| back 8 C) omnidirectional
|
front 9 Flow is a response to pressure _____ or _____. | back 9 difference, gradient
|
front 10 If the pressure is greater at on end of a liquid-filled tube or vessel than it is at the other, the liquid will flow from the _____-pressure end to the _____-pressure end.
| back 10 A) higher, lower
|
front 11 The volumetric flow rate in a tube is determined by _____ difference and _____. | back 11 The volumetric flow rate in a tube is determined by pressure difference and resistance.
|
front 12 Flow increases if _____ increases.
| back 12 D) A and B
|
front 13 As flow resitance increases, volumetric flow rate _____. | back 13 decreases
|
front 14 If pressure difference is doubled, volumetric flow rate is _____.
| back 14 D) doubled
|
front 15 If flow resitance is doubled, volumetric flow rate is _____.
| back 15 C) halved
|
front 16 Flow resitance in a vessel depends on _____.
| back 16 D) all of the above
|
front 17 Flow resitance decreases with an increase in _____.
| back 17 B) vessel radius
|
front 18 Flow resistance depends most strongly in _____.
| back 18 B) vessel radius
|
front 19 Volumetric flow rate decreases with an increase in _____.
| back 19 E) C and D
|
front 20 When the speed of a fluid is constant across a vessel, the flow is called _____ flow.
| back 20 E) plug
|
front 21 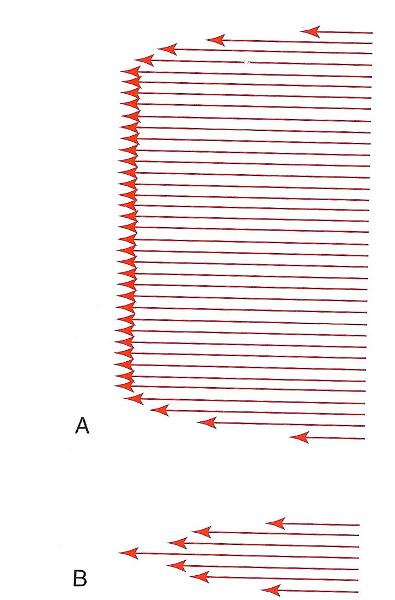 The type of flow (approximately) seen in A is _____.
| back 21 E) plug |
front 22 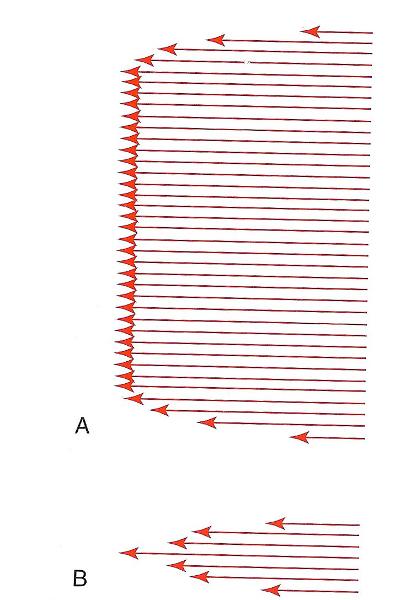 The type of flow seen in B is ____.
| back 22 C) parabolic |
front 23 _____ flow occurs when straight parallel streamlines describing the flow are altered. | back 23 disturbed
|
front 24 _____ flow involves random and chaotic flow patterns, with particles flowing in all directions. | back 24 turbulent
|
front 25 Turbulent flow is more likely proximal of distal to a stenosis. | back 25 distal
|
front 26 A narrowing of the lumen of a tube is called a _____. | back 26 stenosis
|
front 27 Proximal to, at, and distal to a stenosis, _____ must be constant.
| back 27 D) volumetric flow rate
|
front 28 Proximal to, at, and distal to a stenosis, _____ must be constant.
| back 28 A) greater than
|
front 29 Poiseuille's equation predicts a _____ in flow speed with a decrease in vessel radius. | back 29 decreases
|
front 30 The continuity rule predicts a ____ in flow speed with a localized decrease in (stenosis) in vessel diameter. | back 30 increases
|
front 31 In a stenosis, the pressure is _____ the proximal and distal values.
| back 31 A) less than
|
front 32 Added forward flow and flow reversal in diastole can occur with ____ flow.
| back 32 E) pulsatile
|
front 33 As stenosis diameter decreases, _____ pass through a maximum.
| back 33 E) A and D
|
front 34 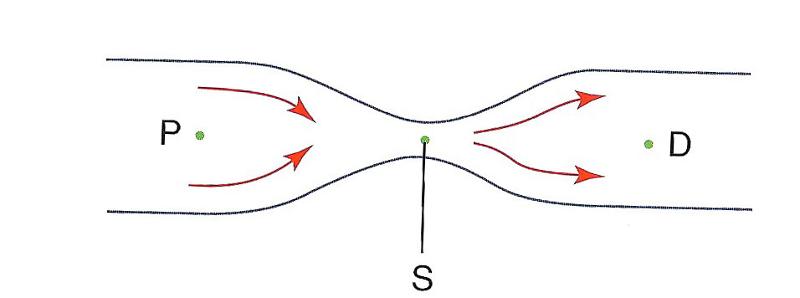 At which point is pressure the lowest?
| back 34 B) S |
front 35 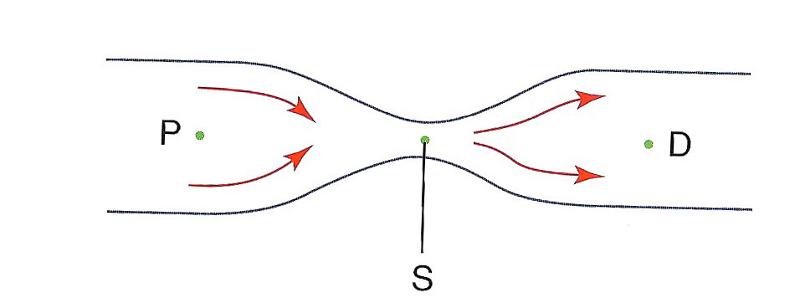 At which point is flow speed the lowest?
| back 35 D) P and D |
front 36 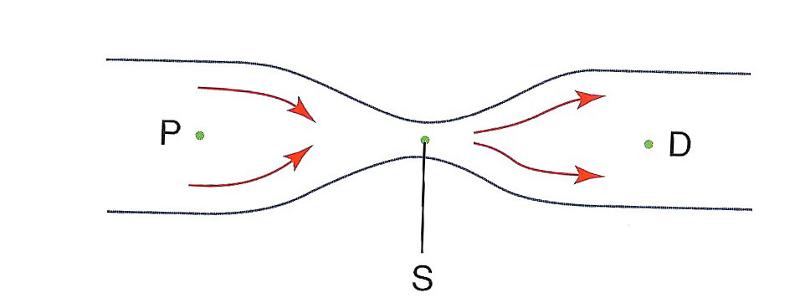 At which point is volumetric flow rate the lowest?
| back 36 E) none of the above |
front 37 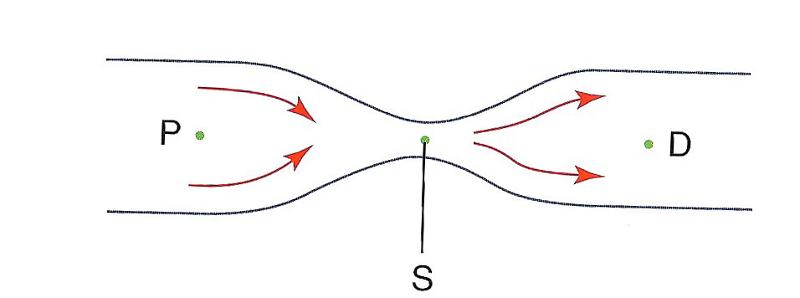 At which point is pressure energy the greatest?
| back 37 D) P and D |
front 38 The _____ effect is used to detect and measure ____ in vessels. | back 38 Doppler, flow
|
front 39 Motions of an echo-generating structure causes an echo to have a different ____ from that of the emitted pulse. | back 39 frequency
|
front 40 If the incident frequency is 1 MHz, the propagation speed is 1600 m/s and the reflector speed is 16 m/s toward the source, the Doppler shift is _____ MHz, and the reflected frequency is _____ MHz. | back 40 .02, 1.02
|
front 41 If 2-MHz ultrasound is reflected from a soft tissue boundary moving at 10 m/s toward the source, the Doppler shift is ____ MHz. | back 41 .026
|
front 42 If 2-MHz ultrasound is reflected from a soft tissue boundary moving at 10 m/s away from the source, the Doppler shift is ____ MHz. | back 42 -.026
|
front 43 The Doppler shift is the difference between _____ and _____ frequencies. | back 43 received, emitted
|
front 44 When incident sound direction and reflector motion are not parrallel, calculation of the reflected frequency involves the _____ of the angle between these directions. | back 44 cosine
|
front 45 If the incident frequency is 1 MHz, the propagation speed is 1600 m/s and the reflector speed is 16 m/s toward the source, the Doppler shift is .02 MHz, and the reflected frequency is 1.02 MHz.
| back 45 If the incident frequency is 1 MHz, the propagation speed is 1600 m/s and the reflector speed is 16 m/s toward the source, the Doppler shift is .02 MHz, and the reflected frequency is 1.02 MHz.
|
front 46 If the incident frequency is 1 MHz, the propagation speed is 1600 m/s and the reflector speed is 16 m/s toward the source, the Doppler shift is .02 MHz, and the reflected frequency is 1.02 MHz.
| back 46 If the incident frequency is 1 MHz, the propagation speed is 1600 m/s and the reflector speed is 16 m/s toward the source, the Doppler shift is .02 MHz, and the reflected frequency is 1.02 MHz.
|
front 47 For an operating frequency of 2 MHz, a flow speed of 10 cm/s and a Doppler angle of 0 degrees, calculate the Doppler shift. | back 47 .26 kHz |
front 48 For an operating frequency of 6 MHz, a flow speed of 50 cm/s and a Doppler angle of 60 degrees, calculate the Doppler shift. | back 48 1.95 kHz |
front 49 For blood flow through a vessel with a plug flow profile, the Doppler shift is _____ across the vessel. | back 49 For blood flow through a vessel with a plug flow profile, the Doppler shift is constant across the vessel.
|
front 50 Which Doppler angle yields the greatest Doppler shift?
| back 50 C) 0 |
front 51 To proceed from a measurement of Doppler shift frequency to a calculation of flow speed, _____ _____ must be known of assumed. | back 51 To proceed from a measurement of Doppler shift frequency to a calculation of flow speed, Doppler angle must be known of assumed.
|
front 52 If operating frequency is doubled, the Doppler shift is _____. | back 52 If operating frequency is doubled, the Doppler shift is doubled.
|
front 53 If flow speed is doubled, the Doppler shift is _____. | back 53 Doubled
|
front 54 If angle is doubled, the Doppler shift is _____. | back 54 decreased
|
front 55 Color Doppler instruments presents two-dimensional, color-coded images representing _____ that are superimposed on gray-scale images representing _____. | back 55 motion, anatomy
|
front 56 Which of the following on a color Doppler display is (are) presented in real time?
| back 56 D) A and B
|
front 57 Color Doppler instruments use an _____ technique to yield Doppler information in real time. | back 57 autocorrelation
|
front 58 Color Doppler instruments use an autocorrelation technique to yield Doppler information in real time.
| back 58 mean, sign, variance, power
|
front 59 True or False?
| back 59 True
|
front 60 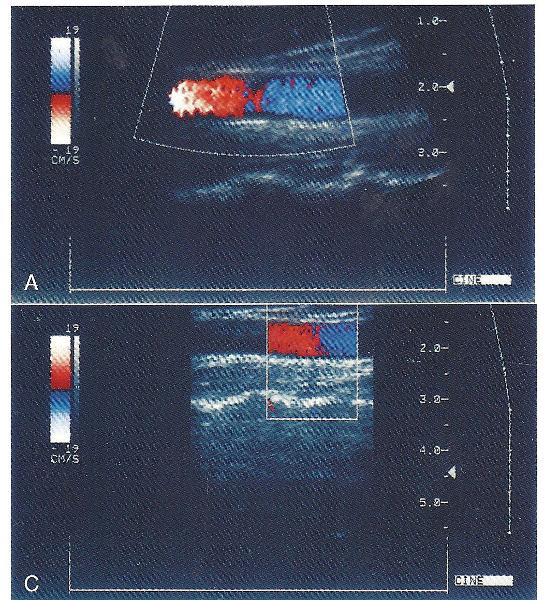 Do the different colors appearing in A and C indicate that flow is going in two different directions in the vessel?
| back 60 no |
front 61 True or False?
| back 61 False |
front 62 In practice, approximately _____ pulses are required to obtain one line of color Doppler information.
| back 62 B) 10
|
front 63 About _____ frames per second are produced by a color Doppler instrument.
| back 63 E) more than one of the above
|
front 64 True or False?
| back 64 False |
front 65 True or False?
| back 65 False
|
front 66 True or False?
| back 66 False
|
front 67 Increasing the ensemble length ____ the frame rate. | back 67 decreases
|
front 68 The _____ technique is commonly used to detect echo Doppler shifts in color Doppler instruments. | back 68 autocorrection
|
front 69 Which of the following reduce the frame rate of a color Doppler image?
| back 69 A) wider color window
|
front 70 Lack of color in a vessel containing blood flow may be attributed to _____.
| back 70 A) low color gain
|
front 71 Increasing ensemble length _____ color sensitivity and accuracy and _____ frame rate.
| back 71 D) improves, decreases
|
front 72 Which control can be used to help with clutter?
| back 72 A) wall filter |
front 73 Color map baselines are always represented by ______.
| back 73 B) black
|
front 74 Doubling the width of a color window produces a ____ frame rate.
| back 74 D) halved
|
front 75 Steering the color window to the right or left produces a _____ frame rate.
| back 75 C) unchanged
|
front 76 Autocorrelation produces _____.
| back 76 B) the mean value of the Doppler shift
|
front 77 Steering the color window to the right or left changes _____.
| back 77 E) more than one of the above
|
front 78 Color Doppler frame rates are _____ gray-scale rates.
| back 78 B) less than
|
front 79 In a single frame, color can change in a vessel because of _____.
| back 79 E) all of the above
|
front 80 True or False?
| back 80 False |
front 81 Compared with Doppler-shift imaging, Doppler-power imaging is _____.
| back 81 E) all of the above
|
front 82 Doppler-power improving indicates (with color) the ____ of flow.
| back 82 A) presense
|
front 83 Doppler-shift improving indicates (with color) the ____ of flow.
| back 83 E) more than on of the above
|
front 84 The function of a Doppler detector include _____.
| back 84 E) all of the above
|
front 85 An earlier gate time means ____ sample volume depth.
| back 85 B) a shallower
|
front 86 Doppler signal power is proportional to _____.
| back 86 D) cell concentration
|
front 87 True or False.
| back 87 False |
front 88 Stenosis affects ____.
| back 88 E) all of the above
|
front 89 Spectral broadening is a _____ of the spectral trace.
| back 89 A) vertical thickening
|
front 90 If all the cells in a vessel were moving at the same constant speed, the spectral trace would be a _____ line.
| back 90 A) thin horizontal
|
front 91 True or False?
| back 91 False |
front 92 True or False?
| back 92 False |
front 93 As stenosis progreses, which of the following increases?
| back 93 E) more than one of the above
|
front 94 True or False?
| back 94 False
|
front 95 Flow reversal in diasole indicates _____.
| back 95 C) high distal resistance
|
front 96 Decrease distal resistance normall causes end diastolic flow to _____.
| back 96 A) increase
|
front 97 If angle correction is set at 60 degrees but should be zero degrees, the display indicates a flow speed of 100 cm/s. The correct flow speed is _____ cm/s.
| back 97 B) 50
|
front 98 If angle correction is set at zero degrees but should be 60 degrees, the display indicates a flow speed of 100 cm/s. The correct flow speed is _____ cm/s.
| back 98 D) 200
|
front 99 If a 5-kHz Doppler shift corresponds to 100 cm/s, then a 2.5-kHz shift corresponds to _____ cm/s. | back 99 50
|
front 100 Which of the following is increased if Doppler angle is increased?
| back 100 C) effect of angle error |