Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 10- Photosynthesis Part B
front 1 _____ has a longer wavelength than _____. | back 1 Red ... green |
front 2 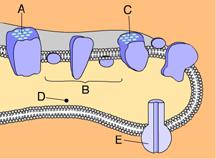 Which of these phosphorylates ADP to make ATP? | back 2 E ATP synthase phosphorylates ADP. |
front 3 _____ releases energy that is used to pump hydrogen ions from the stroma into the thylakoid compartment. | back 3 B The energy released as electrons are passed along the electron transport chain is used to pump protons into the thylakoid compartment. |
front 4 _____ splits water into 1/2 O2, H+, and e- . | back 4 A Photosystem II splits water into 1/2 O2, H+, and e- . |
front 5 Energized electrons from ____ enter an electron transport chain and are then used to reduce NADP+. | back 5 C |
front 6 Chlorophyll can be found in _____. | back 6 A & C |
front 7 In the electromagnetic spectrum, the type of radiation that we call visible light occurs between _____. | back 7 ultraviolet radiation and infrared radiation |
front 8 Which of the following is a product of the light reactions of photosynthesis? | back 8 oxygen, ATP, and NADPH |
front 9 When light strikes chlorophyll molecules, they lose electrons, which are ultimately replaced by _____. | back 9 splitting water |
front 10 Photosynthesis is a redox reaction. This means that H2O is _____ during the light reactions and CO2 is _____ during the Calvin cycle. | back 10 oxidized...reduced |
front 11 In the thylakoid membranes, what is the main role of the pigment molecules in a light-harvesting complex? | back 11 transfer light energy to the reaction-center chlorophyll |
front 12 Which of the events listed below occurs in the light reactions of photosynthesis? | back 12 Light is absorbed and funneled to reaction-center chlorophyll a. |
front 13 Assume a thylakoid is somehow punctured so that the interior of the thylakoid is no longer separated from the stroma. This damage will have the most direct effect on which of the following processes? | back 13 the synthesis of ATP the synthesis of ATP |
front 14 What does the chemiosmotic process in chloroplasts involve? | back 14 establishment of a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane |
front 15 In a plant cell, where are the ATP synthase complexes located? | back 15 thylakoid membrane and inner mitochondrial membrane |
front 16 Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between photosynthesis and respiration? | back 16 Photosynthesis stores energy in complex organic molecules, whereas respiration releases it. |
front 17 In photosynthetic cells, synthesis of ATP by the chemiosmotic mechanism occurs during | back 17 both photosynthesis and respiration. |
front 18 Reduction of oxygen to form water occurs during | back 18 respiration only. |
front 19 look at item 15 | back 19 item 15 |
front 20 Which statement correctly describes how O2 production would be affected? (Assume that the light intensity does not change.) | back 20 The rate of O2 production would decrease because the rate of ADP and NADP+ production by the Calvin cycle would decrease. |
front 21 Which process produces oxygen? | back 21 Photosynthesis Oxygen is a by-product of the photosynthetic process. |
front 22 Which set of reactions uses H2O and produces O2? | back 22 The light-dependent reactions |
front 23 What is the importance of the light-independent reactions in terms of carbon flow in the biosphere? | back 23 The light-independent reactions turn CO2, a gas, into usable carbon in the form of sugars. |
front 24 True or false? The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis use water and produce oxygen. | back 24 True |
front 25 Which of the following molecules is the primary product of photosystem I? | back 25 NADPH note: The NADPH produced by photosystem I is used to supply energy for the production of sugars during photosynthesis. |
front 26 What is the biological significance of the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis? | back 26 They convert carbon dioxide to sugar. |
front 27 Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between the light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis? | back 27 The light-dependent reactions produce ATP and NADPH, which are then used by the light-independent reactions. |
front 28 Which of the following reactions ensures that the Calvin cycle can make a continuous supply of glucose? | back 28 Regneration of RuBP |
front 29 Which of the following products of the light reactions of photosynthesis is consumed during the Calvin cycle? | back 29 NADPH |
front 30 The overall function of the Calvin cycle is _____. | back 30 making sugar |
front 31 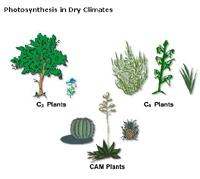 In C3 plants the conservation of water promotes _____. | back 31 photorespiration |
front 32 In C4 and CAM plants carbon dioxide is fixed in the _____ of mesophyll cells. | back 32 cytoplasm |
front 33 C4 plants differ from C3 and CAM plants in that C4 plants _____. | back 33 transfer fixed carbon dioxide to cells in which the Calvin cycle occurs |
front 34 C4 plants occur more commonly in desert conditions because _____. | back 34 they can fix carbon at the lower CO2 concentrations that develop when the stomata are closed |
front 35 CAM plants keep stomata closed in daytime, thus reducing loss of water. They can do this because they | back 35 fix CO2 into organic acids during the night. |
front 36 The alternative pathways of photosynthesis using the C4 or CAM systems are said to be compromises. Why? | back 36 Both minimize photorespiration but expend more ATP during carbon fixation. |
front 37 Plants photosynthesize only in the light. Plants respire | back 37 both in light and dark. |
front 38 The light reactions of photosynthesis supply the Calvin cycle with | back 38 ATP and NADPH. |
front 39 Which of the following sequences correctly represents the flow of electrons during photosynthesis? | back 39 H2O → NADPH → Calvin cycle |
front 40 How is photosynthesis similar in C4 plants and CAM plants? | back 40 In both cases, rubisco is not used to fix carbon initially. |
front 41 Which of the following statements is a correct distinction between autotrophs and heterotrophs? | back 41 Autotrophs, but not heterotrophs, can nourish themselves beginning with CO2 and other nutrients that are inorganic. |
front 42 Which of the following does not occur during the Calvin cycle? | back 42 release of oxygen |
front 43 Select the correct molecule that is the main product of the Calvin cycle. | back 43 G3P |
front 44 In mechanism, photophosphorylation is most similar to | back 44 oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration. |
front 45 Which process is most directly driven by light energy? | back 45 removal of electrons from chlorophyll molecules |
front 46 What is the basic role of CO2 in photosynthesis? | back 46 CO2 is fixed or incorporated into organic molecules. |
front 47 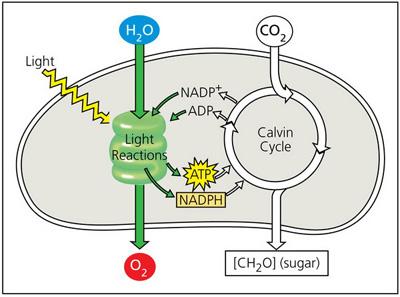 Select the most accurate statement describing the basic function of the light reactions of photosynthesis. | back 47 The basic function of the light reactions of photosynthesis is the conversion of solar energy to chemical energy. |
front 48 Select the correct statement about the Calvin cycle. | back 48 The Calvin cycle has three phases: carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration of RuBP. |
front 49 Why are plants classified as producers? | back 49 Plants are classified as producers because they fix inorganic carbon into organic molecules. |