Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 10- Photosynthesis Part A
front 1 Plants are photoautotrophs. What does this mean? | back 1 They use light energy to drive the synthesis of organic molecules from inorganic materials. |
front 2 The ultimate source of energy to support most life on Earth is _____. | back 2 sunlight |
front 3 Drag the labels from the left to their correct locations in the concept map on the right. Not all labels will be used. | back 3 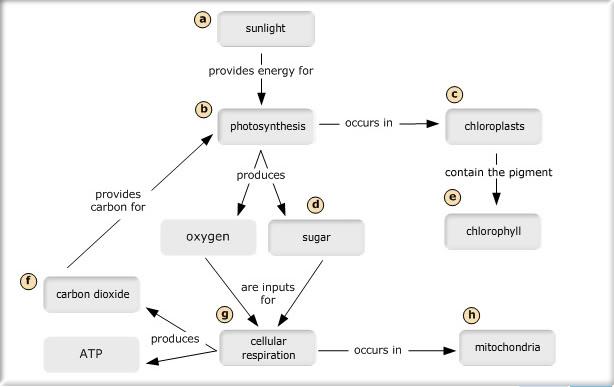 |
front 4 Which of these equations best summarizes photosynthesis? | back 4 6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 |
front 5 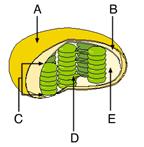 Where does the Calvin cycle occur? | back 5 E Stroma |
front 6 The light reactions of photosynthesis use _____ and produce _____. | back 6 water ... NADPH NADPH is a reactant in the Calvin cycle. |
front 7 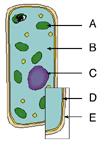 Identify the chloroplast. | back 7 A |
front 8 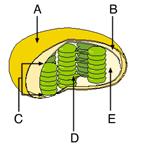 Identify the stroma. | back 8 E |
front 9 Identify a thylakoid. | back 9 D |
front 10 The photosynthetic membranes are found in the _____ in plant cells. | back 10 chloroplasts An elaborate system of interconnected thylakoid membranes segregates the stroma from the thylakoid space in the chloroplast. |
front 11 When oxygen is released as a result of photosynthesis, it is a direct by-product of | back 11 splitting water molecules. |
front 12 Approximately what wavelength of light is best absorbed by chlorophyll a, the pigment that participates directly in the light reactions? | back 12 435 nm |
front 13 Which wavelength of light is best absorbed by chlorophyll b? | back 13 455 nm |
front 14 You obtain the pigments called carotenoids in your diet when you eat carrots. Why do carotenoids appear yellow and orange? | back 14 They absorb blue/green light and reflect yellow and red wavelengths of light. |
front 15 Can you tell from these absorption spectra whether red light is effective in driving photosynthesis? | back 15 One cannot tell from this graph, but because chlorophyll a does absorb red light, we can predict that it would be effective in driving photosynthesis. |
front 16 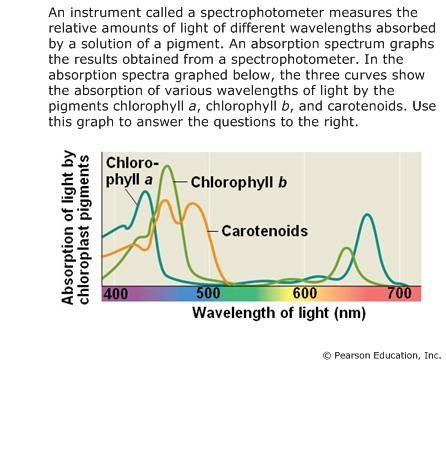 If only chlorophyll a were involved in the light reactions, would blue light (wavelength about 490 nm) be effective in driving photosynthesis? | back 16 The graph indicates that chlorophyll a absorbs very little blue light, so we can predict that blue light would not be effective. |
front 17 An action spectrum plots the rate of photosynthesis at various wavelengths of visible light, and it shows that blue light with a wavelength of about 490 nm is effective in driving photosynthesis. Based on this information and the absorption spectra shown at left, what role may chlorophyll b and carotenoids play in photosynthesis? | back 17 These pigments are able to absorb more wavelengths of light (and thus more energy) than chlorophyll a alone can absorb. As part of light-harvesting complexes in photosystems, they broaden the range of light that can be used in the light reactions. |
front 18 Which term describes ATP production resulting from the capture of light energy by chlorophyll? | back 18 Photophosphorylation The excitation of chlorophyll by light energy initiates a chain of events that leads to ATP production. |
front 19 True or false? The chemiosmotic hypothesis states that the synthesis of ATP generates a proton gradient that leads to electron flow through an electron transport chain. | back 19 False |
front 20 According to the chemiosmotic hypothesis, what provides the energy that directly drives ATP synthesis? | back 20 Proton gradient A proton gradient across chloroplast and mitochondrial membranes drives ATP synthesis by the enzyme ATP synthase. |
front 21 Which of the following particles can pass through the ATP synthase channel? | back 21 Protons |
front 22 True or false? The region of ATP synthase that catalyzes the production of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate spans the chloroplast membrane. | back 22 False |
front 23 Chloroplast membrane vesicles are equilibrated in a simple solution of pH 5. The solution is then adjusted to pH 8. Which of the following conclusions can be drawn from these experimental conditions? | back 23 ATP will not be produced because there is no ADP and inorganic phosphate in the solution. |
front 24 Which wavelengths of light drive the highest rates of photosynthesis? Select the two best answers. | back 24 400-450 nm 670-680 nm |
front 25 input and output of light reactions | back 25 input: light, ADP, NADP+, water
|
front 26 Calvin cycle input and output: | back 26 Input: Co2, ATP, NADPH
|
front 27 In the light reactions, light energy is used to oxidize | back 27 H20 to O2 |
front 28 The Electrons derived from this oxidation reaction in the light reactions are used to reduce | back 28 NADP+ to NADPH |
front 29 The Calvin cycle oxidizes the light reactions product | back 29 NADPH to NADP+ |
front 30 The electrons derived from this oxidation reaction in the calvin cycle are used to reduce | back 30 CO2 to G3p |