Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 15 Display and Image Storage
front 1 Displays | back 1 A television tube, which is a special form of cathode ray tub (CRT), is a glass vacuum tube shaped like a funnel. |
front 2 Electrons | back 2 charged particles |
front 3 How does CRT work? | back 3 electrons fly through electronic controlled, time-varying magnetic fields that focus and seep the electron beam across the inside of the wide end of the tube. The interior surface of the screen is coated with phosphors, which glow when struck by electrons |
front 4 Fields | back 4 525 closely-spaced lines. |
front 5 Odd fields | back 5 The electron beam first writes the odd fields within 1/60 of a sec |
front 6 Even fields | back 6 After the odd fields are written the electron beam writes the even fields within 1/60 of a sec or 60 Hz |
front 7 Frame | back 7  is the combination of one odd field and one even field
|
front 8 interlaced | back 8 the way television are written with odd and even fields |
front 9 Why are CRTs interlaced? | back 9 Humans can detect flicker in non-interlaced displays with frame rates 30 Hz, but not with an interlaced field of 60 Hz |
front 10 Bistable | back 10 Bi means 2
|
front 11 Grayscale | back 11 present multiple levels of grey
|
front 12 contrast | back 12 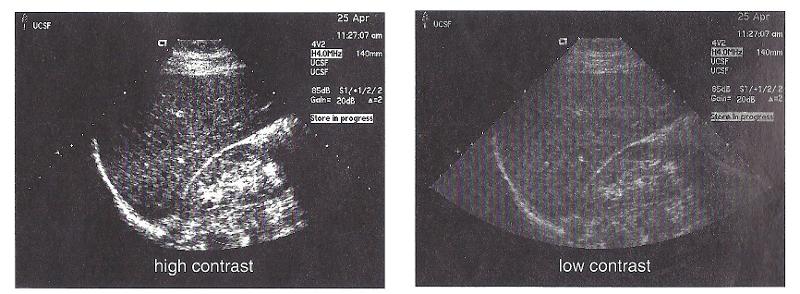 user control
|
front 13 High contrast | back 13 bistable images with only black and white |
front 14 Brightness | back 14 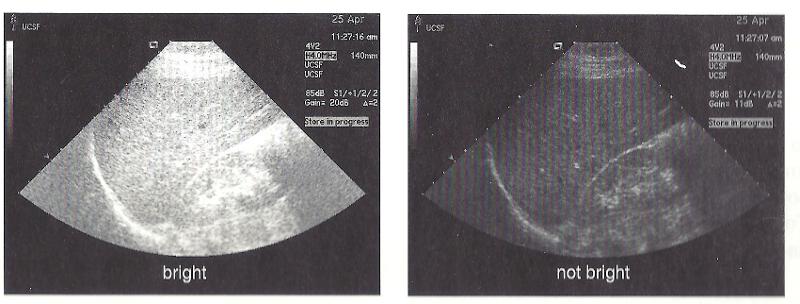 determines the brilliance of the displayed image. |
front 15 Scan converter | back 15  store information and later display
|
front 16 writing | back 16 storage of the image information |
front 17 read | back 17 image information is converted from the scan converter for display on CRT |
front 18 Digital Scan converters | back 18 scan converters that use computer technology rather than older analog |
front 19 Analog numbers | back 19 real world
|
front 20 Digital numbers | back 20 computer world
|
front 21 matrix | back 21 picture divided into millions of tiny dots, each containing an electrical storage item. The electrons stored in the bucket are read to retrieve the image. |
front 22 silicon wafer
| back 22 matrix at the larger end of CRT tube where images are stored |
front 23 Spatial resolution | back 23 image detail
|
front 24 Limitations of analog scan converters | back 24 Image fade - stored charges on the silicon wafer dissipate over time
|
front 25 Advantages of digital scan converter | back 25 Uniformity - consistent grayscale quality throughout the image.
|
front 26 Pixel | back 26 picture element
|
front 27 Pixel Density | back 27  is the # of pixels per inch |
front 28 improves with Higher pixel denesity | back 28 Spatial resolution |
front 29 Low Pixel Density vs. High Pixel Density | back 29  Low Pixel Density
|
front 30 Bit | back 30 is the smallest amount of computer memory
|
front 31 Binary Number | back 31 is a group of bits and is simply a series of zeroes and ones
|
front 32 Decimal numbers | back 32 used in everyday life are based on ten choices 0 through 9 |
front 33 byte | back 33 is a group of eight bits of computer memory
|
front 34 word of computer memory | back 34 made up of two bytes or 16 bits |
front 35 Fewer bit per pixels | back 35  fewer shades of grey
|
front 36 more bit per pixels | back 36  more shades of grey
|
front 37 Calculating the number of gray shades | back 37 raise 2 by the power of (# of bits) |
front 38 What is the number of shades that can be represented by 3 bits? | back 38 8 different shades of gray
|
front 39 What is the number of shades that can be represented by 8 bits? | back 39 256
|
front 40 How many bits are needed to store 10, 11, and 15 shades of grey? | back 40 4
|
front 41 Analog and digital image information | back 41 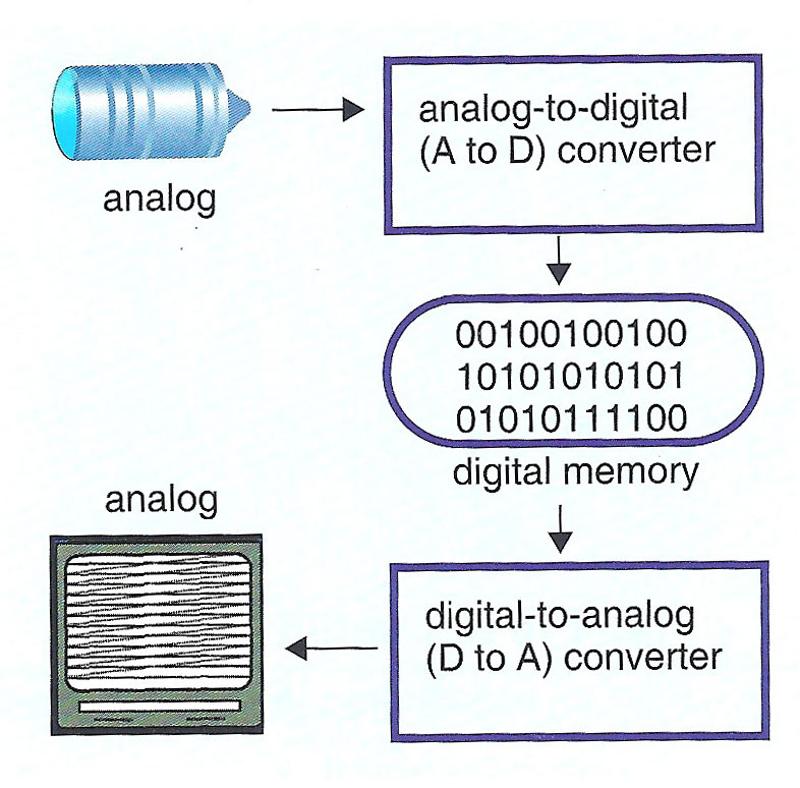 1. converted from analog to digital for by the analog-to-digital scanner (A-to-D)
|
front 42 Preprocessing | back 42 any processing of the electrical signals before storage |
front 43 Can the sonographer control preprocessing? | back 43 yes
|
front 44 Is preprocessing reversible? | back 44 No |
front 45 Postprocessing | back 45 any processing after storage in the digital scan converter |
front 46 Can a sonographer control postprocessing? | back 46 yes |
front 47 is post processing reversible? | back 47 yes
|
front 48 magnification | back 48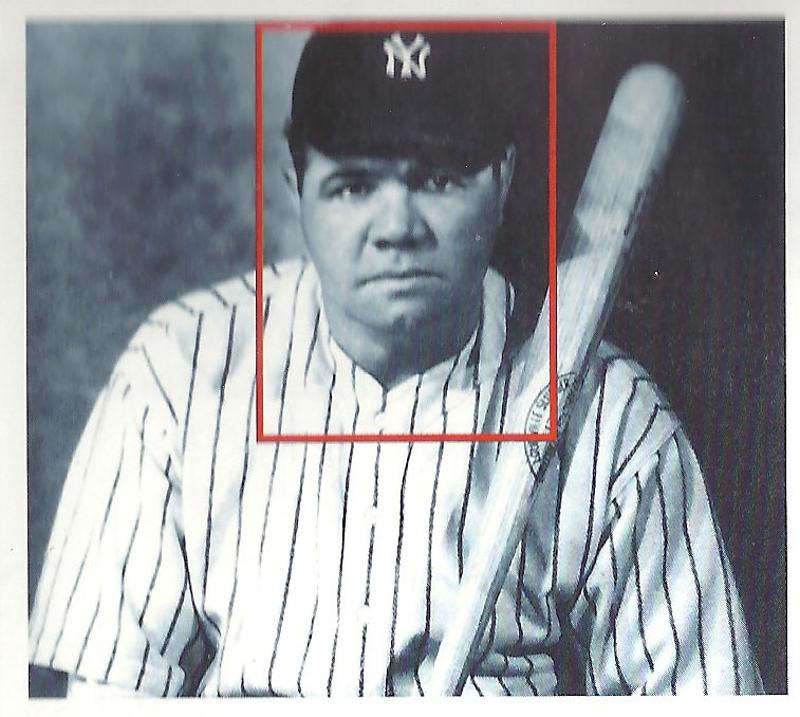  enlarging a portion of an image to fill entire screen |
front 49 ROI | back 49 region of interest |
front 50 Read magnification | back 50  occurs after storage in the scan converter
|
front 51 Write magnification | back 51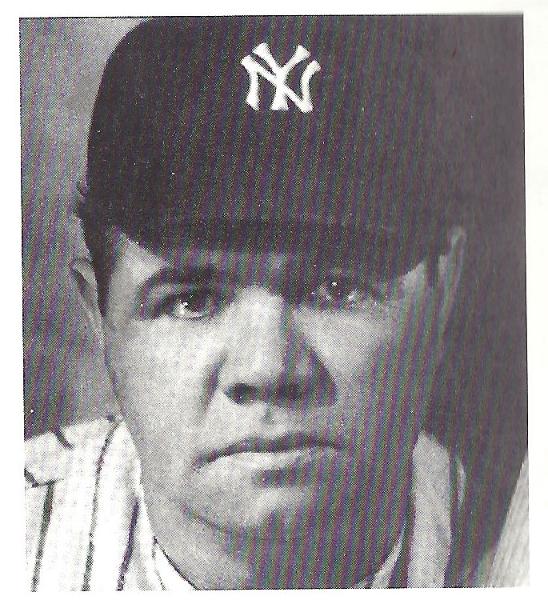  applied during data acquisition, before storage in the scan converter
|
front 52 Can write magnification improve temporal resolution? | back 52 yes if the ROI is shallower than the original image's DOV |
front 53 Read magnification vs. write magnification | back 53 Read magnification
|
front 54 Paper Media | back 54 Examples
|
front 55 Magnetic Media | back 55 Examples
|
front 56 Chemically mediated photographs | back 56 Examples
|
front 57 Optical Media | back 57 Examples
|
front 58 What is a PACS system? | back 58 picture archiving and communications system
|
front 59 PACS advantages | back 59 instant access
|
front 60 What is magneto-optical storage? | back 60 Magneto-optical, or M-O storage is based on a combination of magnetic and laser (optical) technology. PACS often uses M-O disc storage. |
front 61 M-O Storage advantages | back 61 store large amounts
|
front 62 All of the following are true of ordinary cathode ray tubes except:
| back 62 C) There are 600 horizontal scan lines from top to bottom, painted in order from 1 to 600
|
front 63 Which of the following correctly describes a typical television display?
| back 63 A) interlaced |
front 64 Which electronic component is required for grayscale imaging?
| back 64 D) scan converter |
front 65 All of the following are disadvantages of analog scan converters except:
| back 65 B) low-resolution image |
front 66 Which of the following scan converters will provide the best spatial resolution?
| back 66 D) digital with 1000 x 1000 pixels |
front 67 How many gray shades can be represented by a group of
| back 67 4 bits = 16 shades
|
front 68 Which of the following statements regarding a pixel is false?
| back 68 C) it displays up to 3 gray shades, simultaneously |
front 69 Are the following procedures usually pre- or post-processing?
| back 69 post A) modifying a frozen image
|
front 70 Are the following forms of information usually digital or analog?
| back 70 analog A) the signal from the transducer to the receiver
|
front 71 All of the following are characteristics of write magnification except:
| back 71 C) identical regions stored in the scan |
front 72 What is the primary disadvantage of video tape and computer disc methods of image archiving?
| back 72 B) the information is vulnerable |
front 73 All of the following are advantages of PACS systems except:
| back 73 D) images have higher resolution than what appears on the system's display |