Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exercise 4
front 1 Define organelle | back 1 organ of a cell; intracellular structures that do a specific function |
front 2 Define Cell | back 2 basic structural and functional unit of living organisms |
front 3 cell membrane (plasmalemma) | back 3 external boundary of cell; regulates flow of materials into and out of the cell; site of cell signaling |
front 4 lysosomes | back 4 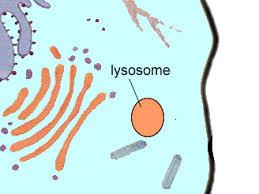 contains digestive enzymes of many varieties; "suicide sac" of the cell |
front 5 mitochondria | back 5 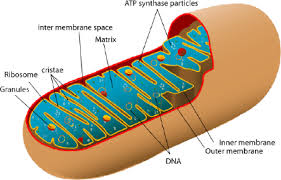 scattered throughout the cell; major site of ATP synthesis |
front 6 microvilli | back 6 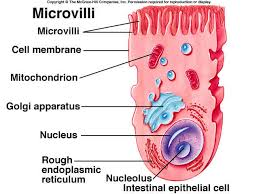 slender extensions of the plasma membrane that increase its surface area |
front 7 inclusions | back 7 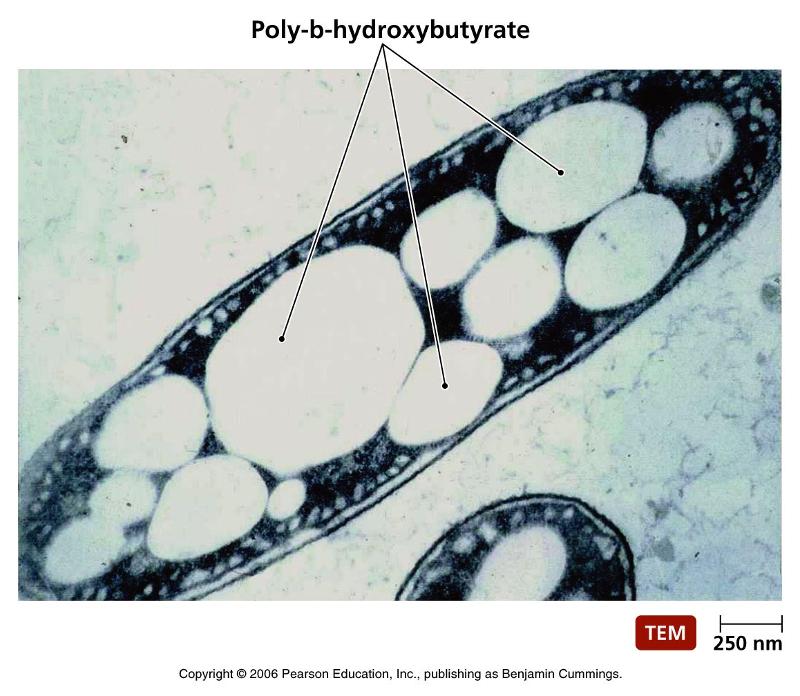 stored glycogen granules, crystals, pigments and so on |
front 8 Golgi body | back 8 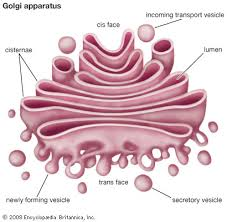 "packaging plant" produces vesicle -> balls of membrane... produce lysomes & peroxisomes. membranous system consisting of flattened sacs and cesicles; packages protiens for export |
front 9 nucleus | back 9 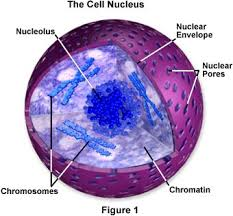 control center of the cell; necessary for cell division and cell life. "control center" of cell. contains chromosomes. - largest organelle. - usually near center of cell. - has double membrane, nuclear envelope. - membrane has openings, nuclear pores. - contains a dark spot -> nucleolus, ribosomes are produced. Typically 1 nucleus per cell |
front 10 Exceptions to 1 nucleous per cell | back 10 1. red blood cells - annucleated 2. placental cell - binucleated 3. skeletal muscle cell - multinucleated |
front 11 centrioles | back 11 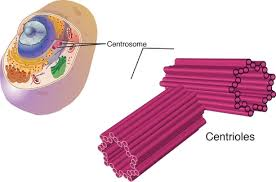 pair of star shapped tubes. - Made of microtubules. - help separate chromatids during cell division. two rod-shaped bodies near the nucleus; associated with the formation of the mitotic spindle |
front 12 nucleolus | back 12 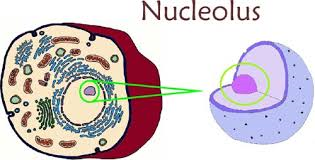 "control center" of cell. contains chromosomes. - largest organelle. - usually near center of cell. - has double membrane, nuclear envelope. - membrane has openings, nuclear pores. - contains a dark spot -> nucleolus, ribosomes are produced. Typically 1 nucleus per cell |
front 13 microfilaments | back 13 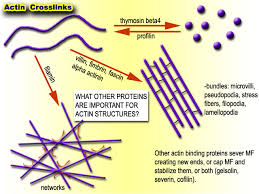 contractile elements of the cytoskeleton |
front 14 endoplasmic reticulum | back 14 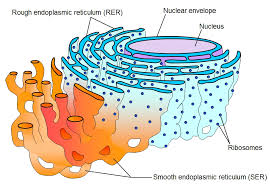 membranous system; involved in intracellular transport of proteins and synthesis of membrane lipids |
front 15 ribosomes | back 15 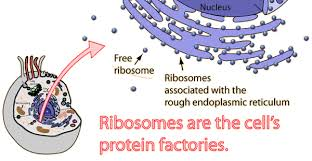 translation process of protien synthesis - chromosomes have genes that code for protiens -> used to express genes. Attached to membrane systems or scattered in the cytoplasm; site of protein synthesis |
front 16 chromatin | back 16 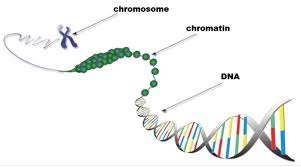 threadlike structures in the nucleus; contain genetic material (DNA) |
front 17 peroxisomes | back 17  site of free radical detoxification |
front 18 significance of the red blood cell being anucleate | back 18 they cannot reproduce & have infinite life span |
front 19 did anucleate red blood cells ever have a nucleous | back 19 Yes - during development |
front 20 what is the importance of cell division | back 20 allows for growth and repair |
front 21 division of the _____ is refered to as mitosis | back 21 nucleus |
front 22 cytokinesis is division of the ____ | back 22 cytoplasm/ organelles |
front 23 the major structural difference between chromatin and chromosomes is tht the latter are _____ | back 23 duplicated & condensed |
front 24 Chromosomes attached to the spindle fibers by undivided structures called _____ | back 24 centromere |
front 25 if a cell undergoes mitosis but not cytokinesis, the product is | back 25 binucleated cell |
front 26 the structure that acts as a scaffolding for chromosomal attachment and movement is called the | back 26 spindle fibers |
front 27 _____ is the period of cell life when the cell is not involved in division | back 27 interphase |
front 28 two cell populations in the body that do not routinely undergo cell division are ___ & ___ | back 28 Skeletal muscle & neurons |
front 29 chromatin coils and condenses, forming chromosomes. | back 29 prophase |
front 30 the chromosomes are V shaped | back 30 anaphase |
front 31 the nuclear envelope re-forms | back 31 teleophase |
front 32 chromosomes stop moving towards the poles | back 32 teleophase (late anaphase) |
front 33 chromosomes line up in the center of the cell | back 33 metaphase |
front 34 the nuclear envelope fragments | back 34 prophase |
front 35 the mitotic spindle forms | back 35 prophase |
front 36 DNA synthesis occurs | back 36 interphase |
front 37 Centrioles replicate | back 37 interphase |
front 38 chromosomes first appear to be duplex structures | back 38 prophase |
front 39 chromosomal centrometers are attached to the kinetochore fibers | back 39 metaphase (late prophase) |
front 40 chleavage furrow forms | back 40 anaphase |
front 41 the nuclear envelope is absent | back 41 metaphase & anaphase |
front 42 what is the physical advantage of the chromatin coiling and condensing to form short chromosomes at the onset of mitosis? | back 42 easier to move the separate daughter chromosomes to he newly forming cells. |
front 43 cell membrane - purpose & structure | back 43 purpose - defines boundary of cell
|
front 44 protiens - 2 types | back 44 integral - go through membrane
|
front 45 protiens uses | back 45 -channels/pores - intake nutrients - carriers/ transporters - receptor-input - cytoskeleton anchor (shape) - enzymes - cell identity markers - cell connectors - fluid mosaic membrane |
front 46 carbohydrates | back 46 blood type |
front 47 cholesterol | back 47 - cell movements across membrane. |
front 48 What are passive movements | back 48 molecules spread through the membranes. Molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, down a concentration gradients. As molecules diffuse, a state of equilibrium will occur - simple diffusion. - channel mediated diffusion. - carrier mediated diffusion. - osmosis. - dialysis. - filtration. |
front 49 passive movements - simple diffusion | back 49 - move directly through phosipolipids. - move from high concentration to low concentration via driving force. - things that can do this are fat soluable... ie. h20, 02, co2, n2, steroids |
front 50 Passive movements - channel medinated diffusion | back 50 - requires channel/pore. - membrane has negative charge. (cations would get stuck/anions would repel) |
front 51 Passive movements - carrier mediated diffusion | back 51 - requires a carrier. - modify substance after it crosses... ie. glucose turns to glucose 6 phosphate. ATP + Glucose -> ADP + glucose 6 phosphate |
front 52 Passive movements - Osmosis | back 52 diffusion of water driven by solute concentration (solute-protein, sugar, salt) |
front 53 passive movements - osmosis - hypertonic | back 53 *Osmosis* net water movement out, cell shrinks |
front 54 passive movements - osmosis - hypotonic | back 54 *Osmosis* net water movement in, cell expands - lysis explodes |
front 55 passive movements - isotonic | back 55 * no osmosis* same concentration - no water movement |
front 56 passive movement - dialysis | back 56 * Osmosis * passive through membrane based on pore size - peritoneum dialysis - shunt tube - blood vessels - in abdominal cavity - as blood flows through blood vessels & filter through poresin capilaries |
front 57 passive movement - dialyisis - filtration | back 57 * Osmosis* in kidney - movement across a membrane due to pressure difference. |
front 58 Active methods & types | back 58 1 - pumping a. requires ATP * carrier molecule required * Moving opposite of concentration (lower to higher) * Na/K pump 2. a. |
front 59 Membrane "Shape" Organs - types | back 59 Endocytosis * Exocytosis |
front 60 active transport - endocytosis | back 60 moves substances into the cell by means of a vesicle. |
front 61 active transport - endocytosis - phagocytosis | back 61 cell eating. large particles are engulfed by plasma membrane and enter the vesicle - the vesicles fuse with lysosomes, which digest the particles |
front 62 active transport - endocytosis - pinocytosis | back 62 cell drinking. fluid and the substances dissolved in it enter the cell |
front 63 Active transport - Endocytosis - receptor mediated | back 63 receptor molecules recognize substances to be brought into the cell |
front 64 Active transport - Exocytosis | back 64 movement out of the cell - contains secretory vesicle - neurotransmitters & some hormones released this way. large molecules (proteins) can leave the cell even though they are too big - enclosed in vesicle then pulled to plasma membrane via cytoskeleton. |
front 65 Role of active transport processes | back 65 a. active transport requires energy use by the membrane b. pumps - concrentrate substances on one side of membrane, as when stroing an ion inside of an organelle c. vesicle-mediated (endocytosis, exocytosis) - move large volumes of substances at once, as in secretion of hormones and neurotransmitters |
front 66 cell - cell connections | back 66 a. tight junctions - prevents movement between cell b. desmosomes - connection that allow movement together c. gap juncions have tubes(connections) that allow direct cell to cell communication ie. heart |
front 67 cell membrane modifications | back 67 1. microvilli 2. cilia 3. flagellium |
front 68 cell membrane modifications - microvilli | back 68 extensions that increase the cells of surface area |
front 69 cell membrane modifications - cilia | back 69  hair like structure - beat = move substances over their surface ie lungs and fallopian tube |
front 70 cell membrane modifications - flagellium | back 70  long, whip like tail ->provides mobility ie. sperm tail |
front 71 Ribosome process | back 71 DNA(code) -> RNA(Copy) -> Protien ribosome translate the RNA codes. Ribosomes are formed in nucleus |
front 72 DNA process | back 72 Chromatin -> Chromosomes -> Chromotids. DNA = genetic code. stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid. 2 strands of nucleotides twisted around each other in a double helix. Each side consists of sugar & phosphate. Runs - base pairs |
front 73 DNA - T | back 73 thymine |
front 74 DNA - A | back 74 Adenine |
front 75 DNA - C | back 75 Cytosine |
front 76 DNA - G | back 76 Guanine |
front 77 Chromotin | back 77 DNA wraps around protein beads called histones. Form loose, tangled strains, normal form in cell |
front 78 Chromosomes | back 78 formed in division. X shaped structures. condensed duplicated chromotin. human cells have 23 pairs & 46 chromosomes. xy = men. xx = woman |
front 79 centromere | back 79 middle, central part of chromosome |
front 80 chromatid | back 80 half of the chromosome after it divides - also called sister chromatids (daughter chromosomes) |
front 81 Cell life cycle - 4 phases | back 81 G1 - growth - normal cell function. S phase - Synthesis - DNA replicates, centride replication. G2 - growth 2 - normal activity - final preparations for division. M - Mitosic - division of nucleous, cytoplasm & organelles. |
front 82 Metabolism | back 82 set of chemical reactions in a cell. Catabolism & Anabolism |
front 83 anabolism | back 83 build up reactions. creates A+B -> AB + H20 |
front 84 catabolism | back 84 breaksdown reactions. AB + Hw0 -> A+B - hydrolysis, digestion, food (cellular respiration pathways) -> ATP |
front 85 mitotic cell division - Mitosis is? | back 85 Cell Division process - makes exact copies of cell for growth and repair |
front 86 mitotic cell division - Mitotic base pairing - 5 phases of Mitosis | back 86 IPMAT - Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, anaphase, telophase |
front 87 mitotic cell division - Interphase - G, S, & G2 | back 87 DNA synthesis - production of cytoplasm - replication of centrosomes and DNA in anticipation of cell division |
front 88 mitotic cell division - Interphase - DNA Synthesis - Base Pairing | back 88 DNA strand uncoils and strands come apart - strands are rebuilt in opposite directions, 1 strand strand that has telomeres. Telomers are segments at the end of DNA, that rebuild by the enzyme telomerase. T=A A=T G=C C=G -> will always be prepaired together, on opposite sides. 2 new strands are chromatids |
front 89 mitotic cell division - Prophase | back 89 "before phase" 1. chromatin condenses to chromosomes 2. nuclear membrane disappears 3. nucleoi disappear 4. centrioles begin to move to opposite ends, spidle fibers form between them |
front 90 mitotic cell division - Metaphase | back 90 "position changing phase" 1. chromosomes attach to spindle fibers 2. chromosomes align to the middle of cell |
front 91 mitotic cell division - anaphase | back 91 "apart phase" 1. chromosomes split into chromatids 2. chromatids pulled to cellic pole by centrioles & spindle fibers. centromere of each chromosome splits to form 2 chromosomes, each consisting of a single DNA molecule 4. each chromosome is pulled toward the nearest pole to form 2 separate, but identical, pools of genetic information |
front 92 mitotic cell division - telophase | back 92 "end phase" 1. division of cell membrane -> furrowing 2. cytokinesis -> division of cytoplasm/organelles 3. chromatid becomes chromotin 4. nuclear membrane reforms 5. nucleoli reappear 6. each daughter cells begin interphase to develop into mature cell |
front 93 summary of Mitosis | back 93 1. DNA replication 2. 1 round of division 3. forms 2 identicle cells (daughter cells) |
front 94 Why do cells divide | back 94 1. get too big - problems surface area to volume. 2. growth factors, a. HGH - human growth hormone b. PDGF - platelet derived growth factor. 3. cyclic factors |
front 95 What stops division | back 95 1. removal of growth factors 2. removal of cyclic factors 3. contact inhibition 4. natural killer (NK) cells 5. Tumor suppressor Gene (TSG) protiens |
front 96 Cancer | back 96 uncontrolled cell growth -> crowd out healthy tissue, impair normal function cells change methology, cancer can spread |
front 97 Causes of Cancer | back 97 1. carcinogens 2. Radiation 3. Oncogenes 4. loss of TSG 5. NK cell problems 6. Age 7. Virus infection -> that have oncogenes themselves |