Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 25 The Urinary System
front 1 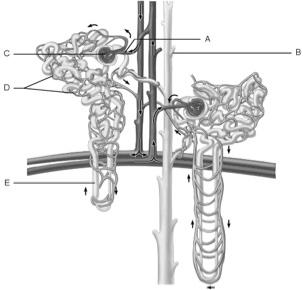 Glomerulus | back 1 C |
front 2 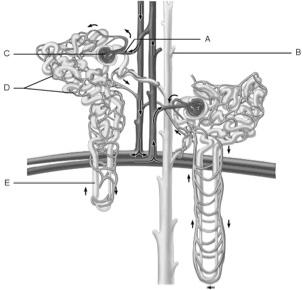 Afferent arteriole | back 2 A |
front 3 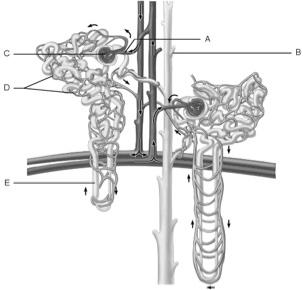 Collecting duct | back 3 B |
front 4 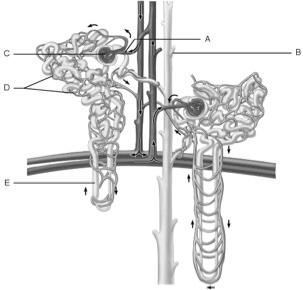 Loop of Henle | back 4 E |
front 5 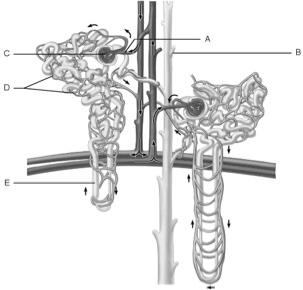 Peritubular capillaries | back 5 D |
front 6 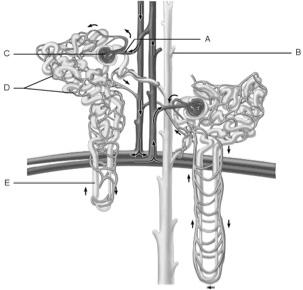 Structure most closely associated with granular cells | back 6 A |
front 7 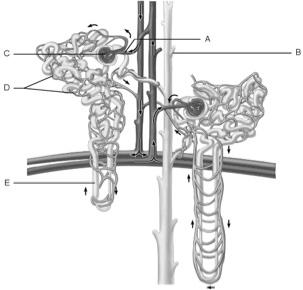 Medulla of the kidney | back 7 E |
front 8 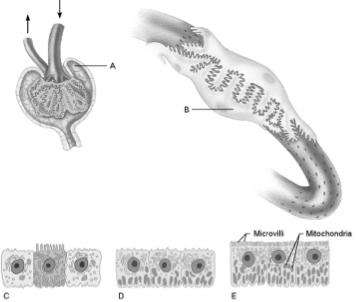 Podocyte | back 8 B |
front 9 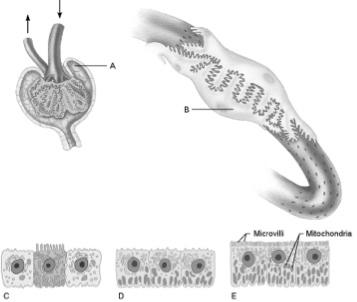 Is composed of simple squamous epithelium | back 9 A |
front 10 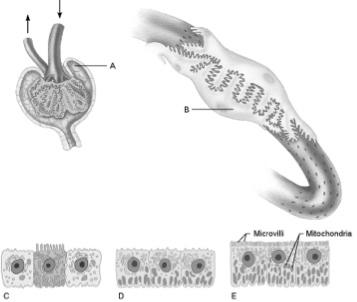 Collecting duct cells | back 10 C |
front 11 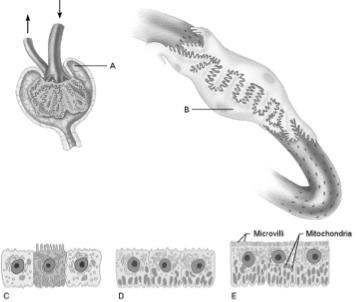 Proximal convoluted tubule cells | back 11 E |
front 12 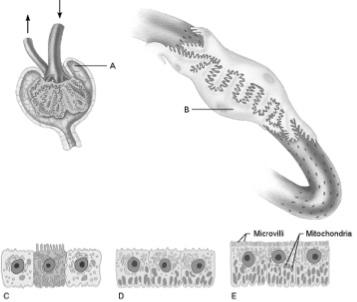 Filtrate at the site of these cells is about the same osmolarity as blood plasma | back 12 E |
front 13 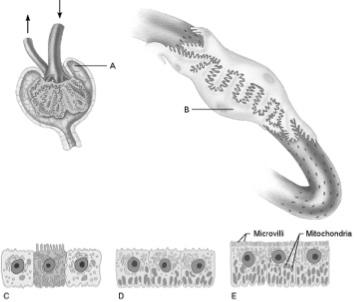 Cells that are the most active in reabsorbing the filtrate | back 13 E |
front 14 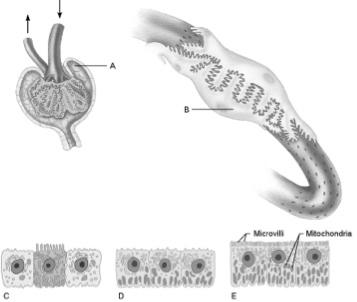 Cells that reabsorb virtually all the nutrients | back 14 E |
front 15 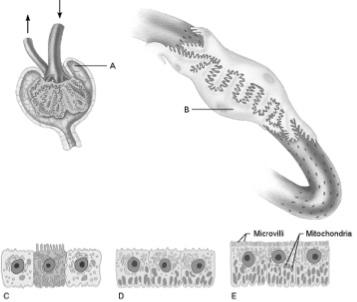 Cells that are most affected by ADH | back 15 C |
front 16 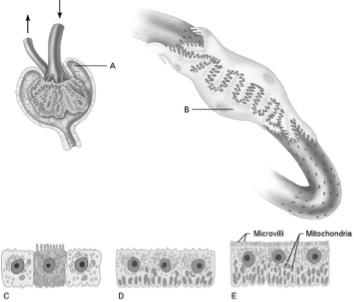 Almost no water is absorbed in these cells | back 16 D |
front 17 Proximal convoluted tubule
| back 17 A) Site at which most of the tubular reabsorption occurs. |
front 18 Glomerulus
| back 18 C) Site of filtrate formation. |
front 19 Peritubular capillaries
| back 19 B) Blood supply that directly receives substances from the tubular cells. |
front 20 Collecting duct
| back 20 D) Site that drains the distal convoluted tubule. |
front 21 True/False Questions
| back 21 False |
front 22 True/False Questions
| back 22 True |
front 23 True/False Questions
| back 23 True |
front 24 True/False Questions
| back 24 True |
front 25 True/False Questions
| back 25 True |
front 26 True/False Questions
| back 26 True |
front 27 True/False Questions
| back 27 True |
front 28 True/False Questions
| back 28 True |
front 29 True/False Questions
| back 29 False |
front 30 True/False Questions
| back 30 True |
front 31 True/False Questions
| back 31 False |
front 32 True/False Questions
| back 32 True |
front 33 True/False Questions
| back 33 False |
front 34 True/False Questions
| back 34 True |
front 35 True/False Questions
| back 35 False |
front 36 True/False Questions
| back 36 False |
front 37 True/False Questions
| back 37 False |
front 38 True/False Questions
| back 38 True |
front 39 True/False Questions
| back 39 False |
front 40 True/False Questions
| back 40 False |
front 41 True/False Questions
| back 41 True |
front 42 True/False Questions
| back 42 False |
front 43 True/False Questions
| back 43 True |
front 44 True/False Questions
| back 44 False |
front 45 True/False Questions
| back 45 True |
front 46 True/False
| back 46 True |
front 47 True/False Questions
| back 47 False |
front 48 The mechanism that establishes the medullary osmotic gradient depends most on the permeability properties of the ________.
| back 48 A) loop of Henle |
front 49 Urine passes through the ________.
| back 49 B) pelvis of the kidney to ureter to bladder to urethra |
front 50 Which of the following is not associated with the renal corpuscle?
| back 50 B) a vasa recta |
front 51 An increase in the permeability of the cells of the collecting tubule to water is due to a(n) ________.
| back 51 B) increase in the production of ADH |
front 52 The urinary bladder is composed of ________ epithelium.
| back 52 A) transitional |
front 53 The kidneys are stimulated to produce renin ________.
| back 53 C) by a decrease in the blood pressure |
front 54 Which of the choices below is not a function of the urinary system?
| back 54 D) eliminates solid, undigested wastes and excretes carbon dioxide, water, salts, and heat |
front 55 Which gland sits atop each kidney?
| back 55 A) adrenal |
front 56 The ________ artery lies on the boundary between the cortex and medulla of the kidney.
| back 56 B) arcuate |
front 57 The glomerulus differs from other capillaries in the body in that it ________.
| back 57 C) is drained by an efferent arteriole |
front 58 The descending limb of the loop of Henle ________.
| back 58 D) contains fluid that becomes more concentrated as it moves down into the medulla |
front 59 Select the correct statement about the ureters.
| back 59 C) The ureters are capable of peristalsis like that of the gastrointestinal tract. |
front 60 The fatty tissue surrounding the kidneys is important because it ________.
| back 60 B) stabilizes the position of the kidneys by holding them in their normal position |
front 61 The renal corpuscle is made up of ________.
| back 61 A) Bowman's capsule and glomerulus |
front 62 The functional and structural unit of the kidneys is the ________.
| back 62 A) nephron |
front 63 The juxtaglomerular apparatus is responsible for ________.
| back 63 D) regulating the rate of filtrate formation and controlling systemic blood pressure |
front 64 The chief force pushing water and solutes out of the blood across the filtration membrane is ________.
| back 64 C) glomerular hydrostatic pressure (glomerular blood pressure) |
front 65 Which of the following statements describes the histology of the ureters?
| back 65 A) They are trilayered (mucosa, muscularis, and adventitia). |
front 66 Which of the following statements is a false or incorrect statement?
| back 66 A) The male urethra serves both the urinary and reproductive systems at the same time. |
front 67 Which of the following acts as the trigger for the initiation of micturition (voiding)?
| back 67 A) the stretching of the bladder wall |
front 68 The filtration membrane includes all except ________.
| back 68 C) renal fascia |
front 69 The mechanism of water reabsorption by the renal tubules is ________.
| back 69 B) osmosis |
front 70 Most electrolyte reabsorption by the renal tubules is ________.
| back 70 C) hormonally controlled in distal tubule segments |
front 71 The macula densa cells respond to ________.
| back 71 D) changes in solute content of the filtrate |
front 72 Which of the following is not reabsorbed by the proximal convoluted tubule?
| back 72 D) creatinine |
front 73 The fluid in the glomerular (Bowman's) capsule is similar to plasma except that it does not contain a significant amount of ________.
| back 73 D) plasma protein |
front 74 Alcohol acts as a diuretic because it ________.
| back 74 D) inhibits the release of ADH |
front 75 The function of angiotensin II is to ________.
| back 75 A) constrict arterioles and increase blood pressure |
front 76 A disease caused by inadequate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) by the pituitary gland with symptoms of polyuria is ________.
| back 76 B) diabetes insipidus |
front 77 An important characteristic of urine is its specific gravity or density, which is ________.
| back 77 B) 1.001-1.035 |
front 78 Place the following in correct sequence from the formation of a drop of urine to its elimination from the body.
| back 78 D) 3, 6, 2, 1, 5, 4 |
front 79 Select the correct statement about the nephrons.
| back 79 A) The parietal layer of the glomerular capsule is simple squamous epithelium. |
front 80 What would happen if the capsular hydrostatic pressure were increased above normal?
| back 80 B) Net filtration would decrease. |
front 81 Which of the following is not a part of the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
| back 81 C) podocyte cells |
front 82 Tubular reabsorption ________.
| back 82 B) by active mechanisms usually involves movement against an electrical and/or chemical gradient |
front 83 Which of the following is not a reason why substances are either not reabsorbed or are incompletely reabsorbed from the nephron?
| back 83 D) They are extremely complex molecules. |
front 84 Reabsorption of high levels of glucose and amino acids in the filtrate is accomplished by ________.
| back 84 D) secondary active transport |
front 85 Which of the choices below is a function of the loop of Henle?
| back 85 B) form a large volume of very dilute urine or a small volume of very concentrated urine |
front 86 Fetal kidneys do not have to work very hard because ________.
| back 86 C) the placenta allows the mother's urinary system to clear the waste from fetal blood |
front 87 Which of the following best describes kidney function in older adults (70 years or older)?
| back 87 D) Kidney function decreases due to kidney atrophy. |
front 88 The factor favoring filtrate formation at the glomerulus is the ________.
| back 88 B) glomerular hydrostatic pressure |
front 89 If the Tm for a particular amino acid is 120 mg/100 ml and the concentration of that amino acid in the blood is 230 mg/100 ml, the amino acid will ________.
| back 89 C) appear in the urine |
front 90 If one says that the clearance value of glucose is zero, what does this mean?
| back 90 C) Normally all the glucose is reabsorbed. |
front 91 Excretion of dilute urine requires ________.
| back 91 B) impermeability of the collecting tubule to water |
front 92 Which of the choices below is not a method by which the cells of the renal tubules can raise blood pH?
| back 92 D) by secreting sodium ions |
front 93 In the ascending limb of the loop of Henle the ________.
| back 93 D) thick segment moves ions out into interstitial spaces for reabsorption |
front 94 Select the correct statement about urinary system development.
| back 94 A) Kidneys develop from urogenital ridges. |
front 95 Which of the choices below does not describe the importance of tubular secretion?
| back 95 C) ridding the body of bicarbonate ions |
front 96 Which statement is correct?
| back 96 A) Reabsorption of water is hormonally controlled. |
front 97 What is the function of the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
| back 97 A) help regulate blood pressure and the rate of blood filtration by the kidneys |
front 98 Which of the choices below is the salt level-monitoring part of the nephron?
| back 98 A) macula densa |
front 99 Which of the hormones below is responsible for facultative water reabsorption?
| back 99 A) ADH |
front 100 Which of the choices below is not a glomerular filtration rate control method?
| back 100 C) electrolyte levels |
front 101 Which of the choices below are the most important hormone regulators of electrolyte reabsorption and secretion?
| back 101 B) angiotensin II and aldosterone |
front 102 Which cells of the kidney are chemoreceptors that respond to changes in solute content of the filtrate?
| back 102 C) macula densa cells |
front 103 The capillary bed that surrounds the descending and ascending loop of Henle of juxtamedullary nephrons is called the ________. | back 103 Vasa Recta |
front 104 Urine crystals in the renal pelvis are called ________. | back 104 Renal Calculi |
front 105 The need to get up in the middle of the night to urinate is called ________. | back 105 Nocturia |
front 106 The area between the ureters and urethra is called the ________ in a bladder. | back 106 Trigone |
front 107 The ________ mechanism is the general tendency of vascular smooth muscle to contract when stretched | back 107 Myogenic |
front 108 The presence of pus in the urine is a condition called ________. | back 108 Pyuria |
front 109 Sodium-linked water flow across a membrane is called ________ water reabsorption. | back 109 Obligatory |