Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 24 Nutrition, Metabolism, and Body Temperature Regulation
front 1 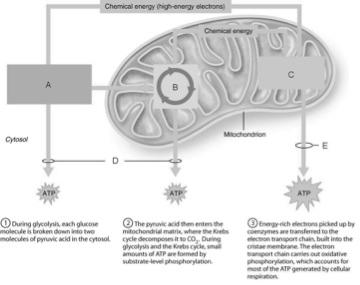 Ten-step enzymatically driven process that converts glucose into pyruvic acid | back 1 A |
front 2 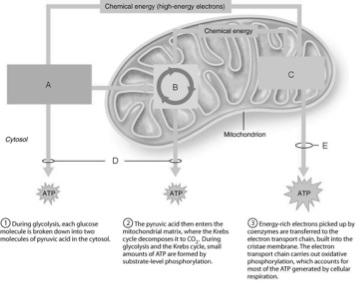 Occurs via substrate-level phosphorylation. | back 2 D |
front 3 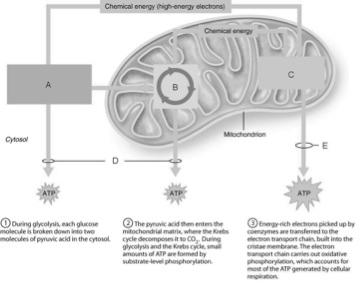 Produces the CO2 involved during glucose oxidation | back 3 B |
front 4 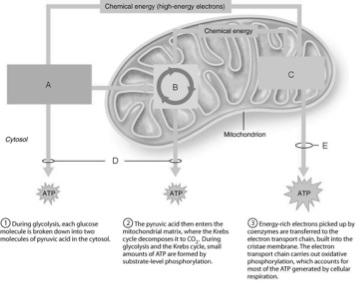 Where the hydrogens removed during the oxidation of food fuels are combined with O2. | back 4 C |
front 5 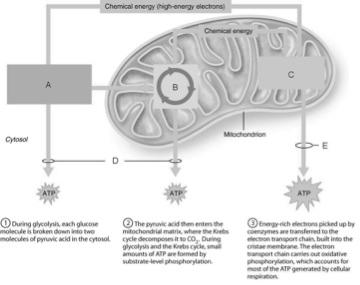 Contains ATP synthases, small rotary motors | back 5 C |
front 6 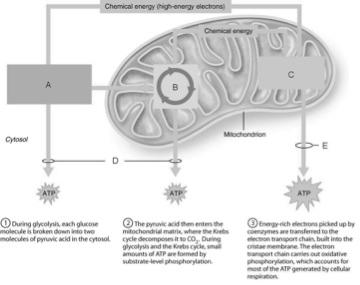 ATP formed by oxidative phosphorylation. | back 6 E |
front 7 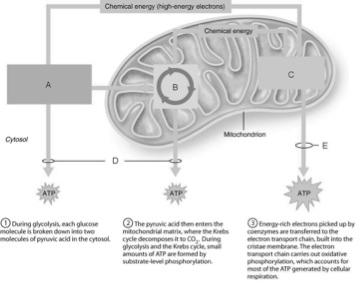 Involves sugar activation, sugar cleavage, and oxidation and ATP formation. | back 7 A |
front 8 Glucose serves as the initial reactant.
| back 8 A |
front 9 Involves the removal of hydrogen electrons and CO2 from the substrate molecule
| back 9 B |
front 10 Occurs in the cytosol of a cell.
| back 10 A |
front 11 Produces the most ATP
| back 11 C |
front 12 Involves the use of oxygen to pick up excess hydrogen and electrons.
| back 12 B |
front 13 Breakdown of glycogen to release glucose.
| back 13 B |
front 14 Formation of glucose from proteins or fats.
| back 14 D |
front 15 Storage of glucose in the form of glycogen
| back 15 A |
front 16 Breakdown of glucose to pyruvic acid.
| back 16 C |
front 17 Synthesis of lipids from glucose or amino acids.
| back 17 C |
front 18 Splitting of triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids.
| back 18 A |
front 19 Conversion of fatty acids into acetyl groups.
| back 19 B |
front 20 Formation of ketone bodies
| back 20 D |
front 21 True/False Questions
| back 21 False |
front 22 True/False Questions
| back 22 True |
front 23 True/False Questions
| back 23 False |
front 24 True/False Questions
| back 24 False |
front 25 True/False Questions
| back 25 True |
front 26 True/False Questions
| back 26 False |
front 27 True/False Questions
| back 27 False |
front 28 True/False Questions
| back 28 True |
front 29 True/False Questions
| back 29 False |
front 30 True/False Questions
| back 30 False |
front 31 True/False Questions
| back 31 False |
front 32 True/False Questions
| back 32 True |
front 33 True/False Questions
| back 33 False |
front 34 True/False Questions
| back 34 True |
front 35 True/False Questions
| back 35 False |
front 36 True/False Questions
| back 36 False |
front 37 True/False Questions
| back 37 False |
front 38 True/False Questions
| back 38 True |
front 39 True/False Questions
| back 39 True |
front 40 True/False Questions
| back 40 False |
front 41 True/False Questions
| back 41 False |
front 42 True/False Questions
| back 42 True |
front 43 True/False Questions
| back 43 False |
front 44 True/False Questions
| back 44 True |
front 45 True/False Questions
| back 45 True |
front 46 True/False Questions
| back 46 False |
front 47 True/False Questions
| back 47 True |
front 48 True/False Questions
| back 48 True |
front 49 True/False Questions
| back 49 True |
front 50 The molecule that serves as the major source of readily available fuel for neurons and blood cells is ________.
| back 50 B) glucose |
front 51 Which of the choices below is not a fate of carbohydrate taken into the body?
| back 51 D) conversion to a nucleic acid |
front 52 Dietary fats are important because they ________.
| back 52 B) help the body absorb fat-soluble vitamins |
front 53 Cholesterol, though it is not an energy molecule, has importance in the body because it ________.
| back 53 A) is a stabilizing component of the plasma membranes and is the parent molecule of steroid hormones |
front 54 Which of the following statements best describes complete protein?
| back 54 D) must meet all the body's amino acid requirements for maintenance and growth |
front 55 The term metabolism is best defined as ________.
| back 55 D) biochemical reactions involved in building cell molecules or breaking down molecules for energy |
front 56 The term metabolic rate reflects the ________.
| back 56 A) energy the body needs to perform only its most essential activities |
front 57 When proteins undergo deamination, the waste substance found in the urine is mostly________.
| back 57 A) urea |
front 58 It is important to ensure that your diet is adequately rich in vitamins because ________.
| back 58 C) most vitamins are coenzymes needed to help the body utilize essential nutrients |
front 59 Oxidation-reduction reactions are catalyzed by which of the following enzymes?
| back 59 A) dehydrogenases and oxidases |
front 60 Which of the choices below describes the pathway of cellular respiration (the complete oxidation of glucose)?
| back 60 A) glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain, oxidative phosphorylation |
front 61 Anabolism includes reactions in which ________.
| back 61 B) larger molecules or structures are built from smaller ones |
front 62 Catabolism would be best described as a process that ________.
| back 62 C) breaks down complex structures to simpler ones |
front 63 The primary function of cellular respiration is to ________.
| back 63 D) break down food molecules and generate ATP |
front 64 The process of breaking triglycerides down into glycerol and fatty acids is known as ________.
| back 64 D) lipolysis |
front 65 Which of the following mechanisms produces the most ATP during cellular respiration?
| back 65 A) oxidative phosphorylation |
front 66 Lipogenesis occurs when ________.
| back 66 D) cellular ATP and glucose levels are high |
front 67 Oxidative deamination takes place in the ________.
| back 67 A) liver |
front 68 Transamination is the process whereby the amine group of an amino acid is ________.
| back 68 C) transferred to a keto acid |
front 69 Glycogen is formed in the liver during the ________.
| back 69 B) absorptive state |
front 70 Which of the following is a normal consequence of the activation of the heat-promoting center?
| back 70 A) release of epinephrine |
front 71 Gluconeogenesis is the process in which ________.
| back 71 B) glucose is formed from noncarbohydrate precursors |
front 72 Glycolysis is best defined as a catabolic reaction based upon the ________.
| back 72 B) conversion of glucose into two molecules of pyruvic acid |
front 73 What is the outcome of ketosis?
| back 73 B) metabolic acidosis |
front 74 Which of the choices below happens during the absorptive state?
| back 74 A) Anabolic processes exceed catabolic ones. |
front 75 In the case of a person who consumes a normal, balanced diet, proteins are essential to the body for all of the following except ________.
| back 75 A) production of energy |
front 76 The most abundant dietary lipids are ________.
| back 76 D) triglycerides |
front 77 Loss of heat in the form of infrared waves is termed ________.
| back 77 A) radiation |
front 78 Which hormone directs essentially all the events of the absorptive state?
| back 78 D) insulin |
front 79 Prostaglandins play a role in ________.
| back 79 D) control of blood pressure |
front 80 Which of the following is the most important function of the liver?
| back 80 D) protein metabolism |
front 81 As the body progresses from the absorptive to the postabsorptive state, only the ________ continues to burn glucose while every other organ in the body mostly switches to fatty acids.
| back 81 B) brain |
front 82 In gluconeogenesis, during the postabsorptive state, amino acids and ________ are converted to glucose.
| back 82 A) glycerol |
front 83 In the liver, the amine group of glutamic acid is removed as ________ in the oxidative state.
| back 83 C) ammonia |
front 84 Which of the choices below is not a mechanism of heat production?
| back 84 C) sweating |
front 85 Heat-loss mechanisms do not include ________.
| back 85 D) vasoconstriction of peripheral blood vessels |
front 86 The amount of ________ produced is probably the most important hormonal factor in determining BMR.
| back 86 B) thyroxine |
front 87 When ketone bodies are present in the blood and urine in large amounts, it usually indicates increased metabolism of ________.
| back 87 B) fatty acids |
front 88 Many factors influence BMR. What is the most critical factor?
| back 88 C) the ratio of surface area to volume (weight) of the body |
front 89 The primary reason elderly people should decrease their caloric intake is that ________.
| back 89 A) muscle mass and metabolism decline with age |
front 90 Which of the choices below is not a major route of heat exchange?
| back 90 D) shivering |
front 91 Which of the following statements is a false or incorrect statement?
| back 91 A) The amino acid pool is the body’s total supply of amino acids in the body’s proteins. |
front 92 Which of the following molecules are considered key molecules at metabolic crossroads?
| back 92 A) glucose-6-phosphate, pyruvic acid, acetyl CoA |
front 93 Which of the following nutrients yield the highest amount of energy per gram when metabolized?
| back 93 A) fats |
front 94 Which of the following does not occur in the mitochondria?
| back 94 B) glycolysis |
front 95 Which of the following is not true of beta oxidation?
| back 95 C) It involves the anabolism of fats. |
front 96 Select the correct statement about proteins.
| back 96 C) Proteins will be used by most cells for ATP synthesis if insufficient carbohydrates are ingested. |
front 97 Oxidation reduction reactions ________.
| back 97 B) may involve the loss of hydrogen and electrons |
front 98 What process primes a molecule to change in a way that increases its activity, produces motion, or does work?
| back 98 A) phosphorylation |
front 99 Which of the choices below is not a source of glucose during the postabsorptive state?
| back 99 C) absorption of glucose from the GI tract |
front 100 Which of the following is correct?
| back 100 B) Oxidation of FADH2 eventually yields four ATP via oxidative phosphorylation. |
front 101 Which of the following food groups are considered good sources of complete proteins?
| back 101 D) eggs, milk, yogurt, meat, and fish |
front 102 Conditions that promote the oxidative deamination and energy use of amino acids include ________.
| back 102 C) excessive amounts of protein in the diet |
front 103 When a person's hypothalamic thermostat is set to a higher level and the actual body temperature is below that level, the person may ________.
| back 103 D) shiver |
front 104 Glucose can be obtained from ________.
| back 104 A) glycogenolysis |
front 105 Which of the following is not a function of LDLs?
| back 105 A) transport cholesterol from the peripheral tissues to the liver |
front 106 Which of the following best defines negative nitrogen balance?
| back 106 A) Protein breakdown exceeds protein synthesis. |
front 107 The Krebs cycle produces ________ ATP molecules per glucose molecule by substrate-level phosphorylation. | back 107 two |
front 108 Which nutritional state constitutes the period during and shortly after eating when nutrients are flushing into the bloodstream from the GI tract? | back 108 absorptive |
front 109 Fat burning causes an accumulation of acetyl CoA, which the liver converts to ________. | back 109 ketones |
front 110 ________ is controlled hyperthermia | back 110 Fever |
front 111 The enzymes that catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions by removing hydrogen are specifically called ________. | back 111 dehydrogenases |
front 112 The process of splitting glucose through a series of steps that produces two pyruvic acid molecules is called ________. | back 112 glycolysis |
front 113 In the Krebs cycle, citric acid is followed by ________ acid. | back 113 isocitric |