Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 23 The Digestive System
front 1 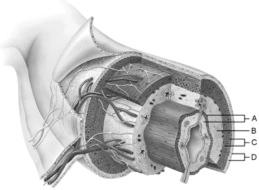 Mucosa | back 1 A |
front 2 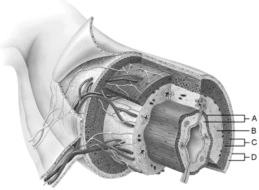 Duodenal glands found here | back 2 B |
front 3 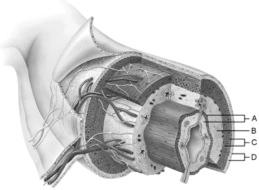 Smooth muscle layer | back 3 C |
front 4 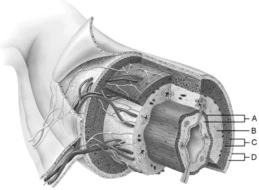 MALT found here | back 4 B |
front 5  Serosa | back 5 D |
front 6 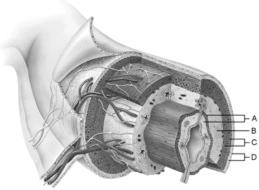 Area of the lamina propria | back 6 A |
front 7 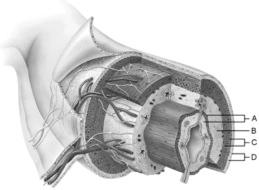 Continuation of the mesentery | back 7 D |
front 8 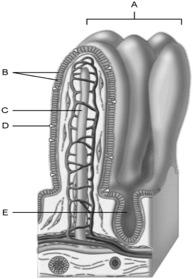 Absorptive cells that line the intestinal tract. | back 8 B |
front 9 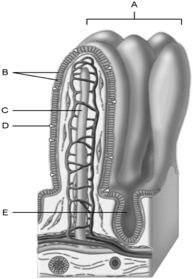 Cell type specialized to secrete mucus into the lumen of the intestinal tract. | back 9 D |
front 10  Structures that increase the absorptive area of the small intestine. | back 10 A |
front 11 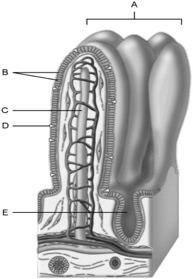 Wide lymph capillary located in the villus | back 11 C |
front 12 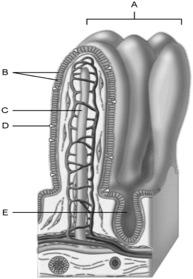 Paneth cells are found here | back 12 E |
front 13 Wavelike smooth muscle contractions that move foodstuffs through the alimentary tube.
| back 13 A |
front 14 Chemical or mechanical process of breaking down foodstuffs to substances that can be absorbed.
| back 14 C |
front 15 Enzymatic breakdown of any type of food molecule.
| back 15 D |
front 16 Process by which the products of digestion pass through the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract into the blood or lymph.
| back 16 B |
front 17 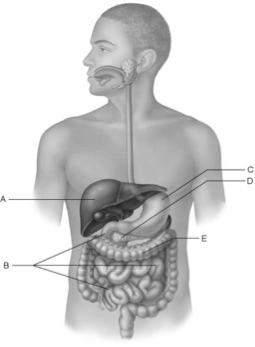 Produces enzymes that break down all categories of foodstuffs. | back 17 D |
front 18 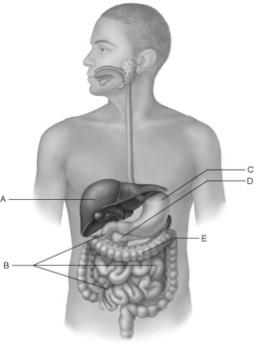 Increases surface area for absorption via villi and microvilli. | back 18 B |
front 19 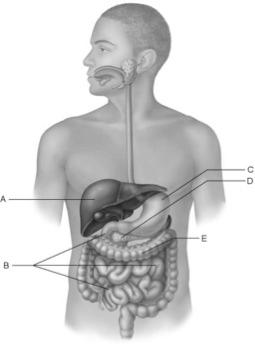 Bacteria process undigested chyme from the small intestine. | back 19 E |
front 20 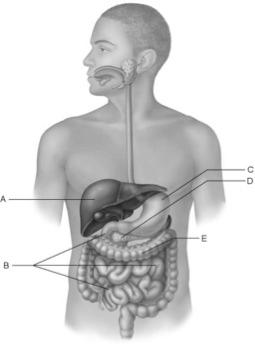 Only digestive structure with three muscle layers. | back 20 C |
front 21 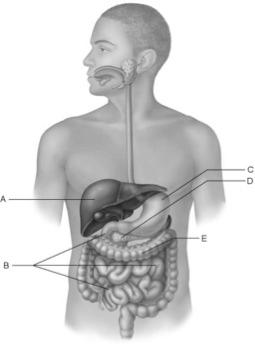 Receives blood via the hepatic portal system. | back 21 A |
front 22 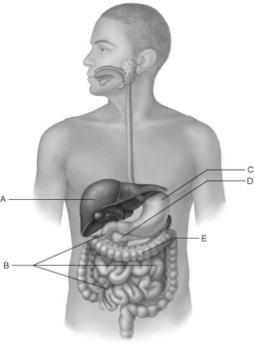 Contains the brush border enzymes that complete digestion of carbohydrates and proteins. | back 22 B |
front 23 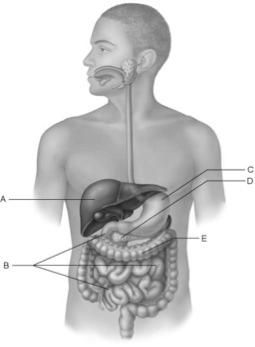 Main function is to filter and process the nutrient-rich blood delivered to it. | back 23 A |
front 24 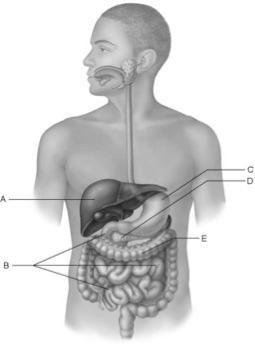 Produces intrinsic factor. | back 24 C |
front 25  Produces a mucoid barrier. | back 25 C |
front 26 True/False
| back 26 True |
front 27 True/False
| back 27 True |
front 28 True/False
| back 28 True |
front 29 True/False
| back 29 True |
front 30 True/False
| back 30 True |
front 31 True/False
| back 31 False |
front 32 True/False
| back 32 True |
front 33 True/False
| back 33 False |
front 34 True/False
| back 34 True |
front 35 True/False
| back 35 True |
front 36 True/False
| back 36 True |
front 37 True/False
| back 37 True |
front 38 True/False
| back 38 True |
front 39 True/False
| back 39 True |
front 40 True/False
| back 40 False |
front 41 True/False
| back 41 True |
front 42 True/False
| back 42 True |
front 43 True/False
| back 43 True |
front 44 True/False
| back 44 True |
front 45 True/False
| back 45 False |
front 46 True/False
| back 46 True |
front 47 True/False
| back 47 True |
front 48 True/False
| back 48 True |
front 49 True/False
| back 49 True |
front 50 True/False
| back 50 True |
front 51 True/False
| back 51 False |
front 52 The mechanical and chemical receptors that control digestive activity are located ________.
| back 52 B) in the walls of the tract organs |
front 53 The function of the hepatic portal circulation is to ________.
| back 53 B) collect absorbed nutrients for metabolic processing or storage |
front 54 The chemical and mechanical processes of food breakdown are called ________.
| back 54 A) digestion |
front 55 When we ingest large molecules such as lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins, they must undergo catabolic reactions whereby enzymes split these molecules. This series of reactions is called ________.
| back 55 C) chemical digestion |
front 56 The sheets of peritoneal membrane that hold the digestive tract in place are called ________.
| back 56 A) mesenteries |
front 57 From the esophagus to the anal canal, the walls of every organ of the alimentary canal are made up of the same four basic layers. Arrange them in order from the lumen.
| back 57 D) mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa |
front 58 Which of the following is not a factor that helps create the stomach mucosal barrier?
| back 58 D) rennin |
front 59 What part of the tooth bears the force of chewing?
| back 59 B) enamel |
front 60 The capillaries that nourish the epithelium and absorb digested nutrients lie in the ________.
| back 60 D) lamina propria |
front 61 Which hormone causes an increased output of enzyme-rich pancreatic juice and stimulates gallbladder contraction to release bile?
| back 61 C) cholecystokinin |
front 62 Choose the incorrect statement regarding bile.
| back 62 D) Bile contains enzymes for digestion. |
front 63 The absorptive effectiveness of the small intestine is enhanced by increasing the surface area of the mucosal lining. Which of the following accomplish this task?
| back 63 A) plicae circulares and intestinal villi |
front 64 Select the statement that is true concerning primary teeth.
| back 64 C) There are 20 primary teeth, and by 24 months of age most children have all 20. |
front 65 Which of the following is true concerning the number and type of permanent teeth?
| back 65 A) There are 32 permanent teeth, and the wisdom teeth are the last to emerge. |
front 66 Which of the following is not true of saliva?
| back 66 B) contains enzymes that begin the breakdown of proteins |
front 67 The salivary glands are composed of which two types of secretory cells?
| back 67 C) serous cells and mucous cells |
front 68 The solutes contained in saliva include ________.
| back 68 D) electrolytes, digestive enzyme, mucin, lysozyme, wastes, and IgA |
front 69 In addition to storage and mechanical breakdown of food, the stomach ________.
| back 69 A) initiates protein digestion and denatures proteins |
front 70 Chyme is created in the ________.
| back 70 B) stomach |
front 71 Hydrochloric acid is secreted by which of the secretory cells of the stomach?
| back 71 B) parietal cells |
front 72 Gastrin, histamine, endorphins, serotonin, cholecystokinin, and somatostatin are hormones or paracrines that are released directly into the lamina propria. Which of the following cell types synthesize and secrete these products?
| back 72 A) enteroendocrine cells |
front 73 There are three phases of gastric secretion. The cephalic phase occurs ________.
| back 73 A) before food enters the stomach and is triggered by aroma, sight, or thought |
front 74 Peristaltic waves are ________.
| back 74 D) waves of muscular contractions that propel contents from one point to another |
front 75 Gastrin is a digestive hormone that is responsible for the stimulation of acid secretions in the stomach. These secretions are stimulated by the presence of ________.
| back 75 B) protein and peptide fragments |
front 76 Pepsinogen, a digestive enzyme, is secreted by the ________.
| back 76 A) chief cells of the stomach |
front 77 You have just eaten a meal high in complex carbohydrates. Which of the following enzymes will help to digest the meal?
| back 77 B) amylase |
front 78 The ducts that deliver bile and pancreatic juice from the liver and pancreas, respectively, unite to form the ________.
| back 78 D) hepatopancreatic ampulla |
front 79 The enzymatic breakdown of any type of food molecule is called ________.
| back 79 C) hydrolysis |
front 80 Short-chain triglycerides found in foods such as butterfat molecules in milk are split by a specific enzyme in preparation for absorption. Which of the following enzymes is responsible?
| back 80 C) lipase |
front 81 Parietal cells of the stomach produce ________.
| back 81 C) hydrochloric acid |
front 82 Hepatocytes do not ________.
| back 82 A) produce digestive enzymes |
front 83 Which of the following is not a phase of gastric secretion?
| back 83 D) enterogastric |
front 84 Which vitamin requires intrinsic factor in order to be absorbed?
| back 84 A) B12 |
front 85 Chief cells ________.
| back 85 C) are found in the basal regions of the gastric glands |
front 86 Chemical digestion reduces large complex molecules to simpler compounds by the process of ________.
| back 86 B) catabolism |
front 87 The ________ contains lobules with sinusoids (lined with macrophages) that lead to a central venous structure.
| back 87 A) liver |
front 88 If an incision has to be made in the small intestine to remove an obstruction, the first layer of tissue to be cut is the ________.
| back 88 A) serosa |
front 89 The terminal portion of the small intestine is known as the ________.
| back 89 B) ileum |
front 90 The dental formula for an adult is 2-1-2-3. What does the 1 stand for?
| back 90 D) canine tooth |
front 91 Digestion of which of the following would be affected the most if the liver were severely damaged?
| back 91 A) lipids |
front 92 ________ is locally regulated in the blood by the active form of vitamin D, which acts as a cofactor.
| back 92 D) Calcium |
front 93 Important peritoneal folds do not include the ________.
| back 93 D) round ligament |
front 94 The lamina propria is composed of ________.
| back 94 A) loose connective tissue |
front 95 ________ is (are) not important as a stimulus in the gastric phase of gastric secretion.
| back 95 B) Carbohydrates |
front 96 Pancreatic amylase does not get to the small intestine via the ________.
| back 96 C) cystic duct |
front 97 The function of the goblet cells is to ________.
| back 97 B) produce mucus that protects parts of the digestive organs from the effects of powerful enzymes needed for food digestion |
front 98 Which of the following is an essential role played by large intestine bacteria?
| back 98 C) synthesize vitamin K and B-complex vitamins |
front 99 Nervous control of gastric secretion is provided by ________.
| back 99 B) the vagus nerve and enteric plexus |
front 100 Which of the following are types of papillae on the tongue that contain taste buds?
| back 100 A) fungiform and circumvallate |
front 101 Which of the following produce intrinsic factor?
| back 101 A) parietal cells |
front 102 Which of the following enzymes is specific for proteins?
| back 102 C) trypsin |
front 103 Surgical cutting of the lingual frenulum would occur in which part of the body?
| back 103 A) tongue |
front 104 A fluid secreted into the small intestine during digestion that contains cholesterol, emulsification agents, and phospholipids is ________.
| back 104 A) bile |
front 105 The layer of the digestive tube that contains blood vessels, lymphatic nodes, and a rich supply of elastic fibers is the ________.
| back 105 B) submucosa |
front 106 Which of the following is not characteristic of the large intestine? It ________.
| back 106 C) is longer than the small intestine |
front 107 What stomach secretion is necessary for normal hemoglobin production in RBCs?
| back 107 C) intrinsic factor |
front 108 How are most nutrients absorbed through the mucosa of the intestinal villa?
| back 108 C) active transport driven directly or indirectly by metabolic energy |
front 109 Select the correct statement about the regulation of gastric secretion.
| back 109 C) Gastric secretion can be stimulated before food has entered the mouth. |
front 110 Paneth cells ________.
| back 110 C) secrete enzymes that kill bacteria |
front 111 Select the correct statement about digestive processes.
| back 111 C) Chyme entering the duodenum can decrease gastric motility via the enterogastric reflex. |
front 112 Chemical digestion in the small intestine involves ________.
| back 112 B) cholecystokinin (CCK), an intestinal hormone responsible for gallbladder contraction |
front 113 Select the correct statement about absorption.
| back 113 C) If intact proteins are transported across the villus epithelium, an immune response may be generated. |
front 114 Select the correct statement about electrolyte absorption.
| back 114 D) Iron and calcium are absorbed mostly by the duodenum. |
front 115 You have just eaten french fries, buttered toast, ice cream, and whole milk. Which of the following glands would be active in helping you to digest this food?
| back 115 A) the pancreas |
front 116 The ingestion of a meal high in fat content would cause which of the following to occur?
| back 116 C) Bile would be released from the gallbladder to emulsify the fat in the duodenum. |
front 117 The mucosa of the developing alimentary tube comes from ________.
| back 117 C) endoderm |
front 118 A baby is admitted to the hospital with a history of projectile vomiting after each feeding. On examination, it is found that the sphincter controlling food passage from the stomach to the duodenum is thickened and does not open readily. Because of the baby's loss of gastric juice, his blood probably indicates ________.
| back 118 C) alkalosis |
front 119 Hormones or paracrines that inhibit gastric secretion include ________.
| back 119 B) secretin |
front 120 Which of these is not part of the splanchnic circulation?
| back 120 B) inferior vena cava |
front 121 Which of these is not a component of saliva?
| back 121 D) nitric oxide |
front 122 There are some 20 known pathogens found in the large intestine; our Ig ________ antibody-mediated response restricts them from going beyond the mucosa and causing problems.
| back 122 B) A |
front 123 The longest portion of the small intestine is the ________. | back 123 ileum |
front 124 ________ is the principal enzyme for breaking down carbohydrates. | back 124 Amylase |
front 125 ________ cells of the stomach secrete HCl. | back 125 Parietal |
front 126 The chief bile pigment is ________. | back 126 bilirubin |
front 127 ________ is another word for vomiting | back 127 Emesis |
front 128 The portal triad contains ________. | back 128 a branch of the hepatic artery, a branch of the hepatic portal vein, and a bile duct. |
front 129 ________ cells are found in the sinusoids of the liver, and they remove debris from the blood as it flows past. | back 129 Kupffer |
front 130 ________ peritoneum covers the external surfaces of most digestive organs. | back 130 Visceral |
front 131 The ________ ligament anchors a tooth in the alveolus of the jaw. | back 131 periodontal |
front 132 The ________ phase of gastric secretions occurs before food enters the stomach. | back 132 cephalic (or reflex) |
front 133 The round ligament is a remnant of the fetal ________. | back 133 umbilical vein |