Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
AMCA Certification - Phlebotomy
front 1 Phlebotomist performs a venous blood draw on a 91 year old patient. The phlebotomist should use what method? | back 1 Hand draw |
front 2 What is the first thing a phlebotomist must do when performing a finger stick? | back 2 Confirm the correct identity of a patient |
front 3 When performing a blood draw the phlebotomist notices red spots forming, what action should the phlebotomist do? | back 3 Release the tourniquet immediately |
front 4 What is appropriate to use when collecting serum chemistry? | back 4 SST (Serum Separator Tube) |
front 5 A phlebotomist collects a blood alcohol level for forensic testing and hands the specimen off to a lab tech. What represents the correct procedure? | back 5 The technologist writes both the time received and his initials on the chain of custody form |
front 6 What result is affected when providone iodine is used to cleans the site for a dermal puncture? | back 6 Potassium |
front 7 What can cause a hemolyzed specimen? | back 7 Shaking the tube vigorously |
front 8 What is an appropriate cleanser for cleansing around the urinary meatus in a clean catch urine collection? | back 8 Benzalkonium chloride |
front 9 What anti-coagulant should the phlebotomist use to collect a PT/PTT test | back 9 Sodium citrate |
front 10 A phlebotomist received an order to draw an infant screening card 02 levels, bilirubin, and DNA. What should be drawn first? | back 10 O2 level |
front 11 What is the correct order of draw? | back 11 Green, Lavender, and Grey |
front 12 A phlebotomist is preparing a hand draw, what instrument should the phlebotomist assemble? | back 12 Winged infusion set and adapter |
front 13 During a venipuncture the patient reports a sharp pain radiating down the arm. What action should the phlebotomist take? | back 13 Release the tourniquet and remove the needle |
front 14 A blood specimen was rejected based on QNS, what does this mean? | back 14 Specimen quantity was insufficient |
front 15 When collecting a sample for CBC, what vessel should the phlebotomist attempt to draw from first? | back 15 Medial cubital vein |
front 16 A diabetic patient states that she prefers to be drawn on the inside of her wrist. What action should the phlebotomist take? | back 16 Attempt to draw from the antecubital region first |
front 17 What is the best protection when drawing blood rom a patient with active tuberculosis? | back 17 N-95 respirator |
front 18 According to CLSI order of draw guidelines, what sample should the phlebotomist collect first? | back 18 Blood cultures |
front 19 A phlebotomist must invert anticoagulant tubes to prevent what? | back 19 Clotting of the sample |
front 20 The following emergency fist aid treatment, maintaining an open airway, control bleeding, and keeping the victim warm until help arrives indicates the patient is suffering from? | back 20 Shock |
front 21 What does the phlebotomist need to do first when collecting a blood culture using a winged infusion set and evacuated tube system? | back 21 Fill the aerobic bottles first |
front 22 I phlebotomist is drawing five blood collection tubes. When should the tourniquet be removed? | back 22 After 1 minute (1-2 times tube) |
front 23 A phlebotomist must choose the correct tube color and additive for the corresponding ....... test? | back 23 Laboratory |
front 24 What is the appropriate action when labeling a specimen> | back 24 Label the specimen at the time of collection in front of the patient |
front 25 Choosing to perform a capillary puncture is best determined by what? | back 25 Test ordered |
front 26 What is the next step after removing the needle from a patients arm? | back 26 Engage the needle safety device |
front 27 What is the first step un the blood collection procedure? | back 27 Test requisition - check that it is clear of labs needed, if not contact the appropriate person for confirmation |
front 28 A 69 year old patient is brought in to the ER. Several blood tests are ordered. The phlebotomist collects blood under ........ consent? | back 28 Informed consent |
front 29 A physician orders a specimen STAT, but the phlebotomist forgets to fill the out the patient ID number. What will the lab do when they receive the specimen? | back 29 The lab rejects mislabeled specimens |
front 30 A patient states that this is his first blood draw. What action is appropriate? | back 30 Describe the procedure |
front 31 When alcohol is used to cleanse the venipuncture site, it must be allowed to air dry prior to the venipuncture because alcohol | back 31 Requires time for the antiseptic to work |
front 32 The phlebotomist needs to draw a GTT on a patient and notices an empty breakfast plate on the bedside table. What action should the phlebotomist take? | back 32 Ask the patient if they have had anything to eat or drink |
front 33 While the phlebotomist is performing a venipuncture, the patient begins to seize, what action must the phlebotomist take? | back 33 Discontinue the draw immediately |
front 34 During a routine phlebotomy procedure the phlebotomist is stuck with a used needle. What action should be taken next? | back 34 Flush the puncture site with running water |
front 35 What statement by a phlebotomist regarding skin preparation for blood cultures is appropriate? | back 35 I will cleanse the area with providone iodine |
front 36 What tube should be collected first for dermal samples? | back 36 Lavender top |
front 37 What is the proper procedure after collecting an ammonia sample? | back 37 Place the specimen tube in an ice water slurry |
front 38 A phlebotomist has a request to collect a routine CBC from a healthy 10 month old infant, what is the appropriate collection site? | back 38 Left heel |
front 39 When performing an ETS venipuncture the phlebotomist should and the needle.......? | back 39 In the same direction as the vein and at a 30 degree angle with the bevel facing up |
front 40 During a venipuncture the patient becomes pale and diaphoretic. What condition is most likely to occur in this patient? | back 40 Syncope (fainting) |
front 41 A phlebotomist walks into a patients room and finds the patient bleeding profusely from the leg. What action should the phlebotomist do first? | back 41 Apply direct pressure to the wound |
front 42 When preparing for transport, what specimen must be placed in a ice bath within 30 mins after collection? | back 42 Arterial Blood Gases (ABG) |
front 43 What is an important question to ask the patient prior to collecting a metabolic panel? | back 43 When was the last time you ate |
front 44 What additive should be used when performing a CBC? | back 44 EDTA (in a lavender tube) |
front 45 What is the name for small red spots caused by the tourniquet? | back 45 Petechiae |
front 46 A phlebotomist performs a urine dipstick on a pediatric inpatient and the value for blood is 4+. What is the best action for the phlebotomist to take when reporting this value? | back 46 Report the result to the patients physician |
front 47 What includes all the appropriate forms of identification in the inpatient setting? | back 47 Verbal, identification band, and tube label |
front 48 Serum sodium level and serum potassium level are main test for? | back 48 Electrolytes evaluations |
front 49 Appropriate tubes to check coagulation factors (PTT, APTT, BT, CT, PTT, TT)? | back 49 Blue top tube |
front 50 Chemical in blue top tube | back 50 Citrate (remember blue = citrate b after c) |
front 51 Medical terminology for red blood cells? | back 51 Erythrocytes |
front 52 Thrombocytes are what kind of cell? | back 52 Platelets |
front 53 Medical terminology for ALL blood cells? | back 53 All of the above - ie, eurthro, thrombo and white |
front 54 Main function of thrombocytes? | back 54 Coagulation |
front 55 Main function red blood cells? | back 55 Transport O2 to cells |
front 56 Life cycle of red blood cell? | back 56 120 days |
front 57 What is not part of a complete blood count (Hemoglobin, Hematocrit and differential are part of the CBC? | back 57 Activate partial thromboplastin time test (APPT) |
front 58 What is the most common occurring lab nosocomial infection? | back 58 HBV |
front 59 Common and routinely performed test in the serology lab department? | back 59 Rapid Plasma Regain (RPR)(SST Tube) |
front 60 What does CBC stand for? | back 60 Complete Blood Count (Lavender tube) |
front 61 What does PTT stand for? | back 61 Prothrombin Time Test (Blue tube) |
front 62 What does BUN stand for? | back 62 Blood, urea, nitrogen (SST tube) |
front 63 What does BT stand for? | back 63 Bleeding time |
front 64 What does GTT stand for? | back 64 Glucose Tolerance Test (SST tube) |
front 65 Which lab department performs hemogram? | back 65 Hematology |
front 66 Most common test for lavender top tube? | back 66 CBC - complete blood count |
front 67 What is the additive present in the lavender top tube? | back 67 EDTA (E after D) |
front 68 What are not included in the antecubital fossa? | back 68 Brachial veins |
front 69 Vein choice order? | back 69 Ante cubital is 1st choice |
front 70 What is the process used to wash and remove blood and tissues from contaminated medical supplies? | back 70 Sanitization |
front 71 What would be the first test the lab worker would draw if the patient is suspected to have FUO (fever unknown origin)? | back 71 Blood culture |
front 72 BNP is a special test used to evaluate | back 72 Cardiac enzymes and cardiac markers |
front 73 ........ is the process where complex substances in the food are broken down into simple substances while releasing energy | back 73 Catabolism |
front 74 Homeostasis definition? | back 74 The condition where healthy body through constant changes remains the same |
front 75 Hemostasis definition? | back 75 Stoppage of excessive blood |
front 76 The blood which contains more oxygen and less carbon dioxide is called? | back 76 Oxygenated blood, which is also red in color |
front 77 The blood contains less oxygen and more carbon dioxide is called? | back 77 Deoxygenated blood and is blue in color |
front 78 Name the main organ of the human body that is closer to the heart and contains deoxygenated blood? | back 78 Superior vena cava |
front 79 What is found in plasma but not in serum? | back 79 Fibrinogen |
front 80 An infection acquired in a health care facility is called? | back 80 Nosocomial |
front 81 Three components of the chain of infection are? | back 81 Source, mode of transmission, and susceptible host |
front 82 Important PPE's in an isolation room? | back 82 Gloves, gown, and mask |
front 83 A sample for fimbrin degradation product testing would be sent to which department? | back 83 Coagulation department |
front 84 What precaution require special air handlings and ventilation? | back 84 Airborne diseases |
front 85 What is the current CDC guidelines for infection control? | back 85 Standard precaution |
front 86 Legal action in which the alleged injured party sues for monetary damages are? | back 86 Civil action |
front 87 The level of care that a person of ordinary intelligence and good sense would exercise under the given circumstance's is the definition of .... care? | back 87 Due care |
front 88 What test is not associated with the muscular system of the human body? | back 88 HCG |
front 89 Guides used to monitor all aspects of proper patient care are called? | back 89 QA Indicators |
front 90 The concentration of H20 (water) in plasma is about 90% the ..... is the concentration of remaining solution in the plasma? | back 90 Dissolved substances |
front 91 If patient has a blood group B, what agglutinins are present in that blood group? | back 91 Anti-A |
front 92 When performing bleeding time test the blood pressure cuff must be inflated to? | back 92 40mm Hg |
front 93 Educate the patient, not allowed to eat and drink anything by mouth, is called? | back 93 NPO (Nothing by mouth) |
front 94 An example of QC measures in phlebotomy is? | back 94 Checking the expiration dates in all different evacuated tubes |
front 95 What, according to CLIS, order of draw guidelines would be last? | back 95 Lavender top tube |
front 96 What lab documents describes in detail the steps to follow specimen collections? | back 96 Procedure manual |
front 97 In order to monitor therapeutic drug level the lab worker needs to know? | back 97 Time of the last dose |
front 98 What test should be collected in a royal blue top tube? | back 98 Magnesium |
front 99 How many tubes are drawn for a 3 hour glucose tolerance test (GTT)? | back 99 4 tubes (1st is always random fasting specimen then 3 tests) |
front 100 If a lab test requires serum, which tube is used? | back 100 Red topped tube |
front 101 Alanine amino transfearas test (ALAST) is associated with which part of the body? | back 101 Liver |
front 102 The principals of right and wrong, as applied to professional issues are defined as? | back 102 Ethics |
front 103 What is the abbreviation for a type of antibody? | back 103 IgM |
front 104 Most coagulation tests require a plasma specimen collected in a ......... top? | back 104 Light blue top |
front 105 What test requires a whole blood specimen? | back 105 CBC |
front 106 Patient with a low grade fever, 1 month, doctor ordered EST, what tube will be used for this test? | back 106 Lavender top tube |
front 107 A SST tube is frequently used for what path lab department (Serum Separator Tube)? | back 107 Chemistry |
front 108 What is the chemical substance present in a serum separator tube (SST)? | back 108 Thixotropic gel |
front 109 Three main parts of a needle? | back 109 Bevel, shaft, hub |
front 110 The clear colorless fluid that functions in protecting and nourishing the ...... and ...... is called the cerebrospinal fluid? | back 110 Brain and spinal cord |
front 111 Identifying the tubes need to collect a PT, Stat, and BC in order? | back 111 Yellow, light blue, plain silicone tube (PST) |
front 112 What is collected in a trace element tube? | back 112 Lead |
front 113 Verbal expressions are not an example of? | back 113 Kinesics |
front 114 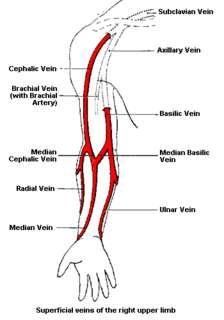 Location of antecubital veins | back 114 Basilic - thumb side |
front 115 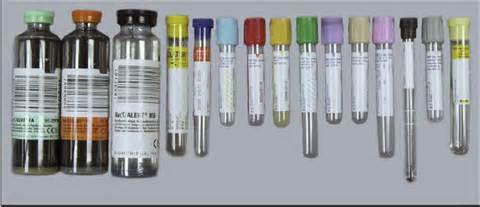 Label the diagram | back 115 Bottles are culture bottles, then label as red, yellow, lavender etc. Yellow and black tube is a tiger top tube. |
front 116 Sterile Blood Culture Tubes or Vials (YELLOW) | back 116 Sterile specimens are drawn first to prevent contamination that can occur during the procedure. The specimens you should draw first are blood culture bottles and SPS (yellow top) tubes. |
front 117 Blue top tubes | back 117 Blue top tubes are used for coagulation studies and contain citrate additives. They have a light blue shield/stopper as well as a clear shield used over the blue stopper. |
front 118 Red top tubes | back 118 These tubes may come with or without clot activator or gel separator. They may look like a red and black tiger top stopper, gold shield, or a red shield/stopper. These are used to draw samples for blood bank and HCG levels (pregnancy hormones). |
front 119 Green top tubes | back 119 These tubes contain heparin as an additive and may come with or without a gel plasma separator. They may have a green and gray stopper, light green shield, as well as the green shield/stopper. These tubes are used to test ammonia and blood chemistry levels. |
front 120 Purple (Lavender)top tubes | back 120 EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid) tubes use a lavender stopper/shield, white (pearl) shield, pink stopper/shield, royal blue shield or tan shield. These tubes can be used to test CBC (Complete Blood Count), Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, and ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate). |
front 121 Grey top tubes | back 121 These glycolytic inhibitor tubes have a gray stopper/shield and are used for a variety of glucose studies |
front 122 Order of draw: | back 122 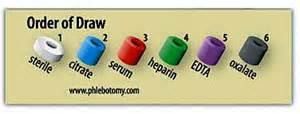 |