Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 19- Blood
front 1 Which of the following is NOT one of the formed elements?
| back 1 Correct Answer:
|
front 2 Which of the following statements about blood is FALSE?
| back 2 It is slightly acidic, with a pH of 6.5. |
front 3 Where are most plasma proteins produced?
| back 3 Correct Answer:
|
front 4 Which category of plasma proteins includes the antibodies?
| back 4 Correct Answer:
|
front 5 Which of the plasma proteins functions in blood clotting?
| back 5 Correct Answer:
|
front 6 Which part of hemoglobin binds oxygen?
| back 6 Correct Answer:
|
front 7 What is the specific term for the production of red blood cells?
| back 7 Correct Answer:
|
front 8 Where are red blood cells produced in an adult? | back 8 red bone marrow |
front 9 Which of the following is NOT a surface antigen that is used in determining blood type?
| back 9 C |
front 10 If a person has type A and Rh surface antigens on the blood cells and anti-B antibodies in the plasma, what is that person's blood type?
| back 10 Correct Answer:
|
front 11 What type of blood would cause a cross-reaction when given to a person with type A-positive blood?
| back 11 type B-positive |
front 12 What is the term for the characteristic of white blood cells whereby they are attracted to a specific chemical stimulus?
| back 12 Correct Answer:
|
front 13 Which type of white blood cell circulates in the blood for about 24 hours before entering the tissues and differentiating into a macrophage?
| back 13 monocyte |
front 14 Which type of white blood cell includes the B and T cells that are responsible for humoral and cell-mediated immunity? | back 14 Correct Answer:
|
front 15 Which of the following types of white blood cells are involved in fighting parasitic infections, such as flukes and roundworms?
| back 15 Correct Answer:
|
front 16 Platelets for formed from large cells called __________.
| back 16 megakaryocytes |
front 17 An abnormally low platelet count is called __________.
| back 17 thrombocytopenia |
front 18 In which phase of hemostasis does local contraction of the injured blood vessel occur?
| back 18 vascular phase |
front 19 In which phase of hemostasis is fibrin deposited, creating a solid blood clot?
| back 19 coagulation phase |
front 20 Which of the following affect almost every aspect of the clotting process?
| back 20 calcium ions and vitamin K |
front 21 Blood __________.
| back 21 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 22 What are the major components of whole blood?
| back 22 plasma and formed elements |
front 23 Which type of healthy human would typically have 4 to 5 liters of blood?
| back 23 adult female |
front 24 Which of the following is NOT a function of blood?
| back 24 coordination of body system responses |
front 25 Which of the following is NOT a reason why venipuncture is usually the preferred method for obtaining a blood sample?
| back 25 Walls of veins are thicker than arteries. |
front 26 What is the plasma protein that plays an important role in protection against foreign proteins and pathogens?
| back 26 immunoglobulin |
front 27 What is the plasma protein that functions in blood clotting?
| back 27 fibrinogen |
front 28 Which of the following is NOT a function of albumin?
| back 28 transporting iron |
front 29 Which blood cells are the most abundant?
| back 29 erythrocytes |
front 30 A hemoglobin molecule consists of __________ chains of polypeptides, and ___________ heme units, which each contain the element ___________.
| back 30 four; four; iron |
front 31 The bond between oxygen and hemoglobin is __________ than that of fetal hemoglobin and oxygen.
| back 31 weaker than |
front 32 The binding of a heme unit's iron ion to an oxygen ion __________.
| back 32 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 33 The lifespan of a typical RBC is about __________.
| back 33 four months |
front 34 Which of the following occurs during the recycling of a red blood cell?
| back 34 Iron and amino acids are recycled to be used in erythropoiesis, while unusable products are excreted into the small intestine in bile. |
front 35 In adults, erythropoiesis occurs in __________.
| back 35 red bone marrow |
front 36 Reticulocytes account for about __________ percent of the erythrocyte population in the blood.
| back 36 1 |
front 37 A normal hematocrit is in the range of __________.
| back 37 37–54 |
front 38 Normal hemoglobin concentrations are in the range of __________ g/dL.
| back 38 12–18 |
front 39 It is an illegal practice for Olympic competitors to receive doses of which hormone, which stimulates the production of red blood cells?
| back 39 erythropoietin |
front 40 Which of the following statements concerning red blood cells is INCORRECT?
| back 40 There are approximately 10,000 red blood cells in a microliter (µL) of blood. |
front 41 Which of the following statements concerning hemoglobin is FALSE?
| back 41 Most of the hemoglobin in red blood cells is in the form of carbaminohemoglobin. |
front 42 What is the most common blood type among Americans?
| back 42 type O |
front 43 Hemolytic disease of the newborn occurs when an Rh-__________ woman bears the second child of an Rh-__________ man.
| back 43 negative; positive |
front 44 If Misty is type A and needs to receive transfusions of blood during a surgery, which blood type(s) could she receive?
| back 44 A and O |
front 45 There are __________ major blood types and __________ different surface antigens.
| back 45 four; three |
front 46 An individual with type AB blood has __________ antigens and __________ antibodies.
| back 46 A and B; no |
front 47 Which blood type can be safely transfused into a person with Type O blood, without a cross-reaction?
| back 47 type O blood given to a person with type O blood |
front 48 Lymphocytes account for __________ percent of circulating white blood cells.
| back 48 20–30 |
front 49 Monocytes leave the circulation to become __________.
| back 49 macrophages |
front 50 Which of the following statements concerning white blood cells is FALSE?
| back 50 Monocytes begin their development in bone marrow and then migrate to the thymus, spleen, or liver to complete the maturation process. |
front 51 Which of the white blood cells is also known as a polymorph?
| back 51 neutrophil |
front 52 During an infection, the white blood cell count may rise, a condition known as __________.
| back 52 leukocytosis |
front 53 Bleeding along the digestive tract and within the skin is symptomatic of __________.
| back 53 thrombocytopenia |
front 54 Which of the following is NOT a function of platelets?
| back 54 formation of a solid clot |
front 55 Which disease state would be characterized by a concentration of up to 1,000,000 platelets/µL in the plasma?
| back 55 thrombocytosis |
front 56 The process of hemostasis includes which of the following?
| back 56 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 57 The platelet phase includes which of the following?
| back 57 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 58 Along with calcium ions, which vitamin is involved in almost every aspect of blood coagulation?
| back 58 K |
front 59 Which of the following factors does NOT restrict the coagulation process?
| back 59 thromboxane A2 |
front 60 Syneresis refers to the process of __________.
| back 60 clot retraction |
front 61 What are the major components of the cardiovascular system?
| back 61 blood, heart, and blood vessels |
front 62 Which of the following is NOT a function of the blood?
| back 62 All of the listed responses are functions of the blood. |
front 63 The formed elements of the blood consist of __________.
| back 63 red and white blood cells and platelets |
front 64 Which of the following is NOT a component of plasma?
| back 64 elastic fibers |
front 65 What are the "patrol agents" in the blood that defend the body against toxins and pathogens?
| back 65 white blood cells and antibodies |
front 66 To check the efficiency of gas exchange at the lungs, blood may be required via __________.
| back 66 arterial puncture |
front 67 Blood temperature is roughly _____°C, and the blood pH averages _____.
| back 67 38°C; 7.4 |
front 68 Which type of plasma protein serves as a carrier for the hormones T3 and T4?
| back 68 albumins |
front 69 In addition to water and proteins, what else is part of plasma?
| back 69 electrolytes, nutrients, and organic wastes |
front 70 Circulating mature RBCs lack __________.
| back 70 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 71 The primary function of a mature red blood cell is which of the following?
| back 71 The primary function of a mature red blood cell is which of the following? |
front 72 Which part of the hemoglobin molecule directly interacts with oxygen?
| back 72 the iron ion |
front 73 Coloration of urinary and digestive wastes is the result of the presence of which products from the breakdown of red blood cells?
| back 73 urobilins and stercobilins |
front 74 The iron extracted from heme molecules during hemoglobin recycling is stored in the protein–iron complexes __________.
| back 74 ferritin and hemosiderin |
front 75 During RBC recycling, each heme unit is stripped of its iron and converted to __________.
| back 75 biliverdin |
front 76 What is the primary site of erythropoiesis in the adult?
| back 76 bone marrow |
front 77 Erythropoietin appears in the plasma when peripheral tissues, especially the kidneys, are exposed to __________.
| back 77 low oxygen concentrations |
front 78 Agglutinogens are contained (on, in) the __________, whereas the agglutinins are found (on, in) the __________.
| back 78 cell membrane of the RBC; plasma |
front 79 If you have type A blood, your plasma holds circulating __________ that will attack __________ erythrocytes.
| back 79 anti-B agglutinins; type B |
front 80 Which of the following is an agranular leukocyte that becomes a tissue macrophage after approximately 24 hours in circulation?
| back 80 monocyte |
front 81 Which type of granular leukocyte can engulf up to two dozen bacteria and also produces a respiratory burst that creates harsh chemical agents such as hydrogen peroxide?
| back 81 neutrophil |
front 82 Megakaryocytes are specialized cells of the bone marrow responsible for __________.
| back 82 formation of platelets |
front 83 The rate of megakaryocyte activity and platelet formation is regulated by __________.
| back 83 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 84 Which of the following statements is FALSE concerning T cells and B cells?
| back 84 B cells differentiate into T cells and produce antibodies against foreign antigens. |
front 85 The process of hemostasis includes five phases. What is the correct order of the phases as they occur after injury?
| back 85 vascular, platelet, coagulation, clot retraction, clot destruction (fibrinolysis) |
front 86 Because the concentration of dissolved gases is different between the plasma and the tissue fluid __________.
| back 86 O2 will tend to diffuse from the plasma to the interstitial fluid, and CO2 will tend to diffuse in the opposite direction |
front 87 If blood comprises 7 percent of the body weight in kilograms, how many liters of blood would there be in an individual who weighs 85 kg?
| back 87 5.95 |
front 88 How is it that liver disorders can alter the composition and functional properties of the blood?
| back 88 The liver is the primary source of plasma proteins. |
front 89 When plasma O2 concentrations are falling, the rising plasma CO2 binds to the __________ of the hemoglobin molecule.
| back 89 alpha and beta chains |
front 90 Hemoglobin molecules released into the bloodstream by the breakdown of RBCs by hemolysis will be excreted in the __________.
| back 90 kidney |
front 91 Signs of iron deficiency anemia include __________.
| back 91 decrease in hematocrit, hemoglobin content, and O2-carrying capacity |
front 92 On average, 1 microliter of blood contains __________ erythrocytes.
| back 92 5.2 million |
front 93 The process in which packed RBCs that were previously removed are reintroduced before an athletic event is called __________.
| back 93 blood doping |
front 94 Protein synthesis in a mature RBC occurs primarily in __________.
| back 94 Mature red blood cells cannot synthesize proteins. |
front 95 If agglutinogen B meets with agglutinin anti-A, what is the result?
| back 95 No agglutination occurs. |
front 96 What is the precursor of all blood cells in the human body?
| back 96 hemocytoblast |
front 97 Reticulocytes are nucleated immature cells that develop into mature __________.
| back 97 erythrocytes |
front 98 In which pregnancy is an Rh-positive mom and an Rh-positive child at risk of developing erythroblastosis fetalis?
| back 98 no pregnancy |
front 99 In the first pregnancy of an Rh-negative mother with an Rh-positive child, why are there usually NO symptoms of erythroblastosis fetalis?
| back 99 Blood between mother and child does not mix until birth. |
front 100 Which of the following occurs in hemolytic disease of the newborn?
| back 100 The mother's agglutinins cross the placental barrier and destroy fetal red blood cells. |
front 101 The number of eosinophils increases dramatically during __________.
| back 101 an allergic reaction or a parasitic infection |
front 102 A typical microliter of blood contains __________ leukocytes.
| back 102 5000–10,000 |
front 103 Under "normal" conditions, neutrophils comprise __________ of the circulatory white blood cells.
| back 103 50–70 percent |
front 104 Which of the following is a notable feature of leukemia?
| back 104 excessive numbers of white blood cells |
front 105 Myeloid stem cells will differentiate into progenitor cells, which give rise to all white blood cells EXCEPT __________.
| back 105 lymphocytes |
front 106 Clot destruction involves a process that begins with __________.
| back 106 activation of the proenzyme plasminogen, which initiates the production of plasmin |
front 107 The major effect of vitamin K deficiency in the body is that it leads to __________.
| back 107 a breakdown of the common pathway, inactivating the clotting system |
front 108 A vitamin B12 deficiency results in the type of anemia known as __________.
| back 108 pernicious anemia |
front 109 A change in the amino acid sequence of DNA coding for one of the globin chains of the hemoglobin molecule results in a condition known as __________.
| back 109 sickle cell anemia |
front 110 Jessica has just moved to Denver, Colorado, from Orlando, Florida. What condition is she experiencing now that is stimulating the production of erythropoietin and, consequently, more red blood cells?
| back 110 hypoxia caused by an increase in her elevation above sea level |
front 111 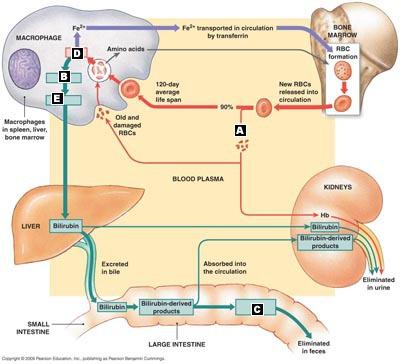 Correctly match the terms with the correct location of the diagram of red blood cell turnover. | back 111 A. Hemolysis
|
front 112 Correctly match the terms with the formed elements of blood. | back 112 A. Basophil
|
front 113 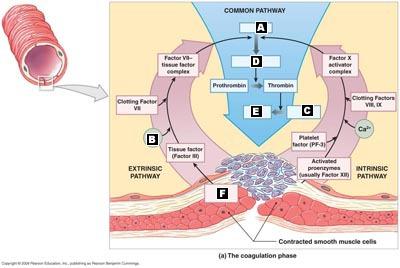 Match the terms in their appropriate locations in the diagram of the coagulation phase of hemostasis. | back 113 A. Factor X
|
front 114 Order of events occurring during the recycling of a red blood cell. | back 114 A. After approximately 120 days, a macrophage consumes a red blood cell.
|
front 115 Correctly list the following steps in clotting in the proper order:
| back 115 B. Endothelial cells contract and expose underlying basal lamina to bloodstream
|
front 116 Correctly list the cells in the steps of erythropoiesis in the correct order. | back 116 hemocytoblast
|
front 117 Surface antigen A and anti-B antibodies | back 117 Type A |
front 118 Surface antigen B and anti-A antibodies | back 118 Type B |
front 119 Surface antigens A and B, no antibodies | back 119 Type AB |
front 120 No surface antigens, anti-A and anti-B antibodies | back 120 Type O |
front 121 Rh surface antigen, no antibodies | back 121 Type Rh positive |
front 122 Attack objects coated with antibodies | back 122 Eosinophil |
front 123 Large phagocytic cells (macrophage precursors) | back 123 Monocyte |
front 124 When stimulated, release histamine and heparin | back 124 Basophil |
front 125 Attack and digest bacteria marked with complement | back 125 Neutrophil |
front 126 Responsible for cell-mediated or humoral immunity | back 126 Lymphocyte |
front 127 True/False. Carbon dioxide binds to the heme group of hemoglobin. | back 127 False. Carbon dioxide binds to the alpha and beta chains of hemoglobin. |
front 128 True/False. Ferritin is responsible for transporting iron around the body. | back 128 False. Ferritin is a storage form for iron, not a transport form. |
front 129 True/False. To prevent excessive platelet plug formation, prostacyclins are released during the platelet phase. | back 129 True |
front 130 True/False. Rh incompatibility exists when the mother is Rh+ and the fetus is Rh%ndash;. | back 130 False. Rh incompatibility exists only when the mother is Rh– and the fetus is Rh+. |
front 131 True/False. Platelets are derived from the breakdown of a large cell called a reticulocyte. | back 131 False. Platelets are derived from a large cell called a megakaryocyte. |
front 132 Biliverdin is formed when ____is broken down. | back 132 heme |
front 133 When an antibody meets its specific antigen, a cross-reaction occurs and the red blood cells clump together, a process known as _____. | back 133 agglutination |
front 134 If Amy is on vacation in a country with poor health standards and she contracts a parasitic roundworm, which type of white blood cells would you expect to see elevated in her blood? ______ | back 134 Eosinophils |
front 135 Almost every aspect of the clotting process is affected by _____ ions and vitamin K. | back 135 calcium |
front 136 Which enzyme digests fibrin strands in a blood clot after healing at the injury site has occurred? _____ | back 136 Plasmin |