Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 22- Lymphatic System & Immunity
front 1 Viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites that are capable of living inside the body and causing harm are called __________.
| back 1 pathogens |
front 2 Which lymphatic vessel collects lymph from the lower half of the body and the left upper half of the body and returns it to venous circulation?
| back 2 The thoracic duct collects lymph from the lower half of the body and the left upper half of the body and returns it to venous circulation. |
front 3 Which type of lymphocyte produces antibodies?
| back 3 B cell |
front 4 Large lymphoid nodules found on the walls of the pharynx are the __________.
| back 4 tonsils |
front 5 The largest collection of lymphoid tissue in the body, which consists of red and white pulp and is found attached to the lateral border of the stomach, is the __________.
| back 5 Correct Answer:
|
front 6 Which innate defense involves cells that engulf pathogens and cell debris?
| back 6 phagocytes |
front 7 Which cells are involved in immunological surveillance?
| back 7 Correct Answer:
|
front 8 Which of the following is a localized tissue response to injury characterized by redness, heat, swelling, and pain?
| back 8 inflammation |
front 9 Which of the following is NOT an effect of complement activation?
| back 9 Correct Answer:
|
front 10 A child is given a vaccine to polio. What form of immunity does this represent?
| back 10 Correct Answer:
|
front 11 What property of adaptive immunity allows a person to have the chickenpox when he is six years old and still be immune to chickenpox at age 45?
| back 11 Correct Answer:
|
front 12 What type of cell surface protein is found only on antigen-presenting cells and lymphocytes and allows them to communicate with each other?
| back 12 Correct Answer:
|
front 13 What type of T cell is responsible for seeking out and destroying abnormal or infected cells?
| back 13 Correct Answer:
|
front 14 What is the name for the type of B cell that synthesizes and secretes large quantities of antibodies?
| back 14 plasma cell |
front 15 Which antibody is the first class of antibody to be secreted in response to an antigen and is a pentamer (made of five antibody molecules)?
| back 15 Correct Answer:
|
front 16 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the secondary response to antigen exposure?
| back 16 Correct Answer:
|
front 17 What type of immune disorder is characterized by autoantibodies that attack body cells and tissues?
| back 17 Correct Answer:
|
front 18 AIDS is an example of __________.
| back 18 an immunodeficiency |
front 19 Which of the following is NOT an effect of advancing age on the immune system?
| back 19 Correct Answer:
|
front 20 The CNS can affect the lymphatic system by __________.
| back 20 Correct Answer:
|
front 21 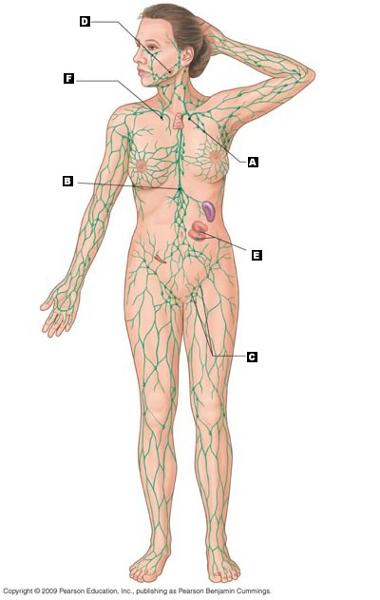 Label the following components in the diagram of the lymphatic system. | back 21 A. thoracic (left lymphatic) duct
|
front 22 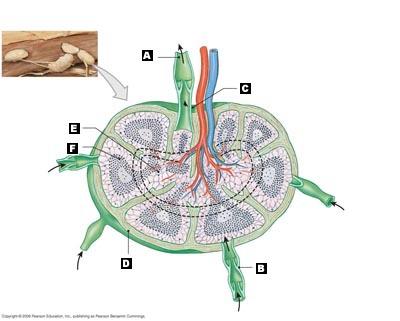 Correctly match the terms with the appropriate structures of the lymph node. | back 22 A. Efferent Vessel
|
front 23 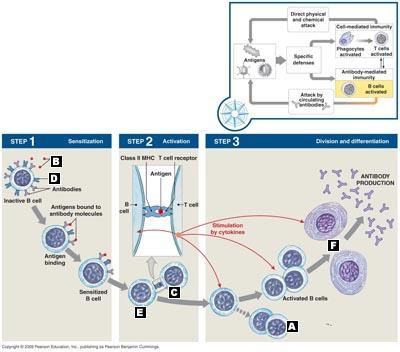 Correctly identify the cells and structures involved in antibody-mediated immunity. | back 23 A. Memory B cells
|
front 24 Place the following stages of a bacterial infection in the proper order from (1) through (6):
| back 24 1. Neutrophils and NK cells migrate into the infected area.
|
front 25 Prevent the approach of and deny access to pathogens | back 25 Physical Barriers |
front 26 Remove debris and pathogens | back 26 Phagocytes |
front 27 Destroys abnormal cells | back 27 Immunological surveillance |
front 28 Increases resistance of cells to viral infection | back 28 Interferon |
front 29 Attacks and breaks down target cell membranes, promoting phagocytosis | back 29 Complement System |
front 30 Mobilizes defenses and accelerates repairs | back 30 Fever |
front 31 Genetically determined, no prior exposure or antibody production involved | back 31 Innate immunity |
front 32 Produced by transfer of antibodies from another person | back 32 Artificially acquired passive immunity |
front 33 Develops after administration of antigen to prevent disease | back 33 Artificially induced active immunity |
front 34 Conferred by transfer of maternal antibodies across placenta or in breast milk | back 34 Naturally acquired passive immunity |
front 35 Develops after exposure to antigens in environment | back 35 Naturally induced active immunity |
front 36 Produced by exposure to an antigen, not present at birth | back 36 Adaptive immunity |
front 37 These originate as blind pockets, may contain lymphocytes and do contain walls with cells not tightly bound together. | back 37 Lymphatic capillaries |
front 38 Located in the mediastinum, this organ is largest in children but diminishes with age, and it is the site of T cell maturation. | back 38 Thymus |
front 39 Containing both red and white pulp, this is a site for the removal of abnormal blood cells and is used to initiate responses by B and T cells. | back 39 Spleen |
front 40 The smallest of organs, these may have a diameter of up to 1 inch and contain afferent and efferent lymphatics. | back 40 Lymph Nodes |
front 41 Most people have five of these structures, which are located in the oral, nasal, and pharyngeal areas. | back 41 Tonsils |
front 42 The ability of the immune system to ignore normal, self antigens while responding to foreign, nonself antigens. | back 42 Tolerance |
front 43 The ability of the immune system to respond to tens of thousands of antigens by producing an enormous number of lymphocyte populations, each with sensitivity to a unique set of antigens. | back 43 Versatility |
front 44 The ability of the immune system to produce a response to a particular antigen and no other. This is a result of the ability to activate specific lymphocytes. | back 44 Specificity |
front 45 The ability of the immune system to "remember" specific antigens through the production of memory cells, which are produced after an initial exposure and are saved in case of a second exposure to an antigen. | back 45 Memory |
front 46 Which of the following are functions of the lymphatic system?
| back 46 defense of the body against pathogens and defense of the body against cancer |
front 47 Adaptive responses __________.
| back 47 target a specific antigen each time it is activated |
front 48 The majority of lymph fluid in the body returns to the venous circulation via the __________.
| back 48 thoracic duct |
front 49 B lymphocytes are responsible for __________.
| back 49 humoral immunity |
front 50 T cells originate and complete their development in the __________.
| back 50 thymus |
front 51 Lymphoid tissues __________.
| back 51 are dominated by lymphocytes and lack a distinct boundary |
front 52 Lymphoid organs include which of the following?
| back 52 spleen and tonsils |
front 53 Lymph nodes function as __________.
| back 53 filters and an early warning system |
front 54 The spleen __________.
| back 54 removes abnormal red blood cells from circulation and initiates the immune responses by B cells and T cells in response to circulating antigens |
front 55 The smallest lymphatic vessels are called __________.
| back 55 lymph capillaries |
front 56 Which of the following is NOT a class of lymphocyte?
| back 56 neutrophils |
front 57 Which of the following statements about B cells is INCORRECT?
| back 57 B cells attack and kill cells infected with viruses. |
front 58 Which of the following statements concerning the thymus is INCORRECT?
| back 58 The thymus reaches its greatest size after 25 years. |
front 59 Which of the following terms describes the degeneration of tissue cells that have been damaged or destroyed by injury?
| back 59 necrosis |
front 60 Which of the following are characteristics of free macrophages and microphages?
| back 60 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 61 Natural killer cells destroy other cells by secreting __________.
| back 61 perforins |
front 62 Interferons __________.
| back 62 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 63 Opsonization __________.
| back 63 facilitates phagocytosis |
front 64 Innate defenses include __________.
| back 64 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 65 Which of the following is NOT an effect of phagocytic activity?
| back 65 elevating body temperature to increase body metabolism and potentially limit bacteria and viruses |
front 66 Which of the following statements concerning inflammation and response to injury is INCORRECT?
| back 66 Released histamine decreases capillary permeability and decreases blood flow through the area. |
front 67 T cells are responsible for __________.
| back 67 both cell-mediated immunity and cellular immunity |
front 68 Which of the following is an example of naturally acquired active immunity?
| back 68 An adult contracts a streptococcus infection and recovers in a couple of weeks. |
front 69 Cells of the immune system usually ignore antigens found in the body. This is called __________.
| back 69 tolerance |
front 70 Many American children of the 1950s suffered terribly from the polio virus until the Salk and Sabin vaccines were developed. These vaccines introduced inactivated viruses into the bodies of the vaccine recipients. The type of immunity conferred through this method is called __________.
| back 70 artificially induced active immunity |
front 71 CD4 and CD8 markers __________.
| back 71 are used in the process of costimulation, a necessary activity for the activation of T cells |
front 72 Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I proteins are __________.
| back 72 found in every nucleated cell in the body |
front 73 MHC class II proteins are found __________.
| back 73 only in lymphocytes and phagocytic cells |
front 74 Cytotoxic (killer) T cells can destroy a target cell by each of the following processes EXCEPT __________.
| back 74 secreting antibodies that destroy cell membranes |
front 75 The second response to a single antigen __________ the first response.
| back 75 is stronger and longer-lasting than |
front 76 Which cell is needed to activate B cells?
| back 76 helper T cells |
front 77 The antigen-binding sites are found in the __________.
| back 77 variable segments |
front 78 The antigen–antibody complex may result in __________.
| back 78 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 79 Which type of antibody is secreted first after the arrival of an antigen?
| back 79 IgM |
front 80 A fetus gains most of its immunity from __________.
| back 80 IgG antibodies that cross the placenta from its mother |
front 81 Which of the following diseases is caused by a retrovirus that targets helper T cells and is contracted by intimate contact with the body fluids of infected individuals?
| back 81 AIDS |
front 82 What are colony-stimulating factors?
| back 82 cytokines that stimulate the production of blood cells in bone marrow and lymphocytes in lymph organs and tissues |
front 83 Which of the following is NOT a function of interleukin?
| back 83 decreasing T cell sensitivity to antigens exposed on macrophage membranes |
front 84 A disorder in which the immune response mistakenly targets normal body cells and tissues is known as an __________.
| back 84 autoimmune disease |
front 85 True/False. T cells produce antibodies, thus giving antibody-mediated immunity. | back 85 False
|
front 86 True/False. Immunosurveillance is an innate defense characterized by NK cells destroying cancer cells or cells infected with a virus. | back 86 True |
front 87 True/False. Interferons are important in the resistance of tissues to viral infection. | back 87 True |
front 88 True/False. Lymph is similar to plasma, except lymph contains more proteins. | back 88 False
|
front 89 True/False. The most abundant and diverse class of antibodies is the IgM class. | back 89 False
|
front 90 NK cells destroy other cells by releasing ___ from secretory vesicles. | back 90 perforin |
front 91 The continued secretion of ___ during stress can inhibit the immune response and lower resistance to disease. | back 91 glucocorticoids |
front 92 This saclike chamber collects lymph from the lower abdomen, pelvis and lower limbs. ___ ___ (Use two words.) | back 92 cisterna chyli |
front 93 The cell that is not a specific immunity cell but a type of lymphocyte that provides immunosurveillance is called a(n) ___ cell. | back 93 natural killer
|
front 94 The enhancement of phagocytosis caused by the coating of a pathogen with antibodies is called ____ . | back 94 opsonization |
front 95 To which of the following would the immune system NOT respond?
| back 95 decreased levels of blood flow at the kidney |
front 96 The anatomical barriers and defense mechanisms that CANNOT distinguish one potential threat from another are called __________.
| back 96 innate defenses |
front 97 The MAJOR components of the lymphatic system include the __________.
| back 97 lymphatic vessels, lymph, and lymphatic organs |
front 98 Which of the following is an example of a free macrophage?
| back 98 alveolar macrophage |
front 99 Lymphocytes that assist in the regulation and coordination of the immune response are __________.
| back 99 helper T and suppressor T cells |
front 100 Normal lymphocyte populations are maintained through lymphopoiesis in the __________.
| back 100 bone marrow and lymphatic tissues |
front 101 The largest collection of lymphoid tissue in the body is contained within the __________.
| back 101 adult spleen |
front 102 Mucous, sweat gland secretions, hairs, and sebaceous secretions all contribute to the effectiveness of which type of innate defense?
| back 102 physical barriers |
front 103 The "first line" of cellular defense against pathogenic invasion is __________.
| back 103 phagocytes |
front 104 NK cells contain the proteins perforin and protectin that provide a type of immunity called __________.
| back 104 immunological surveillance |
front 105 What are the two major ways that the body "carries out" the immune response to a specific antigen?
| back 105 direct attack by T cells and attack by circulating antibodies |
front 106 An adaptive defense mechanism is always activated by __________.
| back 106 an antigen |
front 107 Which type of immunity develops as a result of natural exposure to an antigen in the environment?
| back 107 naturally acquired active immunity |
front 108 The fact that people are NOT subject to the same diseases as goldfish describes the presence of __________.
| back 108 innate immunity |
front 109 A cross-reaction following transfusion with an incompatible blood type is an example of which of the following?
| back 109 a cytotoxic reaction |
front 110 Before an antigen can stimulate a lymphocyte, it must first be processed by __________.
| back 110 a macrophage |
front 111 The T cells that limit the degree of immune system activation from a single stimulus are __________.
| back 111 suppressor T cells |
front 112 Which of the following lymphatic structures do(es) NOT display the outer cortex/inner medulla pattern?
| back 112 tonsils and spleen |
front 113 Activated B cells produce plasma cells that are specialized to __________.
| back 113 synthesize and secrete antibodies |
front 114 An antibody exhibits a high degree of flexibility as a result of the interchangeability of the __________.
| back 114 variable segment |
front 115 Antibodies may promote inflammation through the stimulation of __________.
| back 115 basophils and mast cells |
front 116 The epitope site is the certain portion of the antigen's exposed surface where __________.
| back 116 the antibody attaches |
front 117 For a B cell to be activated, it must __________.
| back 117 be bound by a helper T cell at a class II MHC and bind an antigen to a surface antibody |
front 118 The effects of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in the body include which of the following?
| back 118 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 119 The ability to demonstrate an immune response after exposure to an antigen is called __________.
| back 119 immunological competence |
front 120 A baby developing in the womb has _____________________ immunity because it receives __________ antibodies from its mother.
| back 120 naturally acquired passive; IgG |
front 121 When an immune response mistakenly targets normal body cells and tissues, the result is __________.
| back 121 an autoimmune disorder |
front 122 Cells of the immune system influence CNS and endocrine activity by __________.
| back 122 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 123 Depression of the immune system due to chronic stress may cause __________.
| back 123 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 124 Which of the following is NOT an effect of aging on the immune system?
| back 124 increased production of pyrogens, leading to a higher general body temperature |
front 125 Which type of lymphocyte does NOT release perforins?
| back 125 both B cell and helper T cell |
front 126 The primary effects of complement activation include which of the following?
| back 126 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 127 Which of the following nonspecific responses is characterized by the use of C3, properdin, factor B, and factor D?
| back 127 complement, alternative pathway |
front 128 Tissue fluid enters the lymphatic system via the __________.
| back 128 lymph capillaries |
front 129 When an antigen appears, the adaptive immune system response begins with __________.
| back 129 the activation of specific T cells and B cells |
front 130 In what way do mast cells participate in tissue defense?
| back 130 stimulation and coordination of inflammation by release of histamine and heparin |
front 131 Chemical mediators of inflammation include which of the following?
| back 131 histamine, heparin, prostaglandins, and complement |
front 132 T cells that are activated by costimulation involving a class I MHC and CD8 markers are called __________.
| back 132 cytotoxic T cells |
front 133 B lymphocytes differentiate into __________.
| back 133 memory and plasma cells |
front 134 __________ cells may activate B cells, whereas _________ cells inhibit the activity of B cells.
| back 134 Helper T; suppressor T |
front 135 The primary response of CD8 T cell differentiation in cell-mediated immunity is the production of __________ cells.
| back 135 cytotoxic T |
front 136 The vaccination of antigenic materials into the body is called __________.
| back 136 artificially induced active immunity |
front 137 In passive immunity, __________ are introduced into the body by injection.
| back 137 antibodies |
front 138 What is the lymphatic function of the white pulp of the spleen?
| back 138 initiation of immune responses by B cells and T cells |
front 139 Which of the following is characteristic of the secondary response?
| back 139 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 140 The antibodies produced and secreted by B lymphocytes are soluble proteins called __________.
| back 140 immunoglobulins |
front 141 The genes found in a region called the major histocompatibility complex are also called __________.
| back 141 human leukocyte antigens (HLAs) |
front 142 Memory B cells do NOT differentiate into plasma cells UNLESS they __________.
| back 142 are exposed to the same antigen a second time |
front 143 The three-dimensional "fit" between the variable segments of the antibody molecule and the corresponding antigenic determinant site is referred to as the __________.
| back 143 antibody–antigen complex |
front 144 One of the primary nonspecific effects that glucocorticoids have on the immune response is __________.
| back 144 depression of the inflammatory response |