Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 20 The heart
front 1 Which network of blood vessels carries blood to and from the gas exchange surfaces in the lungs? | back 1 Pulmonary Circuit |
front 2 Which vessels have very thin walls and are often called exchange vessels because they allow for the exchange of nutrients, gases, and wastes with surrounding tissues? | back 2 Capillaries |
front 3 Which layer of the heart wall is the visceral pericardium? | back 3 Epicardium |
front 4 Which chamber of the heart receives blood from the superior and inferior venae cavae? | back 4 Right Atrium |
front 5 Which chamber contains trabeculae carneae? | back 5 Right and Left Ventricles |
front 6 The left ventricle pumps blood into the __________. | back 6 Ascending Aorta |
front 7 Which valve is found between the right atrium and the right ventricle? | back 7 Tricuspid Valve |
front 8 The right and left coronary arteries originate at the base of the __________. | back 8 Ascending Aorta |
front 9 A large vein that opens into the right atrium and brings in venous blood from the heart tissue is the __________. | back 9 Coronary Sinus |
front 10 Which of the following is called the cardiac pacemaker? | back 10 The sinoatrial node is called the cardiac pacemaker because it establishes heart rate. |
front 11 What structures in the conduction system conduct impulses very rapidly to the ventricular myocardium? | back 11 Purkinje Fibers |
front 12 The QRS complex on the ECG represents __________. | back 12 Ventricular Depolarization |
front 13 The plateau in the action potential is caused by the entry of ________ ions. | back 13 Calcium |
front 14 What is the term for contraction of a heart chamber? | back 14 Systole |
front 15 What occurs during the first phase of ventricular systole? | back 15 The AV valves close, and ventricular pressure rises. |
front 16 What produces the "lubb" of the first heart sound? | back 16 closing of the atrioventricular valves |
front 17 What is measured in milliliters per beat? | back 17 stroke volume |
front 18 What effect does epinephrine have on the SA node? | back 18 increases heart rate |
front 19 What could increase the strength of the contraction of a ventricle? | back 19 increased stretch on the ventricle |
front 20 Which of the following statements about autonomic tone is FALSE?
| back 20 Sympathetic effects dominate in a resting healthy adult. |
front 21 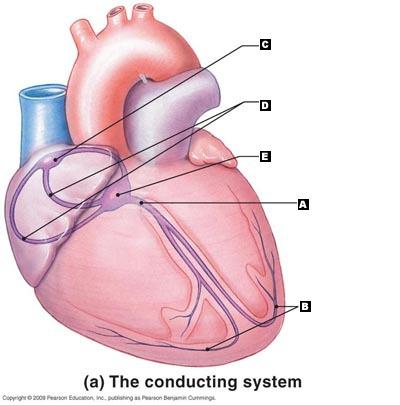 Label the following structures of the conducting system of the heart. | back 21 A. AV Bundle
|
front 22 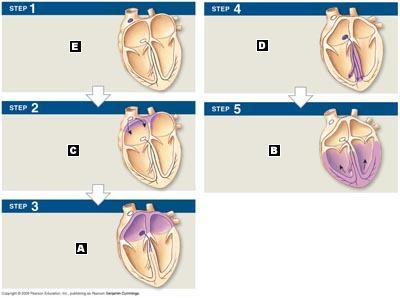 Label the following activities of the impulse conduction through the heart. | back 22 E. SA node activity and atrial activation begin.
|
front 23 Put the following steps to blood flow through the heart in the correct order:
| back 23 A. venae cavae
|
front 24 Beginning at the natural pacemaker region, arrange the components of the heart's conducting system in the order that an action potential would pass, by matching (1) through (6):
| back 24 E. SA node
|
front 25 Put the steps of the cardiac cycle in order, beginning with the resting period between heart beats.
| back 25 C. Atrial Systole
|
front 26 P wave | back 26 Depolarization of the atria |
front 27 P-R Interval | back 27 Transmission of the impulse to contract from the SA node to the AV node and through the ventricles |
front 28 QRS complex | back 28 Ventricular depolarization |
front 29 Q-T interval | back 29 Time required for the ventricles to undergo a single cycle of depolarization and repolarization |
front 30 T wave | back 30 Repolarization of ventricles |
front 31 Vessels that carry blood away from the heart are called __________. | back 31 Arteries |
front 32 When the heart beats, the __________ contract first. | back 32 atria |
front 33 The left atrium collects blood from the __________ and empties into the left ventricle. | back 33 pulmonary circuit |
front 34 When blood is ejected from the heart, it is pushed from the ____ to the _____.
| back 34 apex; base |
front 35 The heart has _____ chambers and ______ valves. | back 35 4;4 |
front 36 The epicardium of the heart is the same as the __________. | back 36 visceral pericardium |
front 37 On the outside of the heart, the boundaries between the right and left ventricles are marked by the __________. | back 37 anterior interventricular sulcus and the posterior interventricular sulcus |
front 38 The expandable outer portion of each atrium is called __________. | back 38 an auricle |
front 39 The right atrium receives blood from the __________.
| back 39 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 40 The AV valves prevent the backflow of blood into the _____, and the semilunar valves prevent backflow of blood into the _____. | back 40 atria; ventricles |
front 41 The right and left AV valves are also called the ______ and _______, respectively. | back 41 tricuspid; bicuspid |
front 42 The free edges of the AV valves are attached to fibers called __________. | back 42 chordae tendineae |
front 43 The left atrium receives blood from the __________. | back 43 pulmonary veins |
front 44 The innermost layer of the heart is called the __________. | back 44 endocardium |
front 45 Deoxygenated blood leaves the right ventricle through a semilunar valve and enters the __________. | back 45 pulmonary trunk |
front 46 Which of the following statements concerning the heart is FALSE?
| back 46 The heart is rotated toward the right. |
front 47 Compared to the right ventricle, the left ventricle __________.
| back 47 has a thicker wall |
front 48 The valve known as the mitral valve is located __________. | back 48 between the left atrium and left ventricle |
front 49 Marginal branches are extensions of the __________. | back 49 right coronary artery |
front 50 In contrast to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle cells have a _______ phase as part of their action potential. | back 50 Plateau |
front 51 The SA node acts as the pacemaker of the heart because these cells are __________. | back 51 the cells that depolarize and reach threshold first |
front 52 The refractory period of cardiac muscles is __________ than that of skeletal muscles. | back 52 longer |
front 53 If undisturbed, the cells of the AV node will depolarize about __________ times per second. | back 53 40–60 |
front 54 Without external interactions, the cells of the SA node depolarize __________ times per minute. | back 54 80-100 |
front 55 The Purkinje fibers __________.
| back 55 conduct impulses rapidly |
front 56 The bundle branches ___________.
| back 56 All of the listed responses are correct |
front 57 The QRS complex represents __________. | back 57 Ventricular Depolarization |
front 58 The P wave represents __________. | back 58 Atrial Depolarization |
front 59 The T wave represents _________. | back 59 Ventricular Repolarization |
front 60 Which of the following correctly describes conducting cells of the SA node?
| back 60 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 61 The contractile cells of the myocardium reach threshold because of an influx of ____. | back 61 cations |
front 62 Which of the following statements concerning contractile cells and the heartbeat is INCORRECT?
| back 62 The plateau phase of the contractile cell's action potential is the result of calcium ions moving out of the cell.
|
front 63 The conduction delay that occurs at the AV node allows __________. | back 63 the atria to contract before the ventricles begin to contract |
front 64 An elderly man is brought into the hospital on a hot, sunny day complaining of light-headedness. You administer an ECG and notice that the P–R interval is 350 msec. His heart sounds are normal. His blood tests indicate that the LDH, SGOT, CK, and CK-MB levels are all normal. What is wrong with this patient? | back 64 The man has a problem with the conduction system of the atria or possibly with the AV node. |
front 65 During ventricular filling, the AV valves are ____, and the semilunar valves are _______. | back 65 open;closed |
front 66 Contraction of the chambers of the heart is called _____, and relaxation of the chambers of the heart is called _____. | back 66 systole;diastole |
front 67 When atrial contraction begins, the ventricles are __________. | back 67 relaxed and filling |
front 68 The dicrotic notch marks the point when the __________. | back 68 aortic valve closes |
front 69 The first heart sound, "lubb," marks the point when __________. | back 69 the atrioventricular valves close |
front 70 There is (are) __________ heart sound(s). | back 70 4 |
front 71 Which of the following statements concerning atrial systole is FALSE?
| back 71 At the start of atrial systole, there is very little blood in the ventricles. |
front 72 Which of the following statements concerning ventricular diastole is FALSE?
| back 72 As the ventricles begin to fill with blood, the pressure in the chamber rises. |
front 73 The stroke volume of the heart is approximately __________. | back 73 80mL |
front 74 Stroke volume is defined as __________. | back 74 the amount of blood ejected from each ventricle during ventricular systole |
front 75 Cardiac output is defined as __________.
| back 75 both HR × SV and HR × (EDV − ESV) |
front 76 Which statement(s) is (are) true with regard to preload?
| back 76 If EDV is greater and ESV is lower, then the stroke volume increases; AND during exercise, increased venous return increases EDV. |
front 77 Starling's law of the heart refers to the relationship between __________. | back 77 EDV and SV |
front 78 Which of the following would be considered a positive inotropic agent?
| back 78 digitalis |
front 79 In a normal resting adult, the effects of the __________ division of the autonomic nervous system dominate. | back 79 parasympathetic |
front 80 The cardiac output (CO) is equal to __________. | back 80 SV x HR |
front 81 Which of the following is NOT a factor that controls stroke volume?
| back 81 cardiac output |
front 82 What is the term for an abnormally slow heart rate? | back 82 bradycardia |
front 83 What does the Frank–Starling principle state? | back 83 There is a direct relationship between the EDV and the SV. |
front 84 True/False. Bradycardia is the term used to describe a faster than normal heart beat. | back 84 False. Tachycardia is the term used to describe a faster than normal heart rate. |
front 85 True/False. Starling’s law of the heart states that increasing the EDV leads to an increase in the stroke volume. | back 85 True |
front 86 True/False. The AV valves are part of the heart’s fibrous skeleton. | back 86 True |
front 87 True/False. The coronary arteries are branches of the superior vena cava. | back 87 False. The coronary arteries are the first branches of the aorta. |
front 88 True/False. The pericardial sac is lined by the visceral pericardium. | back 88 False. The visceral pericardium covers or is attached directly to the heart. |
front 89 Since the absolute refractory period in cardiac muscle is nearly as long as the contraction phase, _____ contractions cannot occur in normal cardiac muscle cells. | back 89 tetanic |
front 90 The end-diastolic volume (EDV) is affected by the filling time and the _____. (use two words) | back 90 Venous return |
front 91 Calcium entry into the cardiac muscle cell creates a _____ in the action potential that lasts about 175 msec. | back 91 Plateau |
front 92 When _____ is released from autonomic neurons at the heart, the repolarization period is shortened and nodal cells reach threshold more quickly. | back 92 norepinephrine; NE |
front 93 The blood vessels in the cardiovascular system are subdivided into three circuits known as the __________. | back 93 coronary, pulmonary, and systemic circuits |
front 94 Which statement is true?
| back 94 If the pacemaker of the heart stops, the AV node will take over. |
front 95 The left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circuit and empties it into the __________.
| back 95 left ventricle |
front 96 The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the __________ circuit pump, while the left side serves as the __________ pump.
| back 96 pulmonary; systemic |
front 97 The coronary arteries emerge at the base of the __________.
| back 97 aorta |
front 98 Which blood vessels are known as exchange vessels?
| back 98 capillaries |
front 99 Blood from the coronary circuit is collected on the posterior aspect of the heart in a blood vessel known as the __________.
| back 99 coronary sinus |
front 100 During the action potential in a contractile cardiac muscle cell, the opening of slow calcium channels results in the______ phase.
| back 100 plateau |
front 101 When deoxygenated blood leaves the right ventricle through a semilunar valve, it is forced into the __________.
| back 101 pulmonary arteries |
front 102 The passageways between cardiac muscle cells that allow ions to pass freely are called __________.
| back 102 gap junctions |
front 103 Which of the following are characteristics of cardiac muscle cells?
| back 103 striated, single central nucleus, and involuntary |
front 104 Cardiac muscle tissue __________.
| back 104 has its own intrinsic conduction system that can set the pace of the beating heart |
front 105 The right coronary artery generally gives rise to __________.
| back 105 the marginal branches and the posterior interventricular artery |
front 106 The left coronary artery supplies blood to __________.
| back 106 the anterior interventricular artery and the circumflex branch |
front 107 What is the correct sequential path of a normal action potential in the heart?
| back 107 SA node, AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches, Purkinje fibers |
front 108 Blood flows from the left atrium through the _______ to the left ventricle.
| back 108 mitral valve |
front 109 The P wave on the ECG indicates __________.
| back 109 the electrical events spreading out over both atria |
front 110 After the AV node is depolarized and the impulse spreads through the atria, there is a slight delay before the impulse spreads to the ventricles. The reason for this delay is to allow __________.
| back 110 the atria to contract |
front 111 Valvular heart disease can be a result of __________.
| back 111 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 112 The QRS complex of the ECG appears as the __________.
| back 112 ventricles depolarize |
front 113 When a chamber of the heart fills with blood and prepares for the start of the next cardiac cycle, the chamber is in __________.
| back 113 diastole |
front 114 During the isovolumetric contraction phase, the pressure in the _____ has to rise above aortic pressure for ventricular ejection to occur.
| back 114 left ventricle |
front 115 How would you define cardiac output?
| back 115 the amount of blood pumped out of the left ventricle in one minute |
front 116 The amount of blood pumped out of each ventricle during a single beat is the __________.
| back 116 stroke volume |
front 117 Under normal circumstances, the factors responsible for making delicate adjustments to the heart rate as circulatory demands change are __________.
| back 117 autonomic activity and circulatory hormones |
front 118 The cardiac centers in the medulla oblongata monitor baroreceptors and chemoreceptors innervated by the __________.
| back 118 glossopharyngeal N IX and vagus N X |
front 119 The difference between the end-diastolic volume (EDV) and the end-systolic volume (ESV) is the __________.
| back 119 stroke volume |
front 120 Parasympathetic stimulation from the vagus nerve results in __________.
| back 120 a decrease in heart rate |
front 121 Which of the following statements is part of Starling's law of the heart?
| back 121 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 122 Physicians are interested in cardiac output because it provides a useful indication of __________.
| back 122 ventricular efficiency over time |
front 123 Which heart chamber has the thickest muscular walls?
| back 123 left ventricle |
front 124 Which of the following medications serves as a positive treatment by interfering with the removal of calcium ions from the sarcoplasm of cardiac muscle cells?
| back 124 digitalis |
front 125 What is the function of the chordae tendineae?
| back 125 to anchor the AV valve flaps and prevent backflow of blood into the atria |
front 126 Which of the following would NOT show up on an electrocardiogram?
| back 126 murmurs |
front 127 During ventricular systole , what occurs when the pressure in the left ventricle rises above that in the left atrium?
| back 127 The left AV valve closes. |
front 128 During ventricular systole, the blood volume in the atria is __________, and the volume in the ventricle is __________.
| back 128 increasing; decreasing |
front 129 Cardiac muscle cells are nourished via blood supply provided from the __________.
| back 129 coronary circuit |
front 130 Pulmonary arteries carry blood to the __________.
| back 130 lungs |
front 131 Which of the following statements is (are) true?
| back 131 During ventricular systole, the papillary muscles contract to keep the AV valves shut and prevents them from swinging up into the atria. |
front 132 The heart sound associated with S2 occurs as the ventricles ____ and the semilunar valves ______.
| back 132 relax; close |
front 133 During isovolumetric systole, pressure is highest in the __________.
| back 133 left ventricle |
front 134 Blood pressure in the large systemic arteries is greatest during __________.
| back 134 ventricular ejection |
front 135 Decreased parasympathetic (vagus) stimulation to the heart results in a situation known as __________.
| back 135 tachycardia |
front 136 Serious arrhythmias that reduce the pumping efficiency of the heart may indicate __________.
| back 136 All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 137 During exercise, the most important control mechanism to increase cardiac output is __________.
| back 137 increased sympathetic activity to the ventricles |
front 138 In the diastole phase of the ventricles, __________.
| back 138 the ventricles are "resting" |
front 139 Which of the following does NOT control the movement of blood through the heart?
| back 139 size of the atria and ventricles |
front 140 Valvular malfunction in the heart __________.
| back 140 interferes with movement of blood through the heart |
front 141 If the bicuspid valve is defective and valvular regurgitation occurs, the end result is __________.
| back 141 an insufficient amount of blood available to be moved into the aorta and systemic circulation |
front 142 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of cardiac muscle cells?
| back 142 multiple nuclei |