Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Cambell Biology in Focus Chapter 37 practice test 1
front 1 1) An organism that lacks integration centers
| back 1 will not be able to interpret stimuli. |
front 2 2) What do muscles, nerves, and glands have in common?
| back 2 A, B, and C |
front 3 3) Integration of simple responses to certain stimuli, such as the patellar reflex, is accomplished by which of the following?
| back 3 spinal cord |
front 4 4) The general functions of the nervous system include which of the following?
| back 4 I, II, and III |
front 5 5) A ganglion is a group of nerve cell bodies
| back 5 in the peripheral nervous system. |
front 6 6) The blood-brain barrier
| back 6 is formed by tight junctions. |
front 7 7) A squirrel chewing the insulation off an electrical wire is analogous to
| back 7 demyelination of the nervous system. |
front 8 8) Which of the following statements is false?
| back 8 The outside of a cell is negative with respect to the inside of a cell. |
front 9 9) If the concentration of potassium in the cytoplasm of a nerve cell with a resting membrane potential of
| back 9 be -69 mV or higher. |
front 10 10) Neurons at rest are not at the equilibrium potential for K+ because the cell membrane is
| back 10 slightly permeable to Na+. |
front 11 11) If an otherwise normal nerve cell were made permeable to large negative ions, what would happen?
| back 11 The membrane potential would not form. |
front 12 12) The sodium-potassium pump of neurons pumps
| back 12 Na+ out of the cell and K+ into the cell. |
front 13 The next questions refer to the following information:
| back 13 no data |
front 14 13) Which of the following is true about the establishment of the resting membrane potential in this cell?
| back 14 A positive resting potential is directly produced by the diffusion of X- out of the cell. |
front 15 14) When neurotransmitter Z is released into the extracellular fluid in contact with a portion of the cell membrane, channels open that allow both X- and Y- through the membrane. Which of the following is incorrect?
| back 15 The magnitude of the potential will immediately increase. |
front 16 15) The threshold potential of a membrane
| back 16 is the depolarization that is needed to generate an action potential. |
front 17 16) Which of the following is a correct statement about a resting neuron?
| back 17 The membrane potential is more negative than the threshold potential. |
front 18 17) A toxin that binds specifically to the voltage-gated sodium channels of axons would
| back 18 prevent the axon from reaching the threshold potential |
front 19 18) After an action potential, how is the resting potential restored?
| back 19 by the opening of voltage-sensitive potassium channels and the closing of sodium activation gates |
front 20 19) Repolarization of the membrane of a neuron after an action potential is a consequence of which of the following?
| back 20 II and III only |
front 21 20) In the sequence of permeability changes that depolarizes and then repolarizes the membrane of a neuron during an action potential, which of the following changes occurs first?
| back 21 Sodium gates open. |
front 22 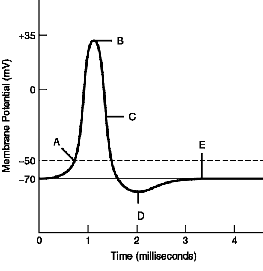 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
| back 22 no data |
front 23 21) The membrane is unable to respond to any further stimulation, regardless of intensity. | back 23 D |
front 24 22) The sodium gates open. | back 24 A |
front 25 23) The threshold potential is reached. | back 25 A |
front 26 24) Repolarization occurs, sodium gates close, and potassium gates reopen. | back 26 C |
front 27 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
| back 27 Two action potentials will be initiated, one going toward the axon terminal and one going back toward the hillock. |
front 28 26) All of the following statements about transmission along neurons are correct except:
| back 28 The intensity of a stimulus is related to the frequency of the action potential. |
front 29 27) Saltatory conduction is a term applied to conduction of impulses
| back 29 along myelinated nerve fibers. |
front 30 28) Which animal movement could be used to represent impulse conductance along a myelinated axon?
| back 30 a frog leaping between lily pads |
front 31 29) Synaptic vesicles discharge their contents by exocytosis at the
| back 31 presynaptic membrane. |
front 32 30) Neurotransmitters are released from presynaptic axon terminals into the synaptic cleft by which of the following mechanisms?
| back 32 exocytosis |
front 33 31) Which of the following offers the best description of neural transmission across a mammalian synaptic gap?
| back 33 Neural impulses cause the release of chemicals that diffuse across the gap. |
front 34 32) Given the steps shown below, which of the following is the correct sequence for transmission at a chemical synapse?
| back 34 3, 2, 5, 1, 4 |
front 35 33) A drug might act as a stimulant of the somatic nervous system if it
| back 35 increases the sensitivity of the postsynaptic membrane to acetylcholine. |
front 36 34) One disadvantage to a nerve net is that it can conduct impulses in two directions from the point of the stimulus. The vertebrate system conducts in only one direction. This one-way conductance occurs
| back 36 because only the postsynaptic membranes can bind neurotransmitters. |
front 37 35) An EPSP facilitates depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane by
| back 37 increasing the permeability of the membrane to Na+. |
front 38 36) The postsynaptic membrane of a nerve may be stimulated by certain neurotransmitters to permit the influx of negative chloride ions into the cell. This process will result in
| back 38 the production of an IPSP. |
front 39 37) During an IPSP, the postsynaptic membrane becomes more permeable to
| back 39 K+. |
front 40 38) Neurotransmitters categorized as inhibitory would not be expected to
| back 40 open Na+ channels. |
front 41 39) A neurotransmitter can trigger different responses in postsynaptic cells due to the
| back 41 Both B and D are correct responses. |
front 42 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
| back 42 40) E
|
front 43 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
| back 43 Several action potentials arrive in fast succession without allowing the postsynaptic cell to return to its resting potential. |
front 44 43) A single inhibitory postsynaptic potential has a magnitude of 0.5 mV at the axon hillock and a single excitatory postsynaptic potential has a magnitude of 0.5 mV. What will be the membrane potential at the hillock after the spatial summation of 6 IPSPs and 2 EPSPs, if the initial membrane potential is -70 mV?
| back 44 -72 mV |
front 45 44) Which statement could be applied to both the nervous system and the endocrine system?
| back 45 A, B, and C are true. |
front 46 45) The major inhibitory neurotransmitter of the brain is
| back 46 GABA. |
front 47 46) Neurotransmitters affect postsynaptic cells by
| back 47 all of the above. |
front 48 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
| back 48 47) C
|
front 49 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
| back 49 radiating from a central nerve ring. |
front 50 50) Centralization of the nervous system seems to be associated with the evolution of
| back 50 bilateral symmetry. |
front 51 51) Which of the following statements is true?
| back 51 Learning does not appear to require a specific number of neurons. |
front 52 52) Cerebrospinal fluid can be described as all of the following except
| back 52 formed from layers of connective tissue. |
front 53 53) The motor division of the PNS can be divided into
| back 53 the somatic and autonomic systems. |
front 54 54) What is the main neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic system?
| back 54 acetylcholine |
front 55 55) Which part of the vertebrate nervous system is most involved in preparation for the "fight-or-flight" response?
| back 55 sympathetic |
front 56 56) Which of the following activities would be associated with the parasympathetic division of the nervous system?
| back 56 resting and digesting |
front 57 57) Which of the following is correct about the telencephalon region of the brain?
| back 57 It gives rise to the cerebrum. |
front 58 58) What controls the heart rate?
| back 58 medulla |
front 59 59) Which area of the brain is most intimately associated with the unconscious control of respiration and circulation?
| back 59 medulla |
front 60 60) Which selection is incorrectly paired?
| back 60 midbrain¹cerebellum |
front 61 61) As you read and answer the questions on this exam
| back 61 your beta brain waves increase. |
front 62 62) If an accident causes trauma to the hypothalamus
| back 62 regulation of body temperature might be affected. |
front 63 63) Circadian rhythms in animals may regulate such processes as
| back 63 all of the above. |
front 64 64) What would you predict would happen if an individual were forced to remain in a cave in isolation for at least two months?
| back 64 It is likely that the person would think that it is night when it is actually day outside. |
front 65 65) The motor cortex is part of which part of the nervous system?
| back 65 cerebrum |
front 66 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
| back 66 66) D
|
front 67 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
| back 67 sophistication of behaviors possible. |
front 68 72) What do Wernicke's and Broca's regions of the brain affect?
| back 68 speech |
front 69 73) If you were writing an essay, which part of the brain would be most active?
| back 69 temporal and frontal lobes |
front 70 74) All of the following statements about the nervous system are correct except:
| back 70 The three evolutionary changes in the vertebrate brain include increases in relative size, increases in compartmentalization of function, and decreases in cephalization. |
front 71 75) The establishment and expression of emotions involves the
| back 71 frontal lobes and limbic system. |
front 72 76) If the membrane potential of a neuron decreases, the membrane potential:
| back 72 a. Becomes more positive |
front 73 77)Identify each statement as TRUE or FALSE.
| back 73 a) true
|
front 74 78) How can instructors address and correct the misconceptions that students have about neurons, synapses, and signaling? | back 74 Students may think of the membrane potential as an absolute value, rather than recognizing that it is a difference in the electrical potential (voltage) across the neuron’s plasma membrane. The negative membrane potential indicates that the inside of the cell is negative relative to the outside. To test for this misunderstanding, ask students whether the membrane potential of a neuron becomes more positive or more negative when the membrane potential decreases. Students who think of membrane potential as an absolute number will answer that the potential becomes more negative. |