Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Ch.20 Cambell bio
front 1 1) Assume that you are trying to insert a gene into a plasmid. Someone gives you a preparation of genomic DNA that has been cut with restriction enzyme X. The gene you wish to insert has sites on both ends for cutting by restriction enzyme Y. You have a plasmid with a single site for Y, but not for X. Your strategy should be to
| back 1 Answer: C |
front 2 2) How does a bacterial cell protect its own DNA from restriction enzymes?
| back 2 Answer: A |
front 3 3) What is the most logical sequence of steps for splicing foreign DNA into a plasmid and inserting the plasmid into a bacterium?
| back 3 Answer: C |
front 4 4) A principal problem with inserting an unmodified mammalian gene into a BAC, and then getting that gene expressed in bacteria, is that
| back 4 Answer: C |
front 5 5) A gene that contains introns can be made shorter (but remain functional) for genetic engineering purposes by using
| back 5 Answer: C |
front 6 6) Why are yeast cells frequently used as hosts for cloning?
| back 6 Answer: D |
front 7 7) The DNA fragments making up a genomic library are generally contained in
| back 7 Answer: A |
front 8 8) Yeast artificial chromosomes contain which of the following elements?
| back 8 Answer: E |
front 9 9) Which of the following best describes the complete sequence of steps occurring during every cycle of PCR?
| back 9 Answer: A |
front 10 10) A researcher needs to clone a sequence of part of a eukaryotic genome in order to express the sequence and to modify the polypeptide product. She would be able to satisfy these requirements by using which of the following vectors?
| back 10 Answer: E |
front 11 11) A student wishes to clone a sequence of DNA of ~200 kb. Which vector would be appropriate?
| back 11 Answer: C |
front 12 12) Sequencing an entire genome, such as that of C. elegans, a nematode, is most important because
| back 12 Answer: D |
front 13 13) To introduce a particular piece of DNA into an animal cell, such as that of a mouse, you would find more probable success with which of the following methods?
| back 13 Answer: B |
front 14 14) The major advantage of using artificial chromosomes such as YACs and BACs for cloning genes is that
| back 14 Answer: C |
front 15 15) Which of the following is used to make complementary DNA (cDNA) from RNA?
| back 15 Answer: E |
front 16 16) Why is it so important to be able to amplify DNA fragments when studying genes?
| back 16 Answer: B |
front 17 17) Pax-6 is a gene that is involved in eye formation in many invertebrates, such as Drosophila. Pax-6 is found as well in vertebrates. A Pax-6 gene from a mouse can be expressed in a fly and the protein (PAX-6) leads to a compound fly eye. This information suggests which of the following?
| back 17 Answer: C |
front 18 18) Why are BACs preferred today rather than bacteriophages for making genomic libraries?
| back 18 Answer: E |
front 19 19) The reason for using Taq polymerase for PCR is that
| back 19 Answer: A |
front 20 20) Why might a laboratory be using dideoxy nucleotides?
| back 20 Answer: D |
front 21 21) In order to identify a specific restriction fragment using a probe, what must be done?
| back 21 Answer: E |
front 22 22) Which of the following modifications is least likely to alter the rate at which a DNA fragment moves through a gel during electrophoresis?
| back 22 Answer: A |
front 23 23) DNA fragments from a gel are transferred to a nitrocellulose paper during the procedure called Southern blotting. What is the purpose of transferring the DNA from a gel to a nitrocellulose paper?
| back 23 Answer: A |
front 24 24) DNA microarrays have made a huge impact on genomic studies because they
| back 24 Answer: C |
front 25 25) Which of the following describes the transfer of polypeptide sequences to a membrane to analyze gene expression?
| back 25 Answer: C |
front 26 26) Which of the following uses reverse transcriptase to make cDNA followed by amplification?
| back 26 Answer: E |
front 27 27) RNAi methodology uses double-stranded pieces of RNA to trigger a breakdown or blocking of mRNA. For which of the following might it more possibly be useful?
| back 27 Answer: B |
front 28 28) A researcher has used in vitro mutagenesis to mutate a cloned gene and then has reinserted this into a cell. In order to have the mutated sequence disable the function of the gene, what must then occur?
| back 28 Answer: A |
front 29 29) Which of the following techniques used to analyze gene function depends on the specificity of DNA base complementarity?
| back 29 Answer: C |
front 30 30) Silencing of selected genes is often done using RNA interference (RNAi). Which of the following questions would not be answered with this process?
| back 30 Answer: C |
front 31 31) In large scale, genome-wide association studies in humans, correlation is sought between
| back 31 Answer: B |
front 32 32) For a particular microarray assay (DNA chip), cDNA has been made from the mRNAs of a dozen patients' breast tumor biopsies. The researchers will be looking for
| back 32 Answer: C |
front 33 33) Which of the following is most closely identical to the formation of twins?
| back 33 Answer: E |
front 34 34) In 1997, Dolly the sheep was cloned. Which of the following processes was used?
| back 34 Answer: D |
front 35 35) Which of the following problems with animal cloning might result in premature death of the clones?
| back 35 Answer: C |
front 36 36) Reproductive cloning of human embryos is generally considered unethical. However, on the subject of therapeutic cloning there is a wider divergence of opinion. Which of the following is a likely explanation?
| back 36 Answer: B |
front 37 37) Which of the following is true of embryonic stem cells but not of adult stem cells?
| back 37 Answer: B |
front 38 38) A researcher is using adult stem cells and comparing them to other adult cells from the same tissue. Which of the following is a likely finding?
| back 38 Answer: A |
front 39 39) In animals, what is the difference between reproductive cloning and therapeutic cloning?
| back 39 Answer: D |
front 40 40) As genetic technology makes testing for a wide variety of genotypes possible, which of the following is likely to be an increasingly troublesome issue?
| back 40 Answer: C |
front 41 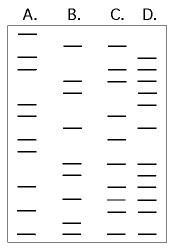 The DNA profiles that follow represent four different individuals.
| back 41 Answer: B |
front 42 42) Which of the following statements is most likely true?
| back 42 Answer: B |
front 43 43) Which of the following are probably siblings?
| back 43 Answer: D |
front 44 A eukaryotic gene has "sticky ends" produced by the restriction endonuclease EcoRI. The gene is added to a mixture containing EcoRI and a bacterial plasmid that carries two genes conferring resistance to ampicillin and tetracycline. The plasmid has one recognition site for EcoRI located in the tetracycline resistance gene. This mixture is incubated for several hours, exposed to DNA ligase, and then added to bacteria growing in nutrient broth. The bacteria are allowed to grow overnight and are streaked on a plate using a technique that produces isolated colonies that are clones of the original. Samples of these colonies are then grown in four different media: nutrient broth plus ampicillin, nutrient broth plus tetracycline, nutrient broth plus ampicillin and tetracycline, and nutrient broth without antibiotics.
| back 44 Answer: D |
front 45 45) Bacteria containing a plasmid into which the eukaryotic gene has integrated would grow in
| back 45 Answer: E |
front 46 46) Bacteria that do not take up any plasmids would grow on which media?
| back 46 Answer: A |
front 47 A group of six students has taken samples of their own cheek cells, purified the DNA, and used a restriction enzyme known to cut at zero, one, or two sites in a particular gene of interest.
| back 47 Answer: C |
front 48 48) Their next two steps, in order, should be
| back 48 Answer:C |
front 49 49) Analysis of the data obtained shows that two students each have two fragments, two students each have three fragments, and two students each have one only. What does this demonstrate?
| back 49 Answer: B |
front 50 50) Which of the following tools of recombinant DNA technology is incorrectly paired with its use?
| back 50 Answer:B |
front 51 51) Plants are more readily manipulated by genetic engineering than are animals because
| back 51 Answer: C |
front 52 52) A paleontologist has recovered a bit of tissue from the 400-year-old preserved skin of an extinct dodo (a bird). To compare a specific region of the DNA from the sample with DNA from living birds, which of the following would be most useful for increasing the amount of dodo DNA available for testing?
| back 52 Answer:B |
front 53 53) DNA technology has many medical applications. Which of the following is not done routinely at present?
| back 53 Answer: C |
front 54 54) In recombinant DNA methods, the term vector can refer to
| back 54 Answer: D |
front 55 55) Which of the following would not be true of cDNA produced using human brain tissue as the starting material?
| back 55 Answer: B |