Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Anatomy Chapter 15a
front 1 Which of the following layer of the eyeball is characterized as the vascular layer? | back 1 choroid |
front 2 This is the white fibrous outer layer that covers the outer posterior portion of the eyeball and serves to protect the inner parts of the eyeball | back 2 sclera |
front 3 This is a transparent, thin, mucous tissue layer that protects the anterior surface of the white portion of the eyeball | back 3 conjunctiva |
front 4 This fluid or gel occupies the anterior segment of the eyeball | back 4 aqueous humor |
front 5 Which is not considered an “accessory structure†of the eye? | back 5 retina |
front 6 A sty (or stye) is caused by | back 6 an infection of the sebaceous ciliary glands |
front 7 This structure secretes a fluid that keeps the eyelids from sticking to each other | back 7 Tarsal (Meibomian) gland |
front 8 This is the transparent portion of the sclera through which light passes | back 8 cornea |
front 9 The main function of this structure is to regulate the amount of light entering the eyeball through the pupil | back 9 iris |
front 10 Which of the following apply to the choroid layer of the eyeball? | back 10 contains melanocytes producing melanin, absorbs stray light within the eyeball, is found between the sclera and retina, and is referred to as part of the vascular tunic |
front 11 This region of the eye is between the lens and the retina | back 11 vitreous/posterior segment |
front 12 Aqueous humor drains from the anterior chamber into the | back 12 schleral venous sinus |
front 13 Intraocular pressure is primarily due to | back 13 an imbalance in the amount of the aqueous humor being produced and being drained |
front 14 Blockage of the scleral venous sinus is likely to result in | back 14 glaucoma |
front 15 Most of the light refraction in human vision occurs at the | back 15 cornea |
front 16 How many extrinsic eye muscles are responsible for moving one eye? | back 16 6 |
front 17 The point of greatest visual acuity (resolution) is the: | back 17 fovea centralis |
front 18 During accommodation for near vision: | back 18 the ciliary muscles contract due to parasympathetic innervation |
front 19 In humans, both eyes focus forward on only one set of objects. This is called | back 19 binocular vision |
front 20 Constriction of the pupil is brought about by contraction of the | back 20 circular muscle of the iris via parasympathetic innervation |
front 21 The photopigment in the rods and cones is imbedded in the | back 21 membrane folds or discs of the outer segment of the photoreceptor cells |
front 22 The most common type of color blindness is: | back 22 red-green color blindness |
front 23 The lens is made of layers of transparent layered proteins called: | back 23 crystallins |
front 24 Which of the following conditions is not related to lens pathology? | back 24 glaucoma |
front 25 Which of the following photoreceptors are functional during bright light situations? | back 25 cones |
front 26 Inflamed blood vessels in this layer show up as bloodshot eyes: | back 26 conjunctiva |
front 27 After light is absorbed in the rods: | back 27 Na+/Ca++ channels close and less inhibitory neurotransmitter is released at the synapse with the bipolar cells |
front 28 When entering a dark room on a sunny day, it takes some time to be able to see because | back 28 it takes time for the retina |
front 29 The bipolar neurons associated with the sensory light receptors are found in the: | back 29 neural layer of the retina |
front 30 In daylight, rods contribute little to vision because | back 30 the rhodopsin is bleached as fast as it is regenerated |
front 31 Which cranial nerve is made up of axons of the ganglion cells of the retina? | back 31 II |
front 32 The first step in visual transduction is | back 32 the absorption of light by the rhodopsin photopigments |
front 33 Binocular vision | back 33 provides for depth perception |
front 34 As the axons of the ganglion cells extend from the retina to the brain, nerve fibers | back 34 from the medial half of each retina cross to reach the opposite visual cortex |
front 35 As a result of an injury, a person loses all sight in the left eye, but has no trouble seeing with the right eye. The injury has probably severed the | back 35 left optic nerve |
front 36 Blue light has both a higher frequency (more oscillations per unit time) and a shorter wavelength than red light. | back 36 True |
front 37 The stacked disc membranes of rods are found in the outer segment of rods. | back 37 True |
front 38 Presbyopia involves a loss in lens elasticity in older people that increases the near point of vision. | back 38 True |
front 39 The differential activation of more than one type of cone is responsible for distinguishing different colors and hues. | back 39 True |
front 40 The area of sharpest vision, called the fovea centralis, consists of all rods. | back 40 False |
front 41 The pupil enlarges when the eye focuses on close objects. | back 41 False |
front 42 The circular smooth muscle of the iris opens the pupil and the radial smooth muscle of the iris closes the pupil. | back 42 False |
front 43 The "light absorbing form" of retinal is the trans form. | back 43 False |
front 44 Processes involving bleaching and regeneration of the photopigments account for much, but not all, of the sensitivity
| back 44 True |
front 45 The nasolacrimal sac empties into the nasal cavity. | back 45 True |
front 46 Diabetes is one of the most common causes of blindness in the U.S. | back 46 True |
front 47 Red light has longer wavelengths than blue light. | back 47 True |
front 48 In light adaptation, the visual system adjusts to brighter environments by increasing sensitivity. | back 48 False |
front 49 In convergence, the both eyeballs move laterally so they are both directed toward the object being viewed. | back 49 False |
front 50 There are more cones in the human retina than rods. | back 50 False |
front 51 Trans-retinal is the form that readily binds to opsin. | back 51 False |
front 52 Isomerization is the chemical term that describes the conversion of cis-retinal to trans-retinal. | back 52 True |
front 53 The blind spot of each eye is where the optic nerve penetrates the eyeball. | back 53 True |
front 54 The aqueous humor is fluid-like and the vitreous humor is more gel-like. | back 54 True |
front 55 Retinal is a derivative of Vitamin K. | back 55 False |
front 56 The deepest layer of the neural retina is formed by the axons of the ganglion neurons. | back 56 False |
front 57 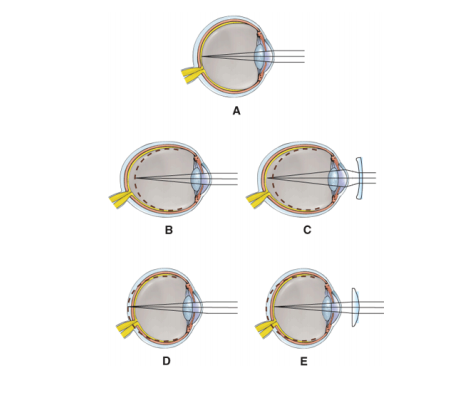 Which diagram represents the
| back 57 A |
front 58 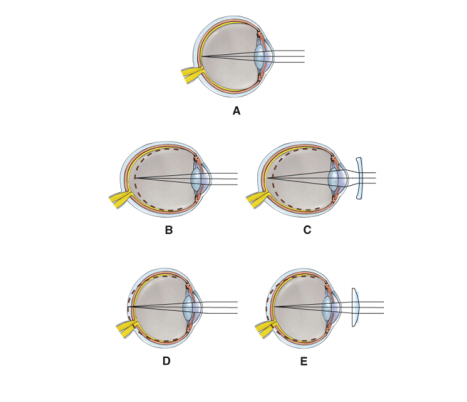 Which diagram represents
| back 58 B |
front 59 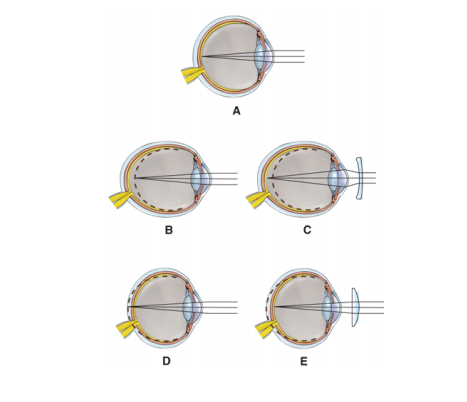 Which diagram demonstrated
| back 59 D |
front 60 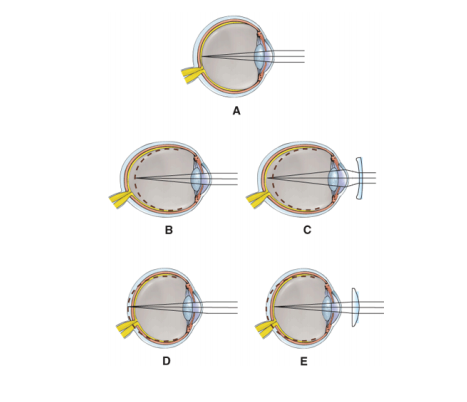 Which diagram is being corrected with a
| back 60 C |
front 61 When viewing an object that is close to your eyes, which member of the following pair, are required for proper image formation on the retina?
| back 61 b. Increased curvature of the lens |
front 62 When viewing an object that is close to your eyes, which member of the following pair, are required for proper image formation on the retina?
| back 62 a. contraction of the ciliary muscle |
front 63 When viewing an object that is close to your eyes, which member of the following pair, are required for proper image formation on the retina?
| back 63 b. convergence of the eyeballs |
front 64 When viewing an object that is close to your eyes, which member of the following pair, are required for proper image formation on the retina?
| back 64 b. constriction of the pupil |
front 65 With age-related macular degeneration, the (central, peripheral) vision is progressively lost. | back 65 central |
front 66 There are (two, three, four) different cone photopigments in the retina. | back 66 three |
front 67 Upon the absorption of light, receptor potentials in the rods and cones (increase, decrease) the release of neurotransmitter. This then induces depolarization in the bipolar cells. | back 67 decrease |
front 68 When photopigments absorb light, the light (increases, decreases) neurotransmitter release thus turning (on, off) the release of inhibitory neurotransmitter so that the excited bipolar cells stimulate the ganglion cells to initiate action potentials in their axons. | back 68 decrease, off |
front 69 All photopigments contain a glycoprotein called _______________, and a derivative of vitamin A called ___________________________. | back 69 opsin, retinal |
front 70 This structure produces the aqueous humor - ____________________ _____________, while this
| back 70 ciliary processes, scleral venous sinus |
front 71 ______________________________ is the increase in the curvature of the lens. | back 71 Accomodation |
front 72 This surface region on the retina that has no rods or cones is known as the _____________ ___________.
| back 72 optic disc, blind spot |
front 73 Place the letters preceding each structure in the correct order of light passage into the eye:
| back 73 D. cornea; A. anterior chamber; B. pupil; F. lens; C. posterior segment; E. vitreous body; G. retina |
front 74 Place the letters preceding each structure in the correct order of nerve impulse passage starting with light absorption.
| back 74 B. rods and cones; E. bipolar cells; A. axons of ganglion cells; F. optic tract; D. optic chiasma; C. optic nerve |
front 75 Light passes through various layers of the retina. Starting with the vitreous chamber, place the letters preceding each of the structures through which light passes before absorption.
| back 75 A. vitreous chamber; D. layer containing axons of ganglion cells; B. layer of ganglionic cells; F. layer of bipolar cells; E. layer containing cell bodies of rods and cones; C. layer containing the outer segments of rods and cones embedded in the pigment layer |