Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exercise 1: The Language of Anatomy
front 1 CHEEK | back 1 BUCCAL |
front 2 PERTAINING TO THE FINGERS | back 2 DIGITAL |
front 3 SHOULDER BLADE REGION | back 3 SCAPULAR |
front 4 ANTERIOR ASPECT OF KNEE | back 4 PATELLAR |
front 5 HEEL OF FOOT | back 5 CALCANEAL |
front 6 PERTAINING TO THE HEAD | back 6 CEPHALIC |
front 7 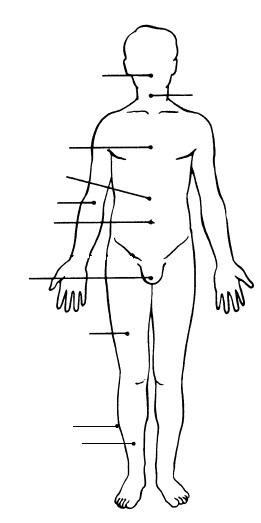 | back 7 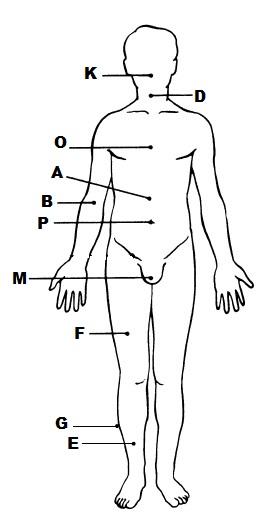 K. ORAL
|
front 8 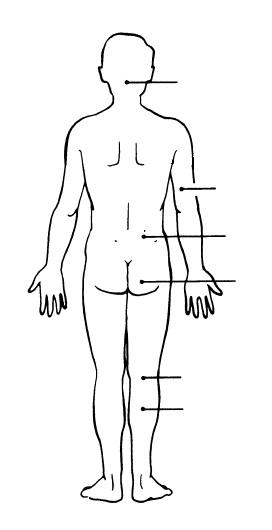 | back 8 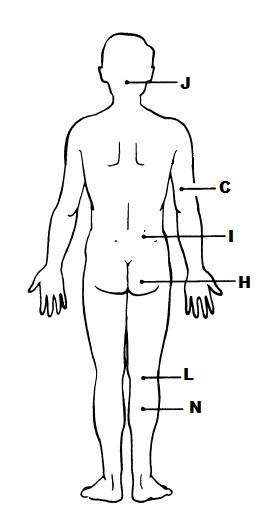 J. OCCIPITAL
|
front 9 CLASSIFY EACH OF THE TERMS IN THE KEY OF QUESTION 2 ABOVE INTO ONE OF THE LARGE BODY REGIONS INDICATED BELOW. INSERT THE APPROPRIATE KEY LETTERS ON THE ANSWER BLANKS.
| back 9 B. ANTICUBITAL
|
front 10 CLASSIFY EACH OF THE TERMS IN THE KEY OF QUESTION 2 ABOVE INTO ONE OF THE LARGE BODY REGIONS INDICATED BELOW. INSERT THE APPROPRIATE KEY LETTERS ON THE ANSWER BLANKS.
| back 10 A. ABDOMINAL
|
front 11 DESCRIBE COMPLETELY THE STANDARD HUMAN ANATOMICAL POSITION. | back 11 IN THE ANATOMICAL POSITION THE HUMAN BODY IS ERECT, WITH THE FEET ONLY SLIGHTLY APART, HEAD AND TOES POINTED FORWARD, AND ARMS HANGING AT THE SIDES WITH PALMS FACING FORWARD. |
front 12 DEFINE SECTION | back 12 A CUT, A PART OF THE BODY OR ORGAN THAT IS CUT TO BE ABLE TO OBSERVE/STUDY IT WITHOUT INCLUDING SURROUNDING AREAS. |
front 13 In the anatomical position, the face and palms are on the (1) body surface; the buttocks and shoulder blades are on the (2) body surface; and the top of the head is the most (3) part of the body. The ears are (4) and (5) to the shoulders and (6) to the nose. The heart is (7) to the vertebral column (spine) and (8) to the lungs. The elbow is (9) to the fingers but (10) to the shoulder. The abdominopelvic cavity is (11) to the thoracic cavity and (12) to the spinal cavity. In humans, the dorsal surface can also be called the (13) surface; however, in quadruped animals, the
| back 13 1. ANTERIOR
|
front 14 If an incision cuts the heart into right and left parts, the section is a (15) section; but if the heart is cut so that superior and inferior portions result, the section is a (16) section. You are told to cut a dissection animal along two planes
| back 14 15. SAGITTAL
|
front 15 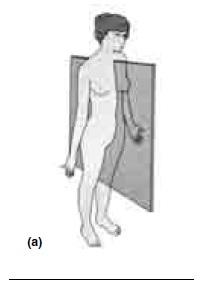 CORRECTLY IDENTIFY EACH OF THE BODY PLANES BY INSERTING THE APPROPRIATE TERM FOR EACH ON THE ANSWER LINE BELOW THE DRAWING. | back 15 MEDIAN (MIDSAGITTAL) PLANE |
front 16 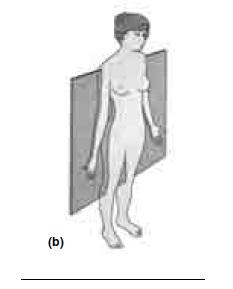 CORRECTLY IDENTIFY EACH OF THE BODY PLANES BY INSERTING THE APPROPRIATE TERM FOR EACH ON THE ANSWER LINE BELOW THE DRAWING. | back 16 FRONTAL PLANE |
front 17 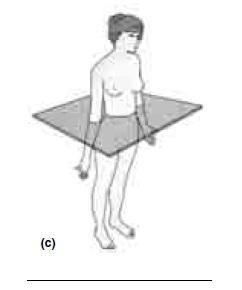 CORRECTLY IDENTIFY EACH OF THE BODY PLANES BY INSERTING THE APPROPRIATE TERM FOR EACH ON THE ANSWER LINE BELOW THE DRAWING. | back 17 TRANSVERSE PLANE |
front 18  Draw a kidney as it appears when sectioned in each of the three different planes. | back 18 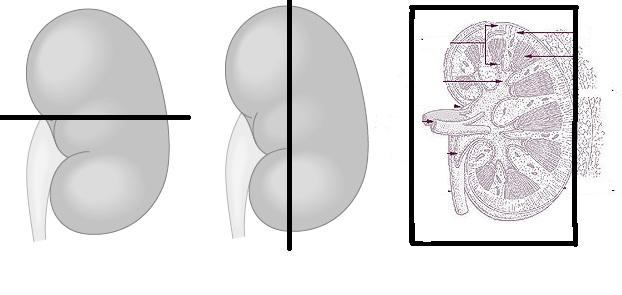 |
front 19 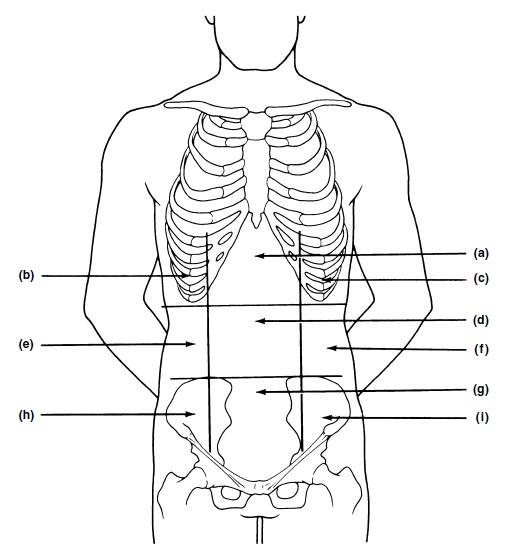 | back 19 A. EPIGASTRIC REGION
|
front 20 Which body cavity would have to be opened for the following types of surgery or procedures?
| back 20 THORACIC; VENTRAL |
front 21 Which body cavity would have to be opened for the following types of surgery or procedures?
| back 21 ABDOMINOPELVIC; VENTRAL |
front 22 Which body cavity would have to be opened for the following types of surgery or procedures?
| back 22 ABDOMINOPELVIC; VENTRAL |
front 23 Which body cavity would have to be opened for the following types of surgery or procedures?
| back 23 ABDOMINOPELVIC; VENTRAL |
front 24 Which body cavity would have to be opened for the following types of surgery or procedures?
| back 24 CRANIAL; DORSAL |
front 25 Which body cavity would have to be opened for the following types of surgery or procedures?
| back 25 SPINAL; DORSAL |
front 26 Name the muscle that subdivides the ventral body cavity. | back 26 DIAPHRAGM |
front 27 Which organ system would not be represented in any of the body cavities? | back 27 SKIN |
front 28 What are the bony landmarks of the abdominopelvic cavity? | back 28 HIP BONES |
front 29 Which body cavity affords the least protection to its internal structures? | back 29 ADOMINAL |
front 30 What is the function of the serous membranes of the body? | back 30 THESE MEMBRANES PRODUCE A THIN LUBRICATING FLUID THAT ALLOWS THE VISCERAL ORGANS TO SLIDE OVER ONE ANOTHER OR TO RUB AGAINST HE BODY WALL WITH MINIMAL FRICTION. ALSO TO COMPARTMENTALIZE THE VARIOUS ORGANS SO THAT INFECTION OF ONE ORGAN IS PREVENTED FROM SPREADING TO OTHERS. |
front 31 Using the key choices, identify the small body cavities described below.
| back 31 ORBITAL |
front 32 Using the key choices, identify the small body cavities described below.
| back 32 ORAL |
front 33 Using the key choices, identify the small body cavities described below.
| back 33 SYNOVIAL |
front 34 Using the key choices, identify the small body cavities described below.
| back 34 MIDDLE EAR |
front 35 Using the key choices, identify the small body cavities described below.
| back 35 NASAL |
front 36 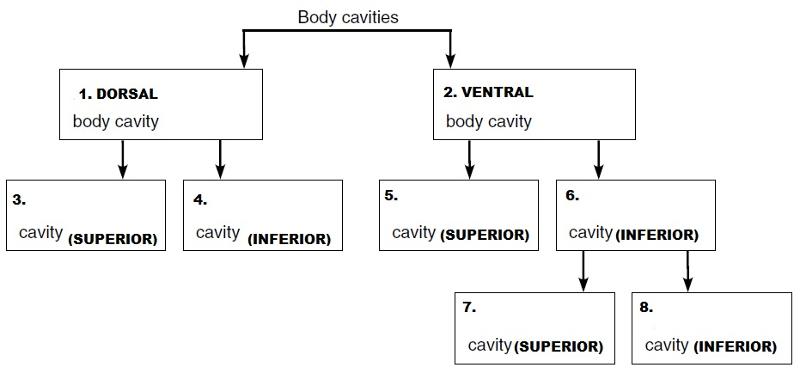 On the incomplete flow chart provided below:
| back 36 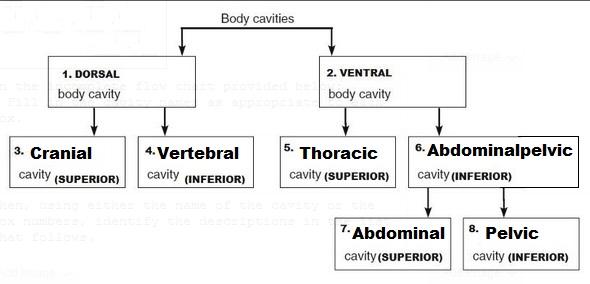 |
front 37 Then, using either the name of the cavity or the box numbers, identify the descriptions in the list that follows.
| back 37 1 - a. contained within the skull and vertebral column
|
front 38 Then, using either the name of the cavity or the box numbers, identify the descriptions in the list that follows.
| back 38 5 - e. contains the heart
|