Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Energetics
front 1 What energy changes occur when chemical bonds are formed and broken?
| back 1 D |
front 2 The temperature of a 2.0 g sample of aluminium increases from 25°C to 30°C. How many joules of heat energy were added? (Specific heat of Al = 0.90 J g–1K–1)
| back 2 C |
front 3 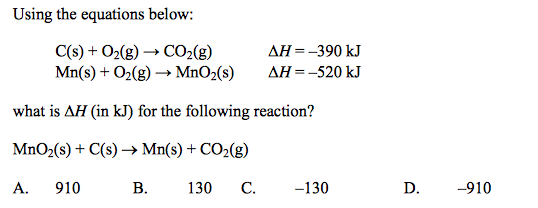 | back 3 B |
front 4  | back 4 D |
front 5  | back 5 B |
front 6 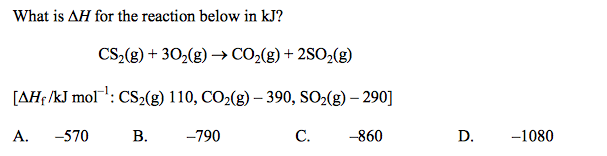 | back 6 D |
front 7 Which statements about exothermic reactions are correct?
| back 7 D |
front 8 A sample of a metal is heated. Which of the following are needed to calculate the heat absorbed by the sample?
| back 8 B |
front 9 The average bond enthalpies for O—O and O==O are 146 and 496 kJ mol–1 respectively. What is the enthalpy change, in kJ, for the reaction below?
| back 9 A |
front 10 Which reaction has the greatest positive entropy change?
| back 10 A |
front 11 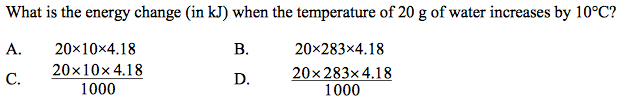 | back 11 C |
front 12  | back 12 B |
front 13 When the solids Ba(OH)2 and NH4SCN are mixed, a solution is produced and the temperature drops.
| back 13 B |
front 14  | back 14 A |
front 15 Which reaction occurs with the largest increase in entropy?
| back 15 B |
front 16 The ∆H and ∆S values for a certain reaction are both positive. Which statement is correct about the spontaneity of this reaction at different temperatures?
| back 16 B |
front 17 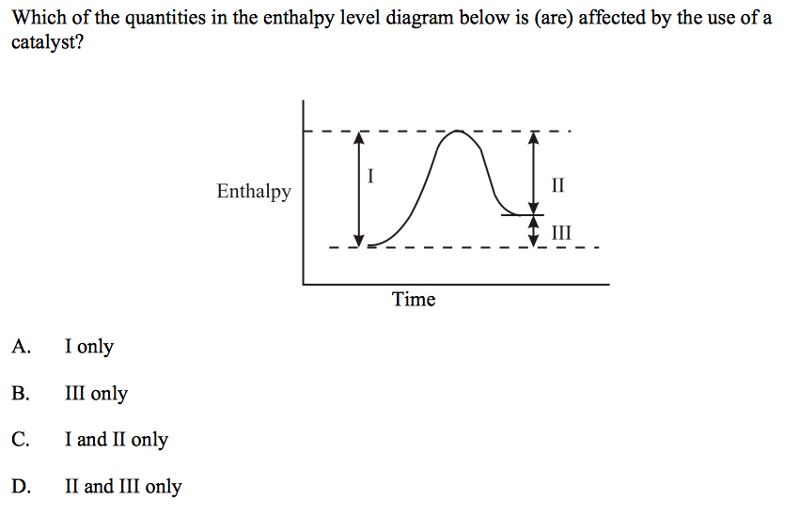 | back 17 C |
front 18 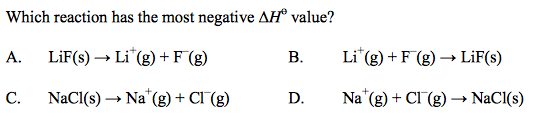 | back 18 B |
front 19 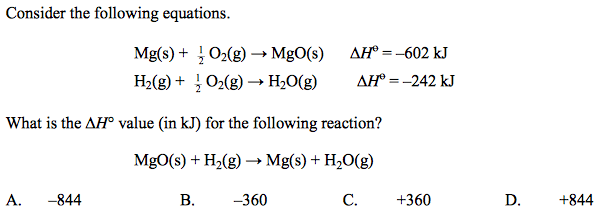 | back 19 C |
front 20 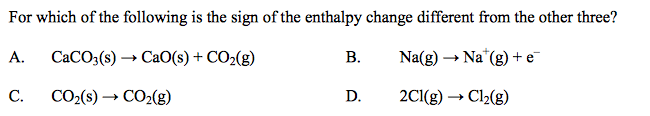 | back 20 D |
front 21 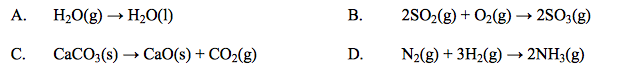 Which reaction has a positive entropy change, ∆S? | back 21 C |
front 22 Separate solutions of HCl(aq) and H2SO4(aq) of the same concentration and same volume were completely neutralized by NaOH(aq). X kJ and Y kJ of heat were evolved respectively. Which statement is correct?
| back 22 B |
front 23  | back 23 A |
front 24 The mass m (in g) of a substance of specific heat capacity c (in J g–1 K–1 ) increases by t°C. What is the heat change in J?
| back 24 A |
front 25 The average bond enthalpy for the C―H bond is 412 kJ mol–1. Which process has an enthalpy change closest to this value?
| back 25 D |
front 26 For a certain reaction at 298 K the values of both ∆H and ∆S are negative. Which statement about the sign of ∆G for this reaction must be correct?
| back 26 D |
front 27 Which type of reaction is referred to in the definition of standard enthalpy change of formation?
| back 27 A |
front 28 The following equation shows the formation of magnesium oxide from magnesium metal.
| back 28 D |
front 29 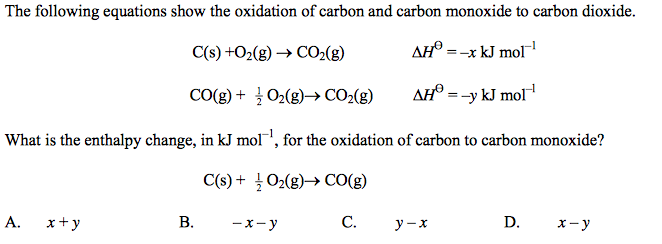 | back 29 C |
front 30 A simple calorimeter was used to determine the enthalpy of combustion of ethanol. The experimental value obtained was –920 kJ mol–1. The Data Booklet value is –1371 kJ mol–1. Which of the following best explains the difference between the two values?
| back 30 B |
front 31 What is the correct order of decreasing entropy for a pure substance? A. gas A. gas > liquid > solid
| back 31 A |
front 32 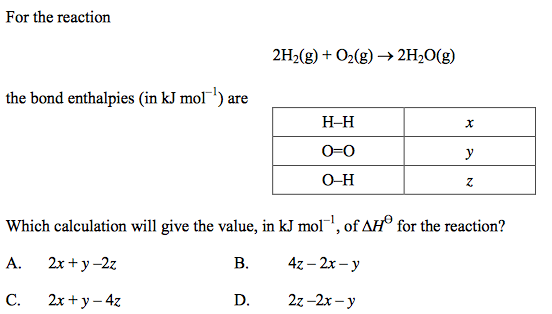 | back 32 C |
front 33 Which statement about bond enthalpies is correct?
| back 33 C |
front 34 An equation for a reaction in which hydrogen is formed is
| back 34 A |
front 35 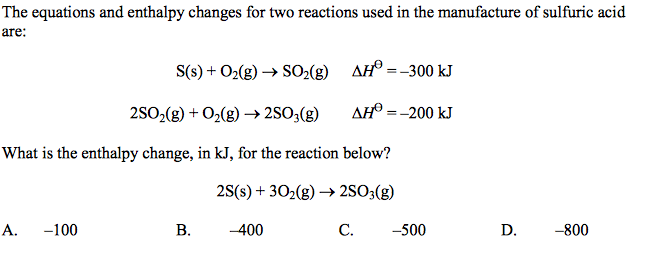 | back 35 D |
front 36 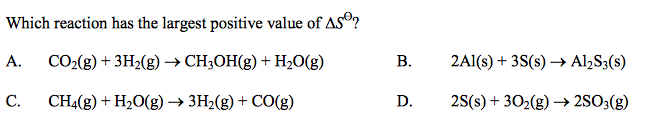 | back 36 C |
front 37 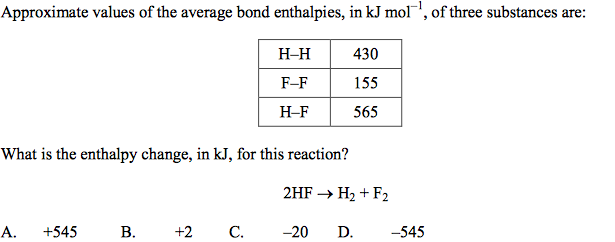 | back 37 A |
front 38 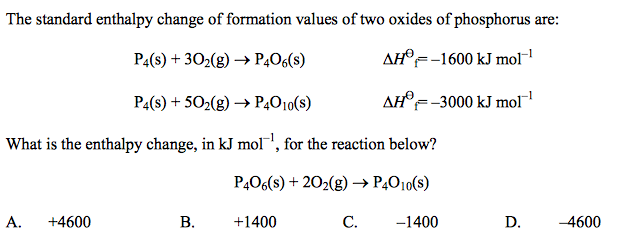 | back 38 C |
front 39  | back 39 D |
front 40 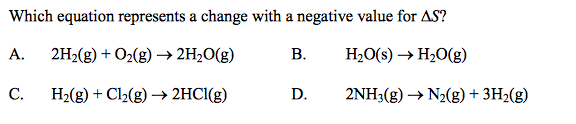 | back 40 A |
front 41 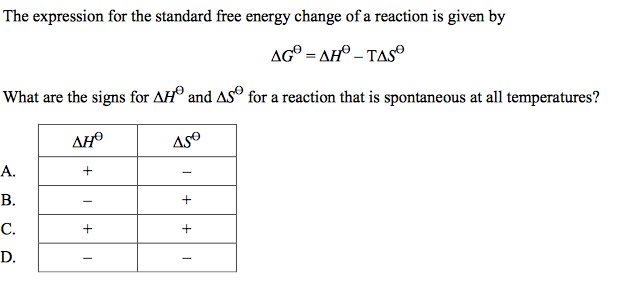 | back 41 B |
front 42 Which statement is correct for an endothermic reaction?
| back 42 C |
front 43 Which statement is correct about the reaction shown?
| back 43 C |
front 44 Which statements are correct for all exothermic reactions?
| back 44 A |
front 45 Which are characteristics of ions in an ionic compound with a large lattice enthalpy value?
| back 45 D |
front 46 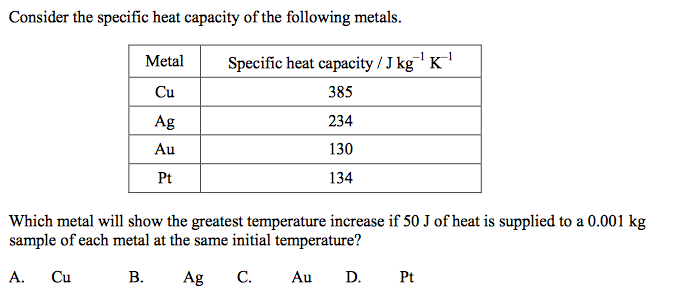 | back 46 C |
front 47 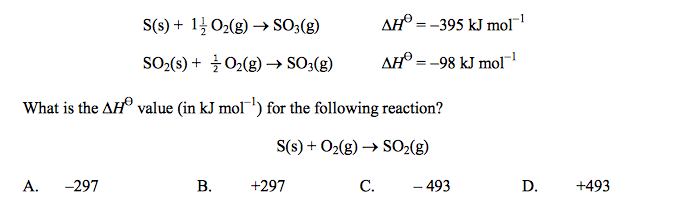 Consider the following reactions: | back 47 A |
front 48 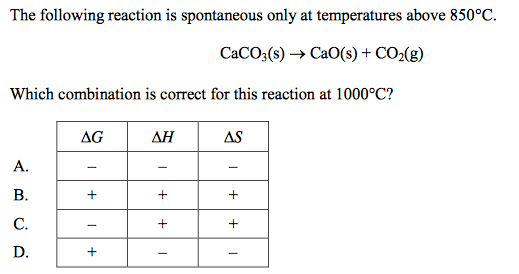 | back 48 C |
front 49 Which statement is correct for an endothermic reaction?
| back 49 B |
front 50 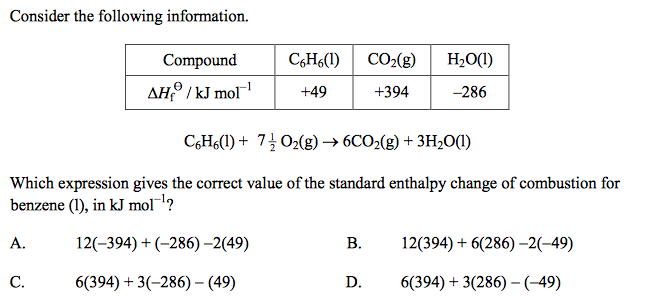 | back 50 C |
front 51  | back 51 D |
front 52 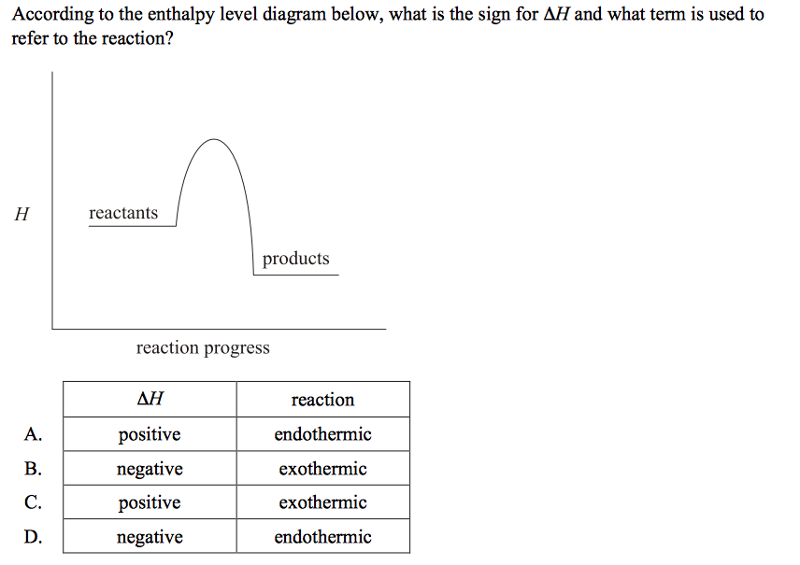 | back 52 B |
front 53 When 40 joules of heat are added to a sample of solid H2O at –16.0°C the temperature increases to –8.0°C. What is the mass of the solid H2O sample? [Specific heat capacity of H2O(s) = 2.0 J g–1K–1]
| back 53 A |
front 54 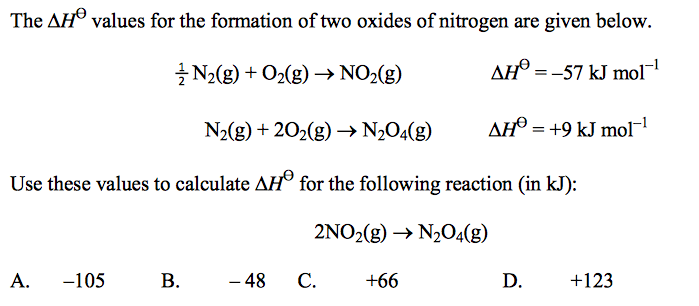 | back 54 D |
front 55 The HӨ and SӨ values for a reaction are both negative. What will happen to the spontaneity of this reaction as the temperature is increased?
| back 55 B |
front 56 How much energy, in joules, is required to increase the temperature of 2.0 g of aluminium from 25 to 30°C? (Specific heat of Al = 0.90 J g–1 K–1).
| back 56 C |
front 57 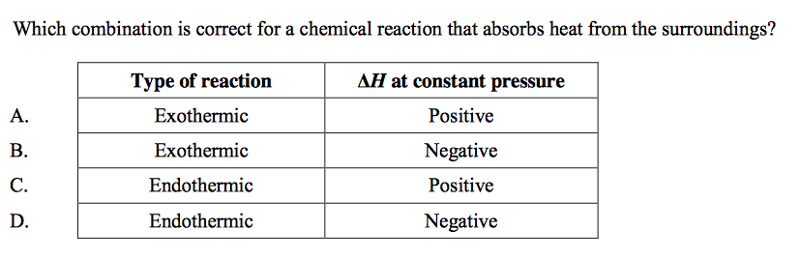 | back 57 C |
front 58 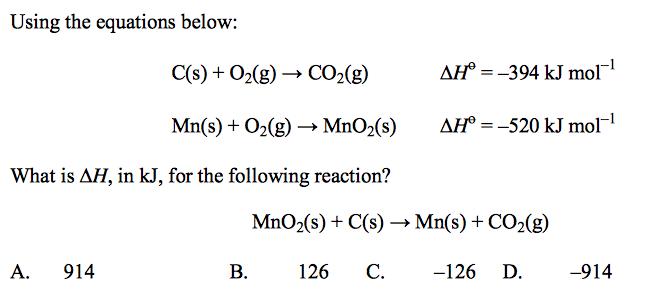 | back 58 B |
front 59 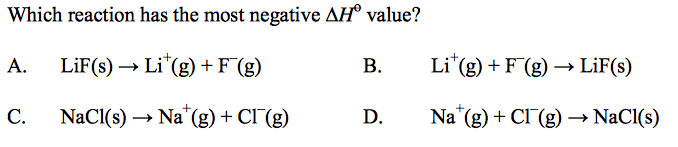 | back 59 B |
front 60  | back 60 C |
front 61 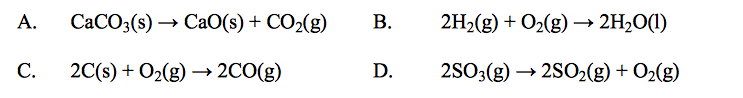 Which reaction causes a decrease in the entropy of the system? | back 61 B |
front 62  | back 62 D |