Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Periodicity
front 1 Which pair of elements reacts most readily?
| back 1 D |
front 2 Which of the following salts form coloured solutions when dissolved in water? I. ScCl3 II. FeCl3 III. NiCl2 IV. ZnCl2
| back 2 B |
front 3 The compounds Na2O, Al2O3 and SO2 respectively are
| back 3 D |
front 4 Which of the following properties of the halogens increase from F to I?
| back 4 B |
front 5 Which pair would react together most vigorously?
| back 5 C |
front 6 Which properties of period 3 elements increase from sodium to argon? I. Nuclear charge II. Atomic radius III.Electronegativity
| back 6 B |
front 7 Which general trends are correct for the oxides of the period 3 elements (Na2O to Cl2O)?
| back 7 C |
front 8 For which element are the group number and the period number the same?
| back 8 B |
front 9 Which of the physical properties below decrease with increasing atomic number for both the alkali metals and the halogens?
| back 9 B |
front 10 Which of the reactions below occur as written?
| back 10 A |
front 11 Rubidium is an element in the same group of the periodic table as lithium and sodium. It is likely to be a metal which has a
| back 11 C |
front 12 When the following species are arranged in order of increasing radius, what is the correct order?
| back 12 B |
front 13 What increases in equal steps of one from left to right in the periodic table for the elements lithium to neon?
| back 13 C |
front 14 Which property decreases down group 7 in the periodic table?
| back 14 B |
front 15 Which two elements react most vigorously with each other?
| back 15 B |
front 16 Which is an essential feature of a ligand?
| back 16 D |
front 17 Which properties are typical of most non-metals in period 3 (Na to Ar)?
| back 17 A |
front 18 A potassium atom has a larger atomic radius than a sodium atom. Which statement about potassium correctly explains this difference?
| back 18 C |
front 19 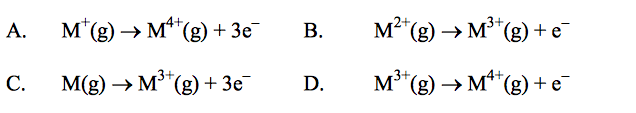 Which equation represents the third ionization energy of an element M? | back 19 B |
front 20 Which factors lead to an element having a low value of first ionization energy?
| back 20 A |
front 21 Which statement about electronegativity is correct?
| back 21 C |
front 22 Which statement is correct for a periodic trend?
| back 22 D |
front 23 Which compound of an element in period 3 reacts with water to form a solution with a pH greater than 7?
| back 23 D |
front 24 Which electrons are lost by an atom of iron when it forms the Fe3+ ion?
| back 24 B |
front 25 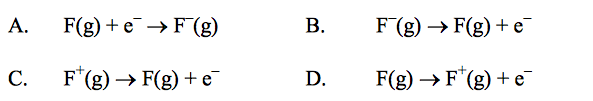 Which equation represents the first ionization energy of fluorine? | back 25 D |
front 26 Which properties are typical of d-block elements?
| back 26 A |
front 27 Which statement is correct for the halogen group?
| back 27 D |
front 28 Which of the following statements are correct?
| back 28 A |
front 29 Which element is a transition metal?
| back 29 B |
front 30 When Na, K, and Mg are arranged in increasing order of atomic radius (smallest first), which order is correct?
| back 30 D |
front 31 Which oxides produce an acidic solution when added to water?
| back 31 C |
front 32 Which combination of ion charge and ion size produces the greatest lattice enthalpy?
| back 32 B |
front 33 Which series is arranged in order of increasing radius?
| back 33 C |
front 34 Which salts form coloured solutions when dissolved in water?
| back 34 A |
front 35 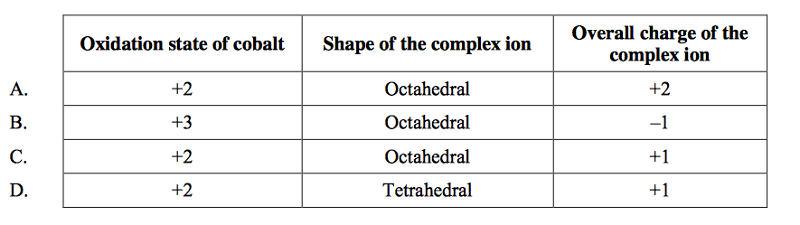 Which combination is correct for the complex ion in [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Cl]Br? | back 35 C |