Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
*Exercise 44: Survey of Embryonic Development
front 1 Define Zygote | back 1 Fertilized egg |
front 2 Describe how you were able to tell by observation when a sea urchin egg was fertilized | back 2 A fertilized membrane is present beneath the outer jelly coat. |
front 3 fusion of male and female pronuclei | back 3 fertilization |
front 4 a solid ball of embryonic cells | back 4 morula |
front 5 process of rapid mitotic cell division w/o intervening growth periods | back 5 cleavage |
front 6 Combination of egg and sperm | back 6 zygote |
front 7 Process involving cell rearrangements to form the three primary germ layers | back 7 gastrulation |
front 8 Embryonic stage in which the embryo consists of a hollow ball of cells | back 8 blastula |
front 9 What is the importance of cleavage in embryonic development? | back 9 It provides a large number of smaller cells for morphogenesis |
front 10 How is cleavage different from mitotic cell division, which occurs later in life? | back 10 During cleavage there are no intervening growth periods between the successive divisions. Therefore the cells get smaller & smaller, bu the embryonic mass remains essentially the same size. |
front 11 Produces the embryonic body | back 11 inner cell mass |
front 12 becomes the chorion and cooperates with uterine tissues to form the placenta | back 12 trophoblast |
front 13 produces the amnion, yolk sac and allantois | back 13 inner cell mast |
front 14 produces the primordial germ cells (an embryonic membrane) | back 14 yolk sac |
front 15 An embryonic membrane that provides the structural basis for the body stalk or umbilical cord | back 15 allantois |
front 16 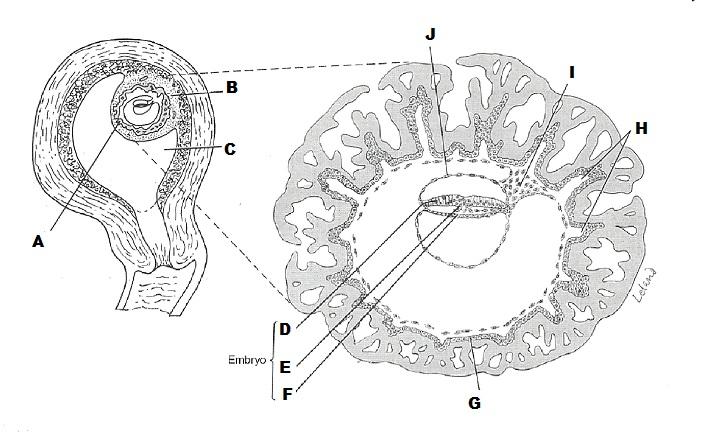 | back 16 A. Decidua basalis
|
front 17 Explain the process and importance of gastrulation | back 17 It involves the migration, movement & rearrangement of embryonic cells, so that a 3-layer embryo is formed (3 primary germ layers) |
front 18 What is the functionof the amnionand the amniotic fluid? | back 18 The amnion is a protective, fluid filled sac that surrounds the embryo. The fluid buffer protects theembryo from phsical trauma & prevents adhesion formation during rapid growth. |
front 19 Describe the process of implantation, noting the role of the tropoblast cells | back 19 The tropoblast cells overlying the inner cell mass adhere to the endometrium. The trophoblast cells then secrete enzymes that erode the endometrial lining to reach the vascular supply beneath. |
front 20 How many days after fertilization is implatation generally completed? | back 20 12-14 |
front 21 What event in the female menstrual cycle ordinarily occurs around mid cycle if implantation does not occur | back 21 Menses, because this is usually the 14th day after ovulation. |
front 22 What name is given to the part of the uterine wall directly under the implanting embryo? What is surrounding the rest of the embryonic structure? | back 22 Decidua basalis; decidua capsularis |
front 23 What does decidua mean? | back 23 "falls off" or is subject to periodic shedding |
front 24 How is the term "deciduas" applied to pregnancy? | back 24 After birth they slough off and are flushed out of the uterus. |
front 25 Which two organ systems are extensively developed in the very young embryo? | back 25 Nervous system and the circulatory system. |
front 26 Describe the direction of development? | back 26 Fill in later |
front 27 Does bodily control during infancy develop in the same direction? Think! Can an infant pick up a common pin (pincer grasp) or wave his arms earlier? is arm-hand or leg-foot control achieved earlier? | back 27 Fill in Later |
front 28 Skeletal muscle develops from | back 28 mesoderm |
front 29 The skeleton develops from | back 29 mesoderm |
front 30 The gut lining develops from | back 30 endoderm |
front 31 The respitory mucosa develops from | back 31 endoderm |
front 32 The circulatory system develops from | back 32 mesoderm |
front 33 The epidermis of the skin develops from | back 33 ectoderm |
front 34 The nervous system develops from | back 34 ectoderm |
front 35 The serosa membrane develops from | back 35 mesoderm |
front 36 The liver, pancreas deveops from | back 36 endoderm |
front 37 15. Fill in later | back 37 15. Fill in later |
front 38 Where in the human uterus do implantation and placentation ordinarily occur? | back 38 High in the Uterus |
front 39 Describe the functions of the placenta | back 39 Provides nutrients and oxygen to the fetus, removes fetal wastes and produces the hormones of pregnancy. |
front 40 What embryonic membranes has the placenta more or less "put out of business"? | back 40 The placenta provides nutrients and oxygen to the fetus, removes fetal wastes, and produces the hormones of pregnancy. The yolk sac and allantois. |
front 41 When does the embryo come to be called a fetus? | back 41 The 9th week of development |
front 42 What is the usual and most desirable fetal position in utero? Why is this the most desirable position? | back 42 head down; because it makes it a whole lot easier on mom and fetus during birth. |
front 43 Describe the gross structure of the human placenta | back 43 Smooth on the side from which the umbilecal cord issues; Torn, rough & bloody on the side that was united w/maternal tissues/blood rich. |
front 44 What is the tissue origin of the placenta? Fetal, maternal or both? | back 44 Both |
front 45 What are the placental barriers that must be crossed to exchange materials | back 45 The membranes of the villi & capillary walls of the fetal vascular supply. |