Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exam 2
front 1 Common causes of inflation: Bigger supply of money. Higher income and willingness to spend. Higher production costs. Certain government policies such as change in taxes and interest rates. International factors such as supply chain disruptions, trade policies, or geopolitical tensions. Inflation expectations that predict rising prices. | back 1 Inflation rate: % change in CPI or GDP deflator |
front 2 Consumer price index (CPI): The average price level of a basket of thousands of goods and services that consumers buy | back 2  CPI formula: |
front 3 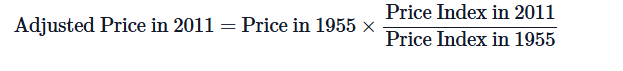 Inflation adjusted price: | back 3 no data |
front 4 Inflation creates uncertainty in the economy because it makes it difficult for both borrowers and lenders to predict the future value of money. When inflation is unpredictable, lenders worry that the money they will be repaid in the future will be worth less than expected, reducing their real returns. To protect themselves against this risk, banks increase interest rates to compensate for potential losses caused by inflation. This higher cost of borrowing makes loans more expensive for consumers and businesses, which can reduce investment and slow economic growth. Therefore, inflation-driven uncertainty leads to higher borrowing costs as lenders try to hedge against the risk of inflation eroding the value of repayments. | back 4 The supply of money is closely associated with inflation because when there is more money circulating in the economy than the available goods and services, the increased demand tends to push prices upward. Essentially, if the money supply grows faster than the economy’s ability to produce goods and services, too much money chases too few goods, leading to inflation. Central banks often control the money supply to manage inflation rates and maintain price stability. Therefore, changes in the money supply directly affect inflation because they influence overall spending and demand within the economy. |
front 5 Most of history the average person was just trying to survive and didn't have time or money to go to Taylor Swift concerts. They wanted to not starve, thirst, or freeze to death. This led to a per capita gdp of $3000 or less. | back 5 there are some places in Africa today with average quality of life we had in the late 1800s in the U.S. |
front 6 Real per capita gdp growth: Nominal GDP change - Price level change - pop. growth | back 6 People invest more in land, investments and businesses when they believe they can earn the rewards from doing so. (Property rights) |
front 7 Stable banks and growth in money allows for less uncertainty in markets. | back 7 xxxxx |
front 8 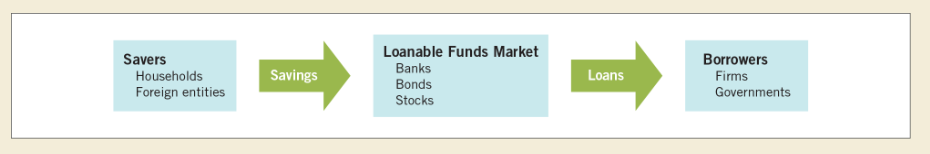 Loanable funds market role: | back 8 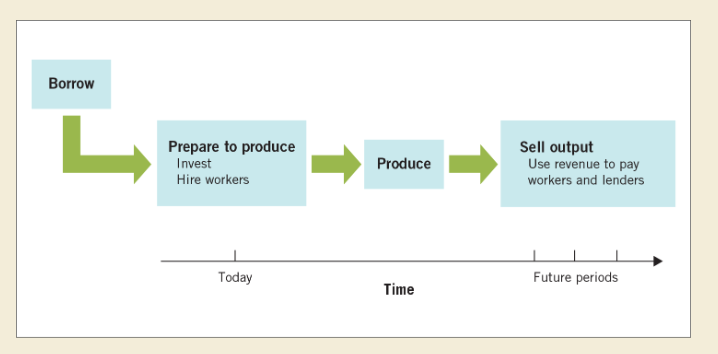 Production timeline: |
front 9 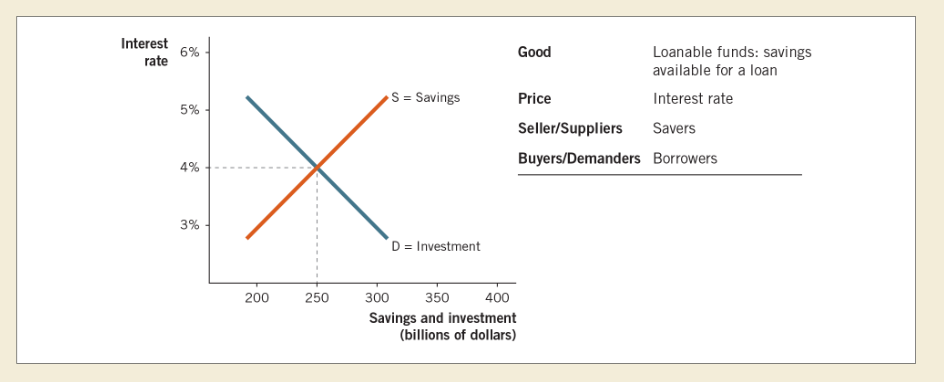 Loanable funds market: | back 9  Interest return example: |
front 10 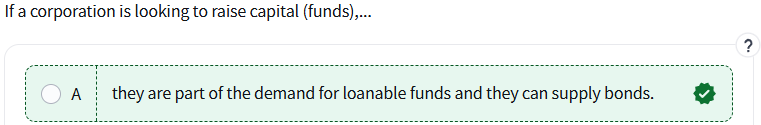 | back 10 More people save when they have more money, so it creates a larger supply of funds. |
front 11 Savers need somewhere to park their money and bonds are an option; demand shifts to the right. | back 11 Direct financing: Going directly to savers for loanable funds through securities and contracts, such as bonds. |
front 12 Indirect financing: Using financial intermediaries for saving and borrowing money | back 12  Bond interest: |
front 13 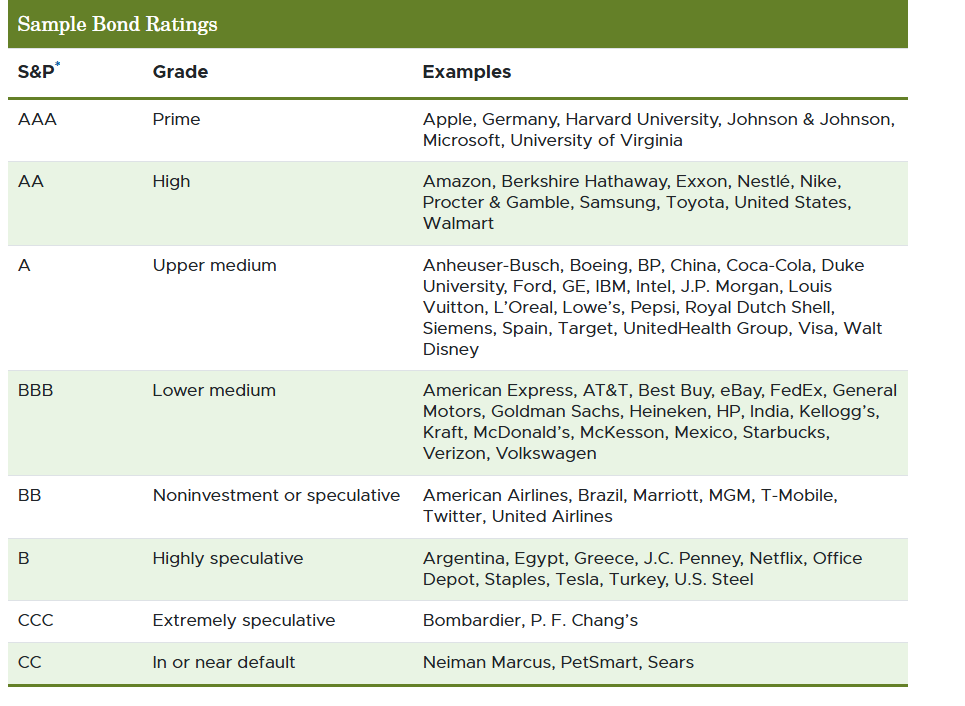 Sample bond ratings: | back 13  Moody's bond ratings: |
front 14 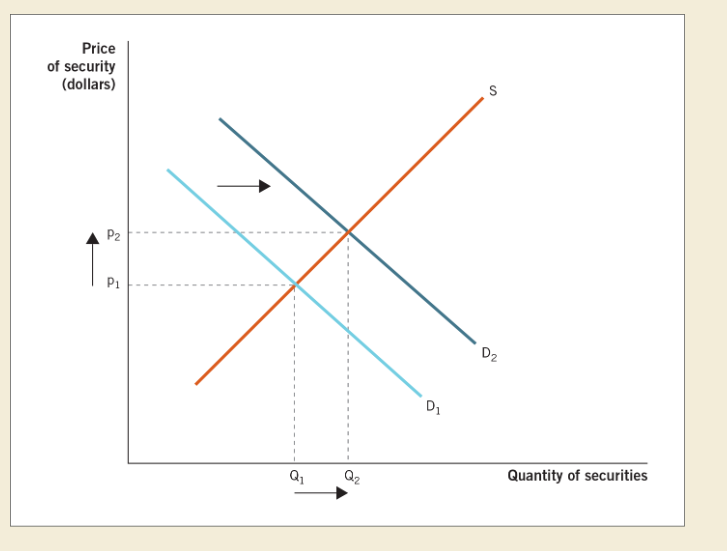 Secondary markets: The existence of secondary markets increases the demand for securities. When demand increases, the price rises (and the interest rate falls). Secondary markets allow firms to borrow at lower interest rates. | back 14 Increase in nominal rate: default risk increases expected inflation increases real interest rate increases |
front 15 I would invest in a mutual fund during my 20s because of compounding interest and then also, tax advantages on my side. Compounding interest grows exponentially when I look at a bar or line graph of it and also, if the rate is high enough, I will really get great money out of it due to the exponential growth. Tax advantages, such as tax-deferral or tax-freeness, make it calm and not too overwhelming when it comes time to withdraw/gain that available money in the mutual fund when you come to retirement. Overall, the nature of these two conditions of mutual funds, plus the management of them by trained professionals, make them a much more appealing option for retirement savings because everyone wants to mitigate risks as much as possible if they can't use risk avoidance as their strategy in something. | back 15 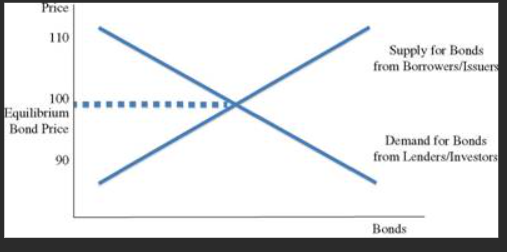 Bond market graph: |