Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
SOCI304- slides
front 1 The body of knowledge regarding crime as a social phenomenon. It includes the processes of making laws, breaking laws, and the social response toward law-breaking within its scope. | back 1 criminology |
front 2 Is an apparatus society uses to enforce the standards of conduct | back 2 criminal justice system |
front 3 What is the general purpose of the criminal justice system? | back 3 To control crime, to prevent crime, and to provide and maintain justice |
front 4 What is the structure and organization of the criminal justice system? | back 4 1. law enforcement 2. Courts 3. Corrections |
front 5 - Includes various levels of organization: federal, state, and local - two models of state police departments: state police and highway patrol - Federal law enforcement agencies include FBI, DEA, and ATF | back 5 Law enforcement |
front 6 - Consists of separate yet interrelated systems: the federal courts and state courts | back 6 courts |
front 7 Authority of a court to hear and decide cases within an area of law or geographic territory | back 7 jurisdiction |
front 8 - An offender is processed in the corrections system - Offenders are required to serve their sentences in a corrections facility like jail or prison | back 8 Corrections |
front 9 Parens patraie: | back 9 essential component to understanding the juvenile justice system - A philosophical perspective that recognizes that the state has both the right and the obligation to intervene on behalf of its citizens in the case of some incompetence or, in the case of juveniles, age and immaturity. |
front 10 Transfer provisions can be categorized into three type: | back 10 -judicial waiver, concurrent jurisdiction, and statutory exclusion |
front 11 A violation of the law | back 11 crime |
front 12 Acts which inherently are deemed evil and immoral | back 12 Mala in se |
front 13 A wrong prohibited which is jurisdiction specifc | back 13 Mala prohibita |
front 14 Unusual behaviors that often violate social norms and various unlawful acts | back 14 deviance |
front 15 What are the main types of crime? | back 15 -violent crime -property crime - white-collar crime - organized crime -consensual or victimless crime |
front 16 Crimes can be generally divided into two categories based on motivation: | back 16 Instrumental crime and expressive crime |
front 17 involves violence that is not directed at the acquisition of anything tangible or designed to accomplish anything specific other than the violent outcome itself. Assaults, disorders, and domestic violence are examples | back 17 Expressive crime |
front 18 Involves behavior that has a specific tangible goal, such as the acquisition of property. predatory crimes, such as theft, burglary, robbery are examples | back 18 Instrumental crimes |
front 19 What are the 2 general perspectives on how behaviors are labeled criminal? | back 19 - consensus perspective of crime - conflict perspective of crime |
front 20 Assumes that members of society by and large agree on what is right and wrong and the law codifies these agreed-upon social values | back 20 consensus |
front 21 Assumes power is the key to make laws. This model asserts that people with political and economical power make laws and protect their interests while keeping marginalized population at a disadvantage. | back 21 Conflict |
front 22 Are often designated for individuals convicted of a minor crime to house individuals awaiting trial | back 22 jail |
front 23 For those convicted of more serious crime with longer sentences | back 23 prison |
front 24 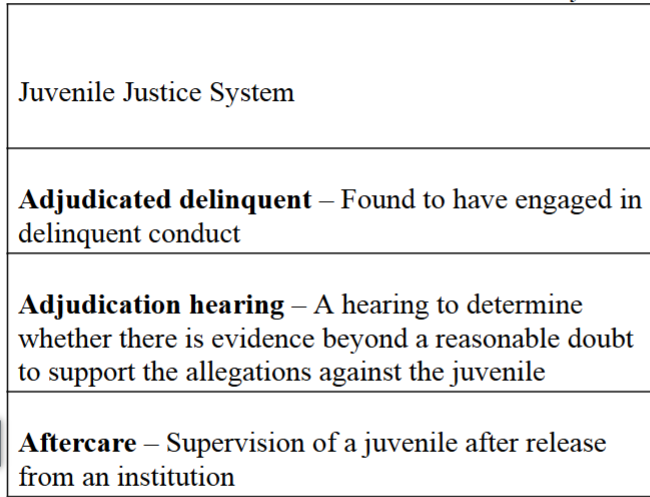 What are these terms in criminal justice system? | back 24 -convict -trial -parole |
front 25  What are these terms in criminal justice system? | back 25 - sentence to prison - crime - criminal - confinement in jail - jail -sentence |
front 26 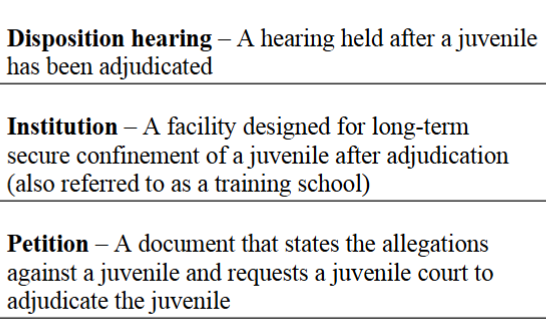 What are these terms in criminal justice system? | back 26 -sentence hearing - prison - indictment |
front 27 Authority to waive juvenile court jurisdiction and transfer the case to criminal court | back 27 judicial waiver |
front 28 Excludes certain juvenile offenders from juvenile court jurisdiction; cases originate rather than juvenile court | back 28 Statutory exclusion |
front 29 a characteristic of a good theory, meaning that it explains a certain phenomenon, such as criminal behavior, with the fewest possible propositions or concepts. | back 29 parsimony |
front 30 refers to the range of criminal behavior that a theory attempts to explain | back 30 scope |
front 31 the extent to which concepts of a theoretical model make sense in terms of face value | back 31 Logical consistency |
front 32 the extent to which a theoretical model can be empirically or scientifically tested through observation and empirical research | back 32 testability |
front 33 The extent to which a theoretical model is supported by scientific research | back 33 Empirical validity |
front 34 the criterion for determining causality: requires that the predictor variable (x) precede the explanatory variable (Y) in time | back 34 Temporal ordering |
front 35 a criterion of causality that requires a change in a predictor variable (x) to be consistently associated with some change in the explanatory variable (y) | back 35 Correlation or covariation |
front 36 Other factors (z) are actually causing two variables (x and y) to occur at the same time; may appear as if x cause y. when in fact they aare both caused by z. | back 36 spuriousness |
front 37 the scientific study of victims | back 37 victimology |
front 38 the increased likelihood of individuals becoming victims of crime due to something they did/didn't do that put them more at risk (not locking their car door) | back 38 Victim precipitation |
front 39 Often paid to victims of violent acts; funds are provided to victims through local, state, or federal governmental agencies | back 39 compensation |
front 40 often ordered by the court to be paid to victims by offenders as part of their sentence. | back 40 restitution |
front 41 Formal statements given by victims in court about the incident in which they were offended, often in person but also in other ways ( written or video), these statements may be considered in determining the offender's sentence | back 41 victim impact statements |
front 42 Why is measuring crime necessary? | back 42 - describing criminal activity -understanding crime trends and patterns - informing public policy and prevention strategies |
front 43 - a nationwide program run by the FBI since 1930 - focuses on reported crimes known to the police - Collects data from 18000 local, state, tribal, and federal law enforcement agencies | back 43 Uniform Crime Report |
front 44 The key measures of uniform crime reports | back 44 -part 1 (index) offenses: more serious crimes (violent crime, murder, rape, robbery, property crime, arson - Part 2 offenses: less serious offenses (fraud, vandalism, drug offenses, etc.) - recent shift: UCR is being phased out and replaced by NIBRS which gives more detailed info |
front 45 What are some advantages of UCR? | back 45 -Nationwide coverage - Long historical record - serious crimes covered -Useful for geographic comparisons - official source |
front 46 What are some disadvantages of UCR? | back 46 -underreporting - police recording bias - limited detail - hierarchy rule -agency participation is voluntary |
front 47 What is national crime victimization survey? | back 47 - A nationally representative household survey conducted by the Bureau of Justice Statistics since 1973 - interviews about 90,000 households and 160,000 individuals age 12+ each year - collects information on people's experiences with crime, regardless of whether those crimes were reported to the police |
front 48 What types of crimes are covered? | back 48 - Violent crime: rape/sexual assault, robbery, aggravated assault - property crimes: burglary, theft, motor vehicle theft - Excludes homicide, arson, and crimes against businesses or institutions |
front 49 What are some advantages of the National Crime Victimization Survey? | back 49 -captures unreported crime - victim-centered data - standardized methodology -helps evaluate police reporting practices - rich detail |
front 50 What are some disadvantages of the National Crime Victimization Survey? | back 50 - excludes some crimes - reliance on memory/ recall - sensitive crimes underreported - sampling limitations -not great for local trends |
front 51 Part of the UCR program. These data provide more detailed information on the incident (regarding the offender and the victim) | back 51 Supplementary homicide reports |
front 52 An enhanced version of the UCR program that collects more detailed information on incidents (regarding the offenders and the victims) | back 52 National incident-based reporting system |
front 53 The best-known hate crime data sources are the Hate Crime Statistics, which collect information on traditional offenses, such as murder and vandalism, that have an additional factor of bias. | back 53 Hate crime data |
front 54 Is a part of the UCR Program and collects data on officer line-of-duty deaths and assaults | back 54 Law enforcement officers killed and assaulted (LEOKA) |
front 55 This type of death occurs when the officer is on or off duty and acting in an official capacity while reacting to a situation that would ordinarily fall within the scope of his or her official duties as a law enforcement officer. | back 55 Line-of-duty death |
front 56 This type of death occurs when an officer is killed because of or while performing his or her official duties, and as a direct result of a criminal act by a subject | back 56 felonious death |
front 57 this type of death occurs when an officer dies as result of an accident he or she is involved in while performing his or her duties (an officer is struck by a vehicle while directing traffic or drowns during a rescue attempt) | back 57 accidental death |
front 58 an annual self-report survey that collects information to measure substance and alcohol use patterns among youths | back 58 Monitoring the future |
front 59 has been used to collect information annually on the use of illegal drugs by individuals in the US | back 59 National survey on drug use and health |
front 60 This program collects information on individuals incarcerated in state and federal prisons | back 60 National prisoner statistics program |
front 61 This type of analysis focuses on crime places. One major aspect is mapping crimes, which illustrates the location of crimes, the distance between them, the direction in which the crimes seem to be moving, and other patterns | back 61 Spatial analysis of crime |
front 62 refers to any instance in which an individual contemplates a criminal act but refrains entirely from or curtails the commission of such an act because he or she perceives some risk of legal punishment and fears the consequences | back 62 Deterrence |
front 63 states when punishment is certain, swift, and appropriately severe crime rates will decline | back 63 deterrance theory |
front 64 The____of punishment refers to how quickly a person will be punished after engaging in crime | back 64 celerity |
front 65 Occurs when apprehended and punished offenders refrain from reoffending in fear of further punishment | back 65 Specific deterrence |
front 66 occurs when the punishments of offenders serve as an example to others who have not committed a crime, instilling in them the fear of punishment and leading them to refrain from crime | back 66 general deterrence |
front 67 Refers to the mere fact that the presence of a legal system and penalties for law violations will, to some (unknown) extent, deter criminality | back 67 absolute deterrence |
front 68 refers to the negative reactions of others when they find out about the arrest and conviction of the offender | back 68 Informal deterrence |
front 69 -Use official criminal justice statistics | back 69 objective measures (measuring deterrence) |
front 70 -use survey data to know people's opinions on the certainty and severity of punishment | back 70 Subjective (perceptual) measures |
front 71 The certainty of punishment (likelihood of being caught and punished) has a stronger deterrent effect than | back 71 the severity of punishment (length or harshness of sentence) |
front 72 An enlightenment ideal or assumption that stipulates an unspecified arrangement among citizens in which they promise the state or government not to commit offenses against other citizens, and in turn gain protection from being violated by other citizens | back 72 Social contract |