Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
lecture 2
front 1 number of constellations according to the IAU | back 1 88 |
front 2 the ecliptic | back 2 the path the sun follows in the sky, crossing the equator at 23.5deg |
front 3 zenith | back 3 point directly overhead |
front 4 meridian | back 4 line running from north to south through the zenith |
front 5 azimuth | back 5 direction along the horizon clockwise from north in degrees |
front 6 altitude | back 6 height above the horizon in degrees |
front 7 angular size | back 7 the angle an object appears to span in your field of view |
front 8 angular distance | back 8 the angle that appears to separate 2 objects |
front 9 angular size / 360deg = | back 9 = physical size / 2pi * distance |
front 10 circumpolar | back 10 stars near the north celestial pole that never dip below the horizon |
front 11 precession | back 11 gradual axial wobble that causes changes in earth's axis over timescales of 26,000 years |
front 12 Right Ascension (RA) | back 12 much like lines of longitude on the earth's surface. measured going east from the vernal equinox in seconds, minutes, and hours |
front 13 Declination (dec) | back 13 much like lines of latitude on earth's surface. measured north (+) or south (-) of the celestial equator in degrees, arcminutes, and arcseconds. |
front 14 the position of Vega during the vernal equinox | back 14 Celestial Position: Dec = +38deg44' RA = 18h35m |
front 15 waxing | back 15 moon phases from new to full |
front 16 waning | back 16 moon phases from full to new |
front 17 crescent | back 17 phases before / after new moon |
front 18 gibbous | back 18 phases before / after full moon |
front 19 stellar parallax | back 19 apparent shift in the position of nearby stars from different parts of earth's orbit |
front 20 retrograde motion | back 20 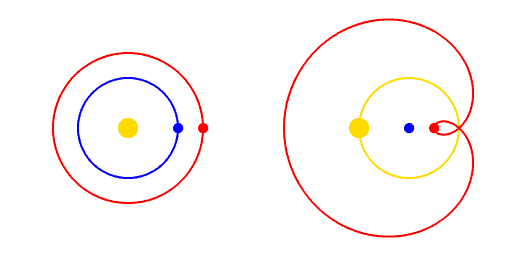 planetary motion relative to stars appears to move backwards then forwards periodically from the perspective of earth. |