Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Bio Ch 42
front 1 Which of the following is most analogous in structure and function to the circulatory systems of bony fishes, rays, and sharks? A) the three-chambered heart of reptiles, where oxygenated and non-oxygenated blood mix in the ventricles B) the portal systems of mammals, where two capillary beds occur sequentially, without passage of blood through a pumping chamber C) the circulatory systems of sponges, where gas exchange in all cells occurs directly with the external environment D) the four-chambered heart of humans, where non-oxygenated blood is pumped to the lungs from one ventricle and oxygenated blood is pumped to the body from another ventricle | back 1 B |
front 2 Which type of circulatory system is most likely present in organisms with a circulating body fluid that is distinct from the fluid that directly surrounds the body's cells? A) an open circulatory system B) a closed circulatory system C) a gastrovascular cavity D) branched tracheae | back 2 B |
front 3 In which of the following organisms does blood flow from the pulmocutaneous circuit to the heart before circulating through the rest of the body? A) annelids B) fishes C) frogs D) insects | back 3 C |
front 4 Which of the following are the only vertebrates in which blood flows directly from respiratory organs to body tissues without first returning to the heart? A) amphibians B) fishes C) mammals D) reptiles | back 4 B |
front 5 Which of the following would an organism need to adjust blood pressure independently in the blood vessels of the gas-exchange surface and in the blood vessels of the general body circulation? A) open circulatory system B) hemocoel C) two-chambered heart D) four-chambered heart | back 5 D |
front 6 A paleontologist discovers the fossilized heart of an extinct animal. The evidence indicates that the organism's heart was large, was well-formed, and had four chambers, with no connection between the right and left sides. Which of the following conclusions is best supported by these observations? A) the animal had evolved from birds B) the animal was endothermic and had a high metabolic rate C) the animal was most closely related to alligators and crocodiles D) the animal had little to no need to regulate blood pressure | back 6 B |
front 7 Circulatory systems help to overcome which of the following physiological challenges? A) temperature differences between the lungs and the active tissue B) the slow rate at which diffusion occurs over large distances C) the problem of communication systems involving only the nervous system D) the need to cushion animals from trauma | back 7 B |
front 8 Which of the following results in the greatest blood pressure in the mammalian aorta? A) systole of the left atrium B) diastole of the right ventricle C) systole of the left ventricle D) diastole of the right atrium | back 8 C |
front 9 Which of the following is the correct sequence of blood flow in birds and mammals? A) left ventricle → aorta → lungs → systemic circulation B) vena cava → right atrium → right ventricle → pulmonary vein C) pulmonary vein → left atrium → left ventricle → pulmonary circuit D) vena cava → right atrium → right ventricle → pulmonary artery | back 9 D |
front 10 What is the theoretical cardiac output of a patient with a heart rate of 70 beats per minute and a stroke volume of 70 mL/beat? A) 1,000 mL/minute B) 1,400 mL/minute C) 2,800 mL/minute D) 4,900 mL/minute | back 10 D |
front 11 Damage to the SA node in humans is most likely to result in a ________. A) blockage of conductance between the bundle branches and the Purkinje fibers B) negative effect on peripheral resistance C) disruption on the rate and timing of cardiac muscle contractions D) direct effect on blood pressure monitors in the aorta | back 11 C |
front 12 While jogging, a person has a stroke volume of 130 mL/beat and a heart rate of 120 beats per minute. Their resting stroke volume is 70 mL/beat and resting heart rate is 60 beats per minute. Which answer best describes the effect of jogging on the person's cardiac output? A) Their cardiac output did not change. Only their respiratory rate changed. B) During exercise, their cardiac output decreased by 11,400 mL/minute. C) During rest, their cardiac output increased by 60 mL/beat. D) Their cardiac output increased from 4,200 mL/minute to 15,600 mL/minute when jogging. | back 12 D |
front 13 Atrial systole ________. A) occurs at the same time as ventricular diastole B) pumps blood to the aorta C) refers to the relaxation of the cardiac muscle D) only occurs in the left heart chambers | back 13 A |
front 14 The greatest difference in the concentration of respiratory gases is found in which of the following pairs of mammalian blood vessels? A) the pulmonary vein and the superior vena cava B) the veins from the right and left legs C) the pulmonary artery and the inferior vena cava D) the pulmonary vein and the aorta | back 14 A |
front 15 How many capillary beds must a red blood cell pass through to move from an artery in the left arm to the left ventricle of the heart? A) one B) two C) three D) four | back 15 B |
front 16 An electrocardiogram (ECG) provides information about ________. A) the pressure of blood in the heart chambers B) the rhythm of heart contractions C) the amount of oxygen in the blood as it leaves the heart D) the speed of blood flow through the blood vessels | back 16 B |
front 17 Which one of the following organisms likely has the highest systolic pressure in its aorta? A) mouse B) human C) hippopotamus D) giraffe | back 17 D |
front 18 The velocity of blood flow is lowest in capillaries because ________. A) the capillaries have internal valves that slow the flow of blood B) the diastolic blood pressure is too low to deliver blood to the capillaries at a high flow rate C) the systemic capillaries are supplied by the left ventricle, which has a lower cardiac output than the right ventricle D) the total cross-sectional area is greater in the capillaries than in any other part of the circulatory system | back 18 D |
front 19 Organisms belonging to a species with a high resting cardiac output are most likely to have which of the following characteristics? A) small compact bodies B) wide-diameter veins C) large distance between its heart and its brain D) a relatively inactive lifestyle | back 19 C |
front 20 Which of the following mechanisms are used to regulate blood pressure in the closed circulatory system of vertebrates? I) changing the strength of heart contraction II) constricting and relaxing smooth muscle in the walls of arterioles III) opening or closing precapillary sphincters A) only I and II B) only I and III C) only II and III D) I, II, and III | back 20 D |
front 21 Which of the following mechanisms are used to regulate blood pressure in the closed circulatory system of vertebrates? I) changing the strength of heart contraction II) constricting and relaxing smooth muscle in the walls of arterioles III) opening or closing precapillary sphincters A) only I and II B) only I and III C) only II and III D) I, II, and III | back 21 D |
front 22 Which biological membranes must atmospheric molecules of oxygen cross to become bound to hemoglobin for transport in mammals? A) one membrane B) two membranes C) four membranes D) five membranes | back 22 D |
front 23 Which of the following indicates a diagnosis of hypertension in adults? A) fatty deposits on the endothelium of arteries B) LDL/HDL ratio in peripheral blood C) % of blood volume made up of platelets D) BP > 140 systolic and/or > 90 diastolic | back 23 D |
front 24 Which of the following is a normal event in the process of blood clotting? A) production of erythropoietin B) conversion of fibrin to fibrinogen C) activation of prothrombin to thrombin D) synthesis of hemoglobin | back 24 C |
front 25 Which hormone is released to stimulate the production of red blood cells? A) growth hormone B) erythropoietin C) cortisol D) acetylcholine | back 25 B |
front 26 Suppose an organism had a mutation in the thrombin gene such that the thrombin protein was nonfunctional. What is the most likely impact? A) cannot produce erythrocytes B) blood would not clot effectively C) weakened immune system D) poor gas exchange | back 26 B |
front 27 Which of the following examples illustrates the process of countercurrent exchange? A) water across fish gills and blood B) blood flow in insects and tracheae C) air in bronchi and pulmonary veins D) water across frog skin and heart ventricle | back 27 A |
front 28 Countercurrent exchange in the fish gill helps to maximize | back 28 _______. A) blood pressure B) diffusion C) active transport D) osmosis _ B |
front 29 Which of the following statements correctly compares respiration in fish and in mammals? A) Fish respiratory medium carries more oxygen B) Countercurrent seen in mammals not fish C) Mammal respiration is bidirectional, fish is unidirectional D) Oxygen transported by plasma in fish | back 29 C |
front 30 What selective pressure likely led to tracheal tube support in both mammals and insects? A) Similar oxygen needs B) Risk of collapse when breathing air C) Endothermic temp regulation D) Decreased environmental CO2 | back 30 B |
front 31 What is the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) if air is 10% oxygen and 400 mm Hg? A) 400 mm Hg B) 82 mm Hg C) 40 mm Hg D) 4 mm Hg | back 31 C |
front 32 When tidal pool water gets warmer and saltier, what happens? A) CO2 increases B) O2 decreases C) Better aerobic support D) Becomes denser | back 32 B |
front 33 PO2 at Mt. Everest summit where pressure is 1/3 of 760 and O2 is 21%? A) 53 mm Hg B) 157 mm Hg C) 255 mm Hg D) 760 mm Hg | back 33 A |
front 34 Premature infants may suffer respiratory failure due to | back 34 _______. A) sudden uterine exit B) overproduction of surfactants C) lung collapse due to lack of surfactant D) lung gene mutations _ C |
front 35 Correct air flow in mammalian lung? A) trachea → bronchioles → bronchi → alveoli B) larynx → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles → alveoli C) trachea → tracheoles → bronchi → alveoli D) alveoli → tracheoles → bronchi → trachea | back 35 B |
front 36 During aerobic exercise, PO2 in muscle cells | back 36 _______, and oxygen diffusion ________. A) decreases; increases B) increases; decreases C) no change D) decreases; decreases _ A |
front 37 Why does a rabbit struggle to get oxygen at high elevation? A) O2 % is lower B) O2 % is higher C) PO2 is lower D) PO2 is higher | back 37 C |
front 38 If fish water flow direction is reversed, what happens? A) gas exchange efficiency drops B) gas exchange efficiency increases C) blood thickens D) blood thins | back 38 A |
front 39 What happens if blood pH drops from 7.4 to 7.2? A) CO2 increases B) bicarbonate increases C) oxygen increases D) H+ decreases | back 39 A |
front 40 Avian lung adaptation aiding flight? A) bidirectional airflow B) more dead space C) countercurrent circulation D) gas exchange during both inhale and exhale | back 40 D |
front 41 How does the body sense gas level changes? A) brain tracks O2 B) medulla monitors pH in CSF C) brain adjusts CSF pH D) lung stretch receptors signal medulla | back 41 B |
front 42 Total lung capacity if vital capacity = 4000 mL and residual volume = 1000 mL? A) 1450 mL B) 4000 mL C) 4450 mL D) 5000 mL | back 42 D |
front 43 What blood gas most affects human breathing rate? A) nitrogen B) oxygen C) carbon dioxide D) carbon monoxide | back 43 C |
front 44 After exhalation, none of the inhaled air remains. Which animal? A) human B) lizard C) turtle D) crow | back 44 D |
front 45 Damage to external intercostal muscles would impair: A) inhalation B) exhalation C) gas exchange D) blood pressure regulation | back 45 A |
front 46 Lowering blood pH from 7.4 to 7.2 causes hemoglobin to: A) release all CO2 B) bind more O2 C) bind fewer H+ D) bind less O2 | back 46 D |
front 47 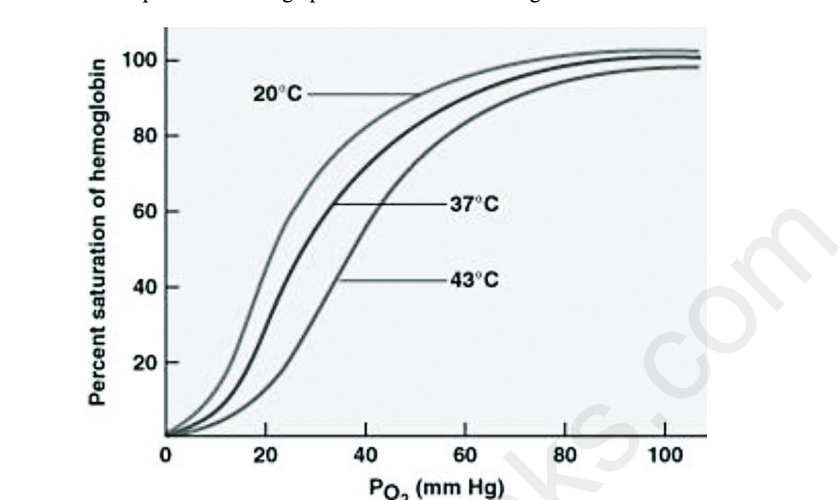 A researcher investigating the effect of temperature on hemoglobin saturation collected the data represented in the graph. Which of the following claims is most consistent with the data? A) The greatest delivery of oxygen from the blood to the surrounding tissues occurs at 37℃. B) Increasing blood pH results in more oxygen unloading in tissues. C) Colder blood temperature results in greater dissociation of oxygen and hemoglobin. D) Hemoglobin has a lower affinity for oxygen under high temperature conditions. | back 47 D |
front 48 Which statement best describes what happens to the carbon dioxide produced by humans? A) It is converted to bicarbonate ions. B) It is bound to hemoglobin. C) It is transported in the erythrocytes as carbonic acid. D) It is simply dissolved in the plasma. | back 48 A |
front 49 Which statement best describes how diving mammals are different than mammals that are not adapted for diving? A) Diving mammals have larger lungs B) Diving mammals can store more oxygen in their muscles C) Diving mammals have smaller blood vessels D) Diving mammals always keep blood flowing to their lungs during a dive | back 49 B |
front 50 The bar-headed goose is one of the highest flying birds in the world, having been observed flying at over 27,000 feet. Which of the following adaptations would provide an advantage for flying at high altitudes? A) hemoglobin with a very high affinity for oxygen B) use of negative pressure breathing C) a low concentration of myoglobin in its muscles D) low tidal volumes | back 50 A |
front 51 Respiratory acidosis is a condition that can result from decreased ventilation rates (hypoventilation). If a sign of respiratory acidosis is decreased blood pH, which of the following is most likely true about the blood in the body? A) There is less hemoglobin in red blood cells. B) There is more hemoglobin in red blood cells. C) There is less CO2 in the blood. D) There is more CO2 in the blood. | back 51 D |
front 52 Which of the following respiratory systems is independent from a fluid-based circulatory system? A) the lungs of a vertebrate B) the gills of a fish C) the tracheal system of an insect D) the skin of an earthworm | back 52 C |
front 53 Blood returning to the mammalian heart in a pulmonary vein drains first into the ________. A) left atrium B) right atrium C) left ventricle D) right ventricle | back 53 A |
front 54 Pulse is a direct measure of ________. A) blood pressure B) stroke volume C) cardiac output D) heart rate | back 54 D |
front 55 When you hold your breath, which of the following blood gas changes first leads to the urge to breathe? A) rising O2 B) falling O2 C) rising CO2 D) falling CO2 | back 55 C |
front 56 One feature that amphibians and humans have in common is ________. A) the number of heart chambers B) a complete separation of circuits for circulation C) the number of circuits for circulation D) a low blood pressure in the systemic circuit | back 56 C |
front 57 A molecule of CO2 released into the blood in your left toe can be exhaled from your nose without passing through which of the following structures? A) the pulmonary vein B) the trachea C) the right atrium D) the right ventricle | back 57 A |
front 58 Compared with the interstitial fluid that bathes active muscle cells, blood reaching these cells in arterioles has a ________. A) higher PO2 B) higher PCO2 C) greater bicarbonate concentration D) lower pH | back 58 A |