Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Bio ch 34
front 1 Which of the following is a characteristic of all chordates at some point during their life cycle? A) jaws B) post-anal tail C) four-chambered heart D) vertebrae | back 1 B |
front 2 Adult urochordates (tunicates) lack notochords, even though larval urochordates have them. What is the function of notochords in larval urochordates? A) they aid in swimming B) they stiffen their bodies C) they induce tissue differentiation D) they organize their nervous systems | back 2 A |
front 3 If a tunicate's pharyngeal gill slits were blocked by a foreign object, which of the following processes would the organism have trouble performing? A) respiring only B) feeding only C) moving D) respiring and feeding | back 3 D |
front 4 In early chordates, the primitive pharyngeal slits carried out which of the following functions? A) the digestive system's opening B) suspension-feeding devices C) components of the jaw D) sites of respiration | back 4 B |
front 5 Which of the following statements is correct regarding lancelets? A) The first fossils resembling lancelets appeared in the fossil record around 10 million years ago. B) Recent work in molecular systematics supports the hypothesis that lancelets are the basal clade of chordates. C) The extant lancelets are the immediate ancestors of the fishes. D) Lancelets do not swim in the same way that fishes do. | back 5 B |
front 6 Which extant chordates are most like the earliest chordates in appearance? A) lancelets B) adult tunicates C) amphibians D) chondrichthyans | back 6 A |
front 7 Which of the following structures do vertebrates and tunicates both possess? A) jaws adapted for feeding B) a high degree of cephalization C) the formation of structures from the neural crest D) a notochord and a dorsal, hollow nerve cord | back 7 D |
front 8 Which of the following statements describes one of the differences between tunicates and other chordates? A) tunicates have 9 Hox genes whereas other chordates have 13 Hox genes B) other chordates have 9 Hox genes whereas tunicates have 13 Hox genes C) chordate characters in tunicates are more apparent in the adult stage than in the larval stage while all other chordates only exhibit these characteristics as larvae D) lancelets and tunicates express different Hox genes that direct the development of the dorsal nerve cord | back 8 A |
front 9 Which of the following groups includes the greatest number of organisms? A) osteichthyans B) amphibians C) gnathostomes D) lobe-fins | back 9 C |
front 10 Which of the following characteristics is shared by a hagfish and a lamprey? A) a rasping tongue B) paired fins C) jaws D) a well-developed notochord | back 10 D |
front 11 A new species of aquatic chordate is discovered that closely resembles an ancient form. It has the following characteristics: external armor of bony plates, no paired lateral fins, and a suspension-feeding mode of nutrition. In addition to these, which of the following characteristics is it most likely to exhibit? A) legs B) no jaws C) an amniotic egg D) endothermy | back 11 B |
front 12 In vertebrates, the earliest known mineralized structures were associated with body parts involved in which of the following processes? A) feeding B) locomotion C) defense D) respiration | back 12 A |
front 13 A team of researchers has developed a poison that has proven effective against lamprey larvae in freshwater cultures. Critics worry about potential effects on lancelets, which are similar to lampreys in many ways. Which of the following arguments best addresses the critics' concerns? A) Lamprey larvae and lancelets have very different feeding mechanisms. B) Lancelets do not have segmental muscles. C) Lancelets live only in saltwater environments. D) Lancelets and lamprey larvae eat different kinds of food. | back 13 C |
front 14 Which reproductive strategy in mammals involves the mother laying eggs that hatch outside of her body? A) oviparous reproduction B) ovoviviparous reproduction C) viviparous reproduction D) asexual reproduction | back 14 A |
front 15 Which of the following statements best explains the different body shapes found in skates and rays compared to sharks? A) Sharks are more closely related to the tube-like lampreys than are skates and rays. B) Skates and rays need enlarged pectoral fins to help them stay level in turbulent water, while sharks do not. C) Skates and rays exchange gases across their skin and thus require a high surface-area-to-volume ratio, while sharks use gills to respire. D) Sharks are streamlined for active swimming at mid-depths, while skates move about mostly on the ocean bed. | back 15 D |
front 16 Which of these statements accurately describes a similarity between sharks and ray-finned fishes? A) They are equally able to exchange gases with the environment while stationary. B) They are highly maneuverable due to their flexibility. C) They have a lateral line that is sensitive to vibrations. D) A swim bladder helps control buoyancy. | back 16 C |
front 17 In a typical ray-finned fish, the swim bladder allows individuals to perform which of the following processes? A) effectively circulate its blood B) use its lateral line system C) use its swim bladder as a respiratory organ D) remain buoyant | back 17 D |
front 18 Which structure in a shark is closest in function to a swim bladder in a ray-finned fish? A) its lateral line system B) its spiral valve C) its liver D) its gills | back 18 C |
front 19 If a ray-finned fish is to both hover (remain stationary) in the water column and ventilate its gills effectively, then what other structure besides its swim bladder will it use? A) its pectoral fins B) its lateral line system C) its caudal (tail) fin D) its operculum | back 19 D |
front 20 In which of the following ways did the evolution of the jaw contribute to diversification of early vertebrate lineages? A) It allowed for smaller body size. B) It was the first stage in the development of a bony skull. C) It made additional food sources available. D) It increased the surface area for respiration and feeding. | back 20 C |
front 21 Jaws first occurred in which of the following group of fishes? A) lampreys B) chondrichthyans C) ray-finned fishes D) placoderms | back 21 D |
front 22 Which of these structures would most likely have been observed in the common ancestor of chondrichthyans and osteichthyans? A) a mineralized, bony skeleton B) opercula C) a spiral valve intestine D) a swim bladder | back 22 A |
front 23 At one time, Chondrichthyes were thought to have diverged from other vertebrates before the evolution of bone. Now we have concluded that the Chondrichthyes diverged after the evolution of bone had started. What does this change demonstrate about the evolution of fishes? A) characteristics can be lost in evolution B) evolution is one-way and straight line C) hagfishes and lampreys have ancestors with bone D) cartilage contributes to keeping sharks light so they do not sink | back 23 A |
front 24 Which of the following characteristics allowed early gnathostomes to become successful predators? A) fins stiffened with bone that increased maneuverability and improved gas exchange through the skin B) fins stiffened with bone that increased maneuverability and improved gas exchange in the gills C) lobe fins that allowed temporary access to land and improved gas exchange through the skin D) lobe fins that allowed temporary access to land and improved gas exchange in the gills | back 24 B |
front 25 Suppose, while out camping in a forest, you found a chordate with a long, slender, limbless body slithering across the ground near your tent. The organism is most likely ________. A) a lamprey B) a mammal C) an amphibian D) a skate | back 25 C |
front 26 While hiking in a tropical rainforest, you find a large, snakelike organism that is 1-meter-long, has smooth skin, and appears to be segmented. You think it might be a snake or an amphibian. Which of the following characteristics, if observed, should help you arrive at a conclusive answer? A) presence of moist, highly vascularized skin B) presence of scales C) presence of a nerve cord D) presence of a digestive system with two openings | back 26 B |
front 27 Which of the following organisms is considered the most recent common ancestor of living tetrapods? A) a sturdy-finned, shallow-water lobe-fin whose appendages had skeletal supports similar to those of terrestrial vertebrates B) an armored, jawed placoderm with two pairs of appendages C) an early ray-finned fish that developed bony skeletal supports in its paired fins D) a salamander that had legs supported by a bony skeleton but moved with the side-to-side bending typical of fishes | back 27 A |
front 28 Which of the following was a trend first observed in the evolution of the earliest tetrapods? A) the appearance of jaws B) feet with digits C) the mineralization of the endoskeleton D) the amniotic egg | back 28 B |
front 29 Ancient fossils that seem to be an intermediate stage in the evolution from fish to tetrapods had which of the following characteristics? A) fins and scales like a fish but ribs to support the body and a bone structure in the front limb like tetrapods B) a pelvis and rear limbs like a fish and gills like a tetrapod C) bones that allowed the head to move like a fish and both gills and lung like a tetrapod D) scales and a tail like a fish and a simple bone arrangement in the back limb like a tetrapod | back 29 A |
front 30 Which of the following is most likely a characteristic of the earliest tetrapod fossils? A) they show evidence of internal fertilization B) they show evidence of having produced shelled eggs C) they indicate limited adaptation to life on land D) they feature the earliest indications of the appearance of jaws | back 30 C |
front 31 What is believed to be the most significant result of the evolution of the amniotic egg? A) Tetrapods are no longer tied to the water for reproduction. B) Tetrapods can now function with just lungs. C) Newborns are much less dependent on their parents. D) Embryos are protected from predators. | back 31 A |
front 32 Which structure of the amniotic egg most closely surrounds the embryo? A) the chorion B) the yolk sac C) the allantois D) the amnion | back 32 D |
front 33 The evolution of similar insulating skin coverings such as fur, hair, and feathers in mammals and birds is a result of which of the following evolutionary processes? A) shared ancestry B) convergent evolution C) homology D) evolutionary divergence | back 33 B |
front 34 Which of the following characteristics evolved independently in mammals and birds? A) amniotic eggs B) jaws C) bone D) endothermy | back 34 D |
front 35 Mammals and birds eat more often than reptiles. Which of the following traits shared by mammals and birds best explains this habit? A) endothermy B) ectothermy C) amniotic egg D) terrestrial habitat | back 35 A |
front 36 Which of these groups of organisms are amniotes? A) amphibians B) fishes C) turtles D) lungfish | back 36 C |
front 37 The respiratory system of birds is one of the most effective respiratory systems of all air-breathing organisms, due to its system of air sacs connected to the lungs. Which of the following can be inferred about the air sacs given the observation that they are neither thin nor highly vascularized? A) They must not belong to the respiratory system. B) They cannot be derived from endoderm. C) They are not efficient sites of gas exchange between air and blood. D) They cannot effectively moisturize the air before it reaches the lungs. | back 37 C |
front 38 Which of these characteristics contributed the most to vertebrate success in relatively dry environments? A) the shelled, amniotic egg B) the ability to maintain a constant body temperature C) two pairs of appendages D) a four-chambered heart | back 38 A |
front 39 Which of the following are the only extant animals that descended directly from dinosaurs? A) lizards B) crocodiles C) birds D) tuataras | back 39 C |
front 40 During chordate evolution, which of the following structures arose first? A) paired fins B) jaws C) four-chambered heart D) amniotic egg | back 40 A |
front 41 Which clade includes humans? A) diapsids B) synapsids C) cyclostomes D) archosaur | back 41 B |
front 42 The ancestors of amniotes laid eggs in water. It could be argued that embryos of amniotes still develop in water for which of the following reasons? A) the shell keeps the embryo from drying out B) the amnion encases each embryo in water C) the chorion, allantois, and yolk sac provide embryos with nutrients and waste disposal D) the amnion protect the embryo in the same way that a seed coat protects plant embryos of flowering plants | back 42 B |
front 43 Primate evolution and behavior, such as hunting skills, have been directed in part by the development of depth perception. What anatomical change made depth perception possible? A) a smaller brain B) the development of compound eyes C) location of the eyes at the front of the head D) diurnal activity | back 43 C |
front 44 What group of mammals display the following characteristics? ∙ embryos that spend more time feeding through the placenta than the mother's nipples ∙ young that feed on milk ∙ a prolonged period of maternal care after leaving the placenta? A) Eutheria B) Marsupiala C) Monotremata D) Lagomorpha | back 44 A |
front 45 Which of the following represents the strongest evidence that two of the three middle ear bones of mammals are homologous to certain reptilian jawbones? A) They are similar in size to the reptilian jawbones. B) They are similar in shape to the reptilian jawbones. C) The mammalian jaw has fewer bones than does the reptilian jaw. D) These bones can be observed to move from the developing jaw to the developing middle ear in mammalian embryos. | back 45 D |
front 46 Which of the following groups includes members that all have fully opposable thumbs? A) apes B) Homo C) anthropoids D) primates | back 46 C |
front 47 Which of the following analyses would best help to determine if a fossil represents a reptile or a mammal? A) look for the presence of milk-producing glands B) look for the mammalian characteristics of a four-chambered heart and a diaphragm C) use molecular analysis to look for the protein keratin D) examine the teeth | back 47 D |
front 48 Female birds lay their eggs, thereby facilitating flight by reducing weight. Which "strategy" seems most likely for female bats to use to achieve the same goal? A) limit litters to a single embryo B) refrain from flying throughout pregnancy (about six weeks long) C) give birth to underdeveloped young, and subsequently carry them in a pouch that has teats D) feed multiple embryos internally using placentas | back 48 A |
front 49 Which of the following characteristics is exhibited by both monotremes and marsupials? A) lack nipples B) have some embryonic development outside the uterus C) lay eggs D) are found in Australia and Africa | back 49 B |
front 50 Which of the following statements about the geographic distribution of marsupials is accurate? A) they occur only in Australia and New Guinea B) they occur on all continents except Antarctica C) they occur in Australia and the Americas D) they occur only in Africa | back 50 C |
front 51 On the back of the human skull, there is a small bump, below which is an opening where the spinal cord enters the skull. Which of the following statements provides the best evolutionary explanation for the location of the opening near the base of the skull? A) It allowed for the hominin brain to grow much larger than other primates. B) It provided greater protection for the spinal cord. C) It is associated with the change to a bipedal stance. D) This change was necessary for the increase in size from prosimian forms to anthropoid forms. | back 51 C |
front 52 Which would be the most feasible method of figuring out to which other hominin species Homo floresiensis was most closely related? A) Compare the type of prey hunted by H. floresiensis to that hunted by each of the other hominin species. B) Compare the average body size of H. floresiensis to that of each of the other hominin species. C) Compare the skeletal morphology of H. floresiensis to that of each of the other hominin species. D) Compare the estimated life span of H. floresiensis to that of each of the other hominin species. | back 52 C |
front 53 In what respect do hominins differ from all other anthropoids? A) lack of a tail B) eyes on the front of the face C) bipedal posture D) opposable thumbs | back 53 C |
front 54 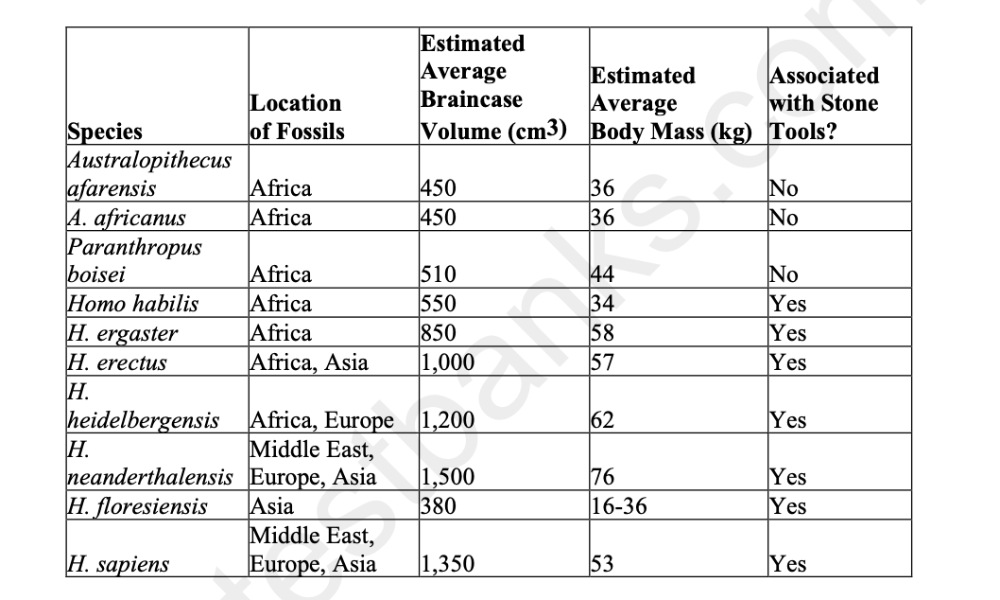 Use the following information to answer the question. Brown et al. and Morwood et al. reported in 2004 that they had found skeletal remains of a previously unknown type of hominin, now dubbed Homo floresiensis, on the Indonesian island of Flores. These hominins were small (approximately 1 m tall) with small braincases (approximately 380 cm3) as compared with other hominins. The remains of H. floresiensis were found alongside handmade stone tools and the remains of dwarf elephants that also inhabited the island, suggesting that H. floresiensis was able both to make tools and to coordinate the hunting of animals much larger than itself. H. floresiensis is estimated to have lived at the site where the remains were found from 700,000 years ago to 60,000 years ago. The table is a comparison of several characteristics of H. floresiensis to those of nine other hominin species (arranged roughly from oldest to most recent). What do these data suggest? A) A large brain is not necessarily required for toolmaking. B) Body mass and braincase volume are completely unrelated. C) Hominins first evolved in and then radiated out from Asia. D) Homo floresiensis is most closely related to Australopithecus afarensis or A. africanus. | back 54 A |
front 55 Arrange the following taxonomic terms in order from most inclusive to least inclusive. A) primates, apes, anthropoids, hominins, Homo B) primates, anthropoids, apes, hominins, Homo C) primates, anthropoids, hominins, Homo D) primates, hominins, apes, anthropoids, Homo | back 55 B |
front 56 Which of these traits is most strongly associated with the evolution of bipedalism? A) enhanced depth perception B) shortened hind limbs C) opposable big toe D) repositioning of foramen magnum | back 56 D |
front 57 Which of the following statements about human evolution is correct? A) Modern humans are the only human species to have evolved on Earth. B) Human ancestors were virtually identical to extant chimpanzees. C) Human evolution has occurred within an unbranched lineage. D) The upright posture and enlarged brain of hominins evolved separately. | back 57 D |
front 58 Which of the following claims about human evolution is most consistent with current scientific understanding? A) Humans and other apes represent divergent lines of evolution from a common ancestor. B) Humans represent the pinnacle of evolution and have escaped from being affected by natural selection. C) Humans evolved from chimpanzees. D) Humans and other apes are the result of disruptive selection in a species of chimpanzee. | back 58 A |
front 59 Which of the following characteristics occur in Homo naledi? A) large brain, feet that allowed bipedal walking, hands able to manipulate small objects B) large brain, feet that allowed occasional erect posture, hands able to manipulate small objects C) small brain, feet that allowed bipedal walking, hands able to manipulate small objects D) small brain, feet that allowed bipedal walking, hands able to swing from branch to branch | back 59 C |
front 60 The history of hominin evolution demonstrates ________. A) unrelated traits (that is, characters of skulls and hips/feet) evolve together B) unrelated traits can evolve at different rates C) the decrease in rainfall favored maintaining the ability to climb trees D) the increase in rainfall favored the ability to walk upright | back 60 B |
front 61 Vertebrates and tunicates share ________. A) jaws adapted for feeding B) a high degree of cephalization C) an endoskeleton that includes a skull D) a notochord and a dorsal, hollow nerve cord | back 61 D |
front 62 Living vertebrates can be divided into two major clades. Select the appropriate pair. A) the chordates and the tetrapods B) the urochordates and the cephalochordates C) the cyclostomes and the gnathostomes D) the marsupials and the eutherians | back 62 C |
front 63 Unlike eutherians, both monotremes and marsupials ________. A) lack nipples B) have some embryonic development outside the uterus C) lay eggs D) are found in Australia and Africa | back 63 B |
front 64 Which clade does not include humans? A) synapsids B) lobe-fins C) diapsids D) osteichthyans | back 64 C |
front 65 As hominins diverged from other primates, which of the following appeared first? A) reduced jawbones B) an enlarged brain C) the making of stone tools D) bipedal locomotion | back 65 D |
front 66 Which of the following could be considered the most recent common ancestor of living tetrapods? A) a sturdy-finned, shallow-water lobe-fin whose appendages had skeletal supports similar to those of terrestrial vertebrates B) an armored, jawed placoderm with two pairs of appendages C) an early ray-finned fish that developed bony skeletal supports in its paired fins D) a salamander that had legs supported by a bony skeleton but moved with the side-to-side bending typical of fishes | back 66 A |