Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Ch 35
front 1 1) Which of the following plant parts absorbs most of the water and minerals taken up from the soil? A) root cap B) root hairs C) taproots D) storage roots | back 1 B |
front 2 2) Which of the following modified roots has a similar function as prop roots? A) strangler roots B) buttress roots C) storage roots D) pneumatophores | back 2 B |
front 3 3) Which of the following structures is a modified horizontal shoot growing along the soil surface? A) rhizome B) tuber C) stolon D) rhizoid | back 3 C |
front 4 4) Which of the following structures cannot be formed by an axillary bud? A) stem branch B) thorn C) flower D) branch root | back 4 D |
front 5 5) Onions are monocots with certain parts adapted for storage. From which of the following plant parts is the main storage structure formed? A) ovary of flower B) herbaceous stem C) leaf sheaths D) taproot | back 5 C |
front 6 6) Which of the following biological molecules is specific to woody sclerenchyma cells? A) cellulose B) starch C) lignin D) chlorophyll | back 6 C |
front 7 7) The following question is based on the figure below In the diagram above, the dark "dots" represent axillary buds. Which diagram illustrates a compound leaf? A) I only B) II only C) III only D) both II and III | back 7 B |
front 8 Some understory plants in dense tropical rain forests have very large leaves. Which of the following is the most likely selective advantage of these leaves? A) The higher oxygen concentration on the forest floor stimulates leaf growth. B) High rates of photosynthesis from these large leaves lower carbon dioxide levels in the interior of the forest. C) Low light levels slow photosynthesis but increase respiration rates to provide energy necessary for leaf growth. D) Increased leaf surface area maximizes light absorption for photosynthesis under low light intensity. | back 8 D |
front 9 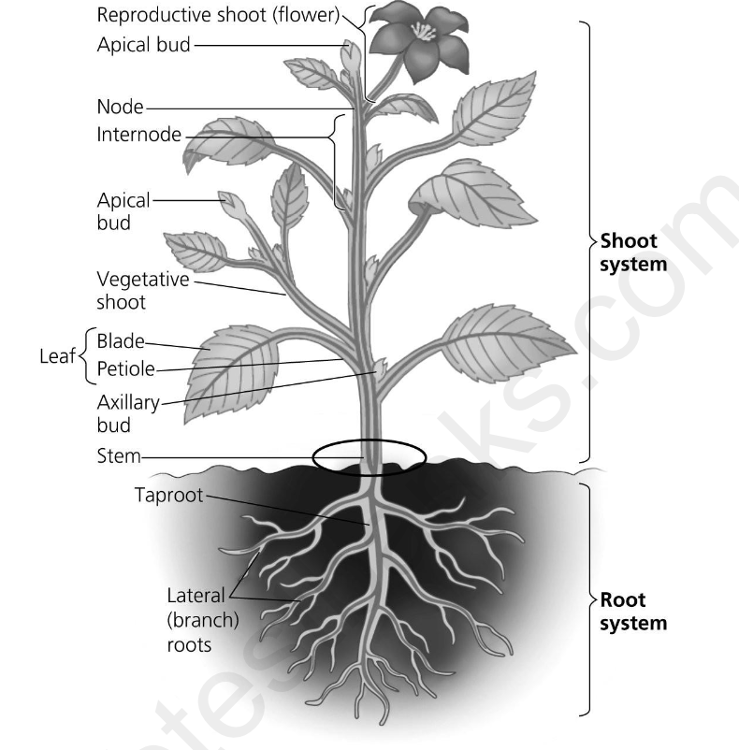 he following question is based on the figure below. Which of the following must have occurred during development in the region between the root and stem circled on this diagram of an herbaceous eudicot? A) the endodermis in the root must convert into the epidermis of the stem B) the xylem in the root must split into separate strands in the stem C) each vascular bundle of the root spreads as it moves up into the stem D) the parenchyma core of the root is continuous with the pith of the stem | back 9 B |
front 10 10) Which of the following describes an anatomical difference between roots and leaves? A) only leaves have phloem and only roots have xylem B) root cells have cell walls and leaf cells do not C) a waxy cuticle covers leaves but is absent from roots D) vascular tissue is found in roots but is absent from leaves | back 10 C |
front 11 11) Which structure is correctly paired with its tissue system? A) root hair–vascular tissue B) guard cell–vascular tissue C) companion cell–ground tissue D) tracheid–vascular tissue | back 11 D |
front 12 12) Which of the following tissues or cell types are always present in a monocot stem? A) pith in the center of the stem B) endodermis around the vascular tissue C) ground tissue beneath the epidermis D) xylem and phloem in separate vascular bundles | back 12 C |
front 13 13) Which of the following cell types retains the ability to undergo cell division? A) a meristem cell near the root tip B) a functional sieve tube element C) a tracheid D) a stem fiber | back 13 A |
front 14 14) Which of the following cell types have unevenly thickened primary walls that support young, growing parts of the plant? A) parenchyma cells B) collenchyma cells C) sclerenchyma cells D) tracheids and vessel elements | back 14 B |
front 15 15) Which of the following structures is correctly paired with its function? A) sclerenchyma–supporting cells with thick secondary walls B) ground meristem–protective coat of woody stems and roots C) guard cells–waterproof ring of cells surrounding the central stele in roots D) periderm–parenchyma cells functioning in photosynthesis in leaves | back 15 A |
front 16 16) Which of the following are water-conducting cells that are dead at functional maturity? A) parenchyma cells B) collenchyma cells C) tracheids and vessel elements D) sieve-tube elements | back 16 C |
front 17 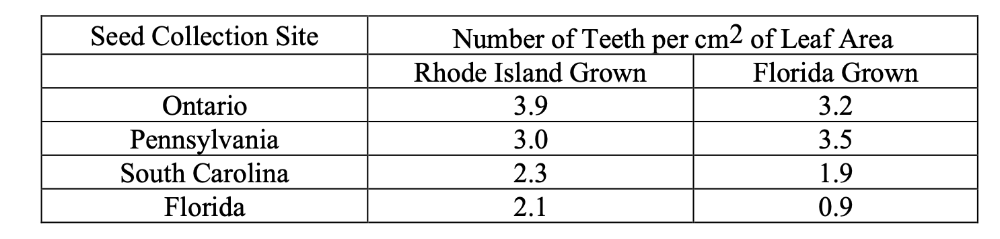 The following question is based on data from Northern Red Maples in the table below (from text box, p. 760) Which data above best illustrates phenotypic plasticity in leaf "toothiness"? A) Rhode Island Grown, Ontario Collected and Florida Grown, Florida Collected B) Florida Grown, Ontario Collected and Florida Grown, Florida Collected C) Rhode Island Grown, Ontario Collected and Rhode Island Grown, Florida Collected D) Rhode Island Grown, Florida Collected and Florida Grown, Florida Collected | back 17 D |
front 18 Which of the following cells transport sugars over long distances? A) parenchyma cells B) sclerenchyma cells C) tracheids and vessel elements D) sieve-tube elements | back 18 D |
front 19 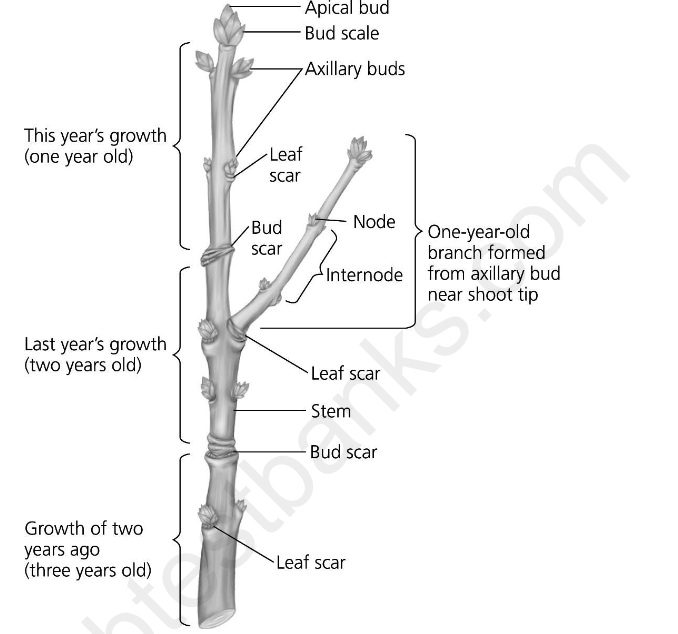 The following question is based on the diagram of three-years-old growth in a winter twig below. If you examined the cut surface at the base of this twig, how many growth rings should be present? A) one B) two C) three D) either two or three, depending on when secondary growth began. | back 19 C |
front 20 20) Which of the following accurately describes meristematic plant cells? A) All tissues throughout the plant contain meristematic cells. B) Meristematic cells are undifferentiated cells that produce new cells. C) Meristematic cells increase the surface area of dermal tissue by developing root hairs. D) Parenchyma, ground meristem, and procambium are three subdivisions of meristematic cells. | back 20 B |
front 21 21) Which of the following best describes the growth of most plant structures, except for flowers? A) perennial B) weedy C) indeterminate D) primary | back 21 C |
front 22 22) Which of the following is unique to the shoot apical meristem region? I) the region of cell division II) leaf primordia III) cells that will give rise to the protoderm, ground meristem, and procambium A) only I B) only II C) only III D) I, II, and III | back 22 B |
front 23 23) Apical meristems of dicots are at the tips of stems and the leaves have determinate growth. Apical meristems of grasses are at ground level, or slightly below, and the leaves have indeterminate growth from meristems at the base of each leaf. What does this mean when considering care of a lawn or soccer field? A) If you mow one inch above ground level, most apical meristems are removed and cut leaves will stop growing. B) If you mow one inch above ground level, most apical meristems are removed but cut leaves can keep growing. C) If you mow one inch above ground level, apical meristems can continue to produce new leaves and cut leaves can continue growing. D) Grass mowed two inches above ground level stops cut leaves from growing but new leaves are produced at a faster rate. | back 23 C |
front 24 24) In a meristematic region, the cell plate during mitosis is perpendicular to the side of the stem. In what direction will the stem grow? A) laterally in width B) vertically in height C) at a 45-degree angle from the ground D) away from the sun | back 24 B |
front 25 25) Which of the following cells or tissues arise from lateral meristem activity? A) secondary xylem B) leaves C) trichomes D) tubers | back 25 A |
front 26 26) Which of the following can be used to determine a twig's age? A) number of apical bud scar rings B) number of leaf scars C) number and arrangement of axillary buds D) length of internodes | back 26 A |
front 27 27) A plant that grows one year, without flowering, and then grows again the following year and produces flowers before it dies is described as which of the following? A) an annual B) a biennial C) a perennial D) not very fit | back 27 B |
front 28 28) Shoot elongation in a growing bud is due primarily to which of the following? A) cell division at the shoot apical meristem B) cell elongation directly below the shoot apical meristem C) cell elongation localized in each internode D) cell division at the shoot apical meristem and cell elongation directly below the shoot apical meristem | back 28 C |
front 29 29) Which of the following is the correct sequence of the zones in the primary growth of a root, moving from the root cap toward the stem? A) zone of cell division, zone of elongation, zone of differentiation B) zone of differentiation, zone of elongation, zone of cell division C) zone of elongation, zone of cell division, zone of differentiation D) zone of cell division, zone of differentiation, zone of elongation | back 29 A |
front 30 30) Which of the following best describes the driving force that pushes the root tip through the soil? A) continuous cell division in the root cap at the tip of the root B) continuous cell division just behind the root cap in the center of the apical meristem C) elongation of cells behind the root apical meristem D) continuous cell division of root cap cells | back 30 C |
front 31 31) Which of the following is true for an emerging lateral root to function? A) a root cap forms from the epidermis of the original root B) xylem of the new lateral root connects to the xylem of the original root C) the emerging lateral root must be in front of the root hairs of the original root D) the lateral root forms by secondary growth from a lateral meristem of the original root | back 31 B |
front 32 32) Which of the following root tissues gives rise to lateral roots? A) endodermis B) phloem C) epidermis D) pericycle | back 32 D |
front 33 33) As a youngster, you drive a nail in the trunk of a young tree that is 3 meters tall. The nail is about 1.5 meters from the ground. Fifteen years later, you return and discover that the tree has grown to a height of 30 meters. About how many meters above the ground is the nail? A) 0.5 B) 1.5 C) 3.0 D) 15.0 | back 33 B |
front 34 34) You find a plant unfamiliar to you and observe that it has vascular bundles scattered throughout the stem cross section. What should you conclude about the plant? A) It is an herbaceous eudicot. B) It will produce annual rings of wood. C) It is a monocot. D) It has begun secondary growth. | back 34 C |
front 35 35) What is a consequence of monocot vascular bundles not having a vascular cambium between the xylem and phloem? A) Monocots are not very efficient at conducting water and sugars. B) The stems of monocots are very thin stems. C) Monocots have no secondary growth. D) Monocots cannot produce lateral shoots. | back 35 C |
front 36 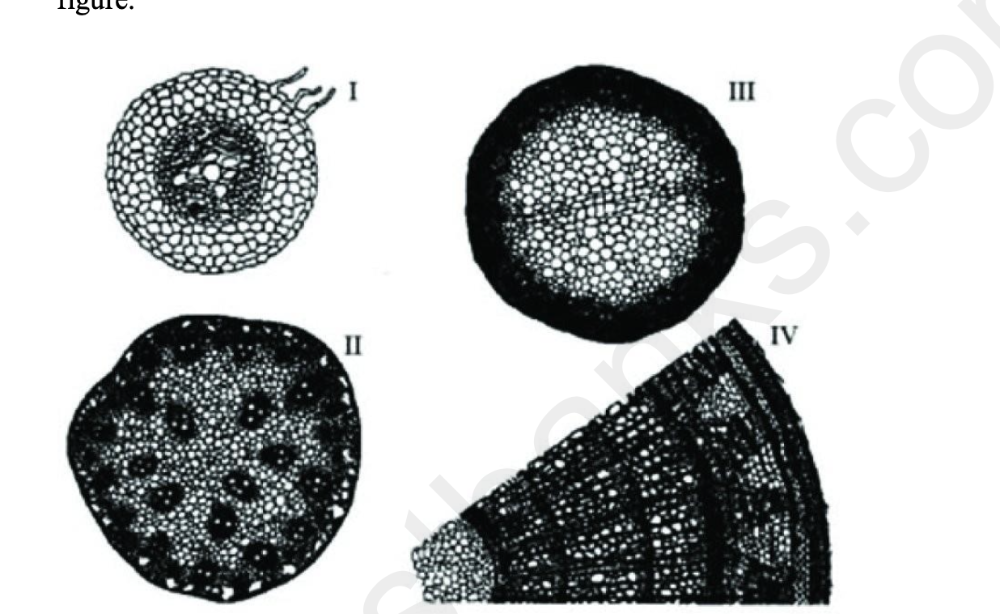 36) The following question is based on the drawings of root or stem cross sections shown in the figure. Refer to the figure. A monocot stem is represented by which of the following? A) I only B) II only C) III only D) IV only | back 36 B |
front 37 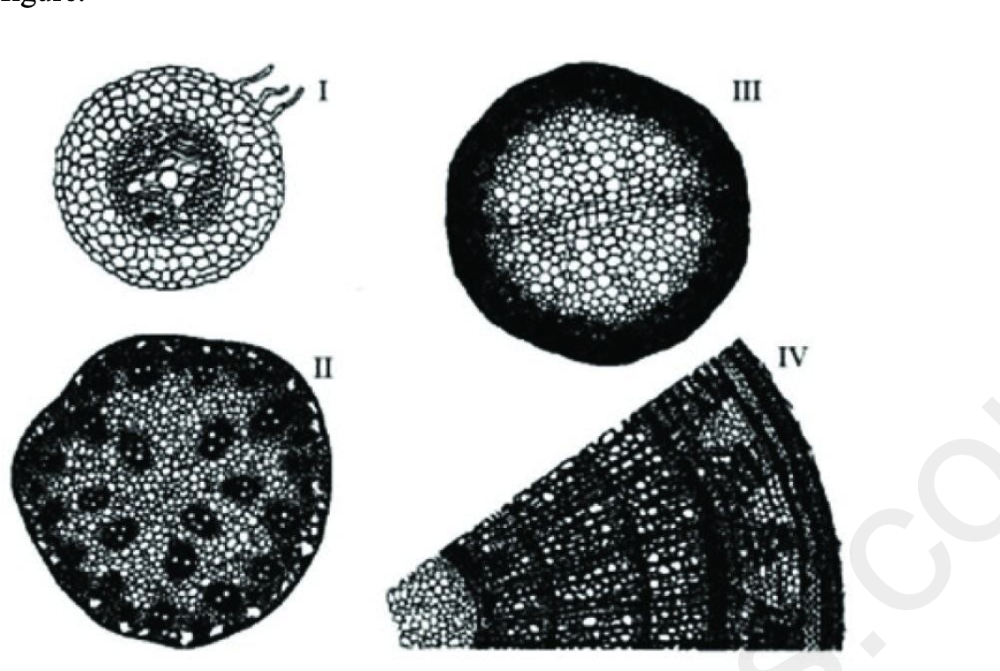 The following question is based on the drawings of root or stem cross sections shown in the figure. Refer to the figure. A woody eudicot is represented by which of the following? A) II only B) III only C) IV only D) I and III | back 37 C |
front 38 The following question is based on the drawings of root or stem cross sections shown in the figure. Refer to the figure. Which of the following represents a plant at least three years old? A) I only B) II only C) III only D) IV only | back 38 D |
front 39 39) A student examining leaf cross sections under a microscope finds many loosely packed cells with relatively thin cell walls. The cells have numerous chloroplasts. What type of cells are they? A) parenchyma B) endodermis C) collenchyma D) sclerenchyma | back 39 A |
front 40 40) The veins of leaves are best described as which of the following? I) composed of xylem and phloem II) continuous, with vascular bundles in the stem III) finely branched to be in close contact with photosynthesizing cells A) only I B) only II C) only III D) I, II, and III | back 40 D |
front 41 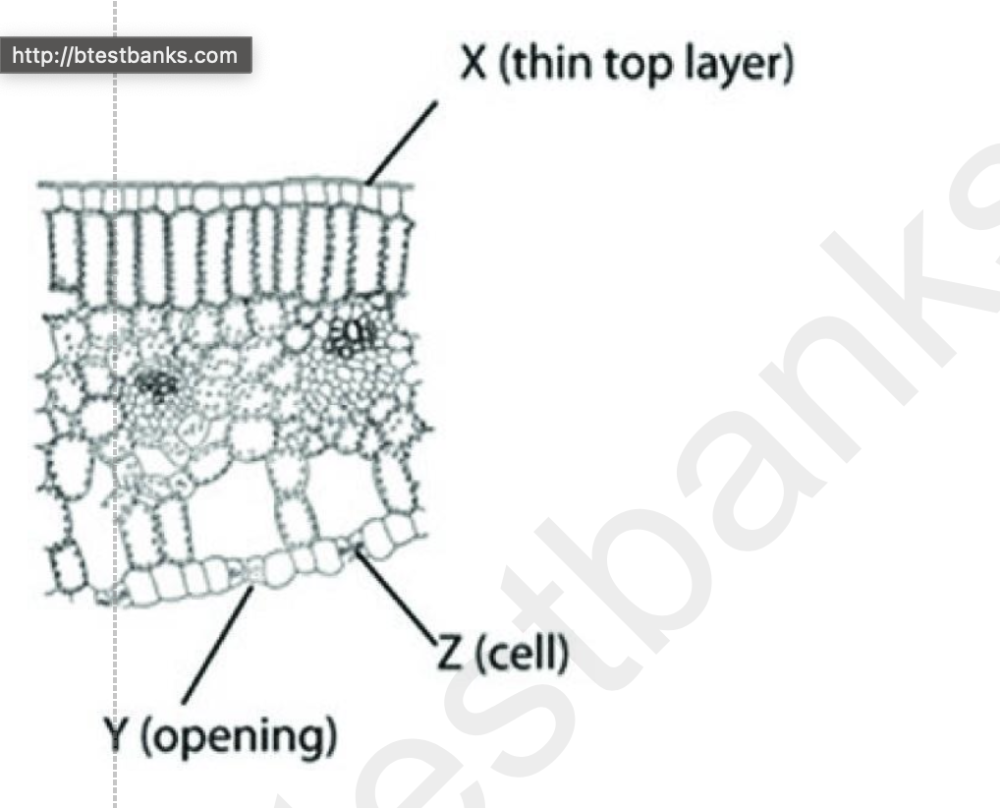 The following diagram is of a cross section of a plant leaf. Use the diagram to answer the question. Which of the following is the main function associated with structure X? A) absorption of carbon dioxide B) retention of water C) collection of light D) release of carbon dioxide | back 41 B |
front 42  The following diagram is of a cross section of a plant leaf. Use the diagram to answer the question. Which of the following is the main function associated with structure Y? A) absorption of carbon dioxide B) absorption of water C) collection of light D) release of carbon dioxide | back 42 A |
front 43 Increasing the number of stomata per unit surface area of a leaf when atmospheric carbon dioxide levels decline is most analogous to which of the following human adaptations? A) breathing faster as atmospheric carbon dioxide levels increase B) putting more red blood cells into circulation when atmospheric oxygen levels decline C) removing red blood cells from circulation when atmospheric oxygen levels increase D) increasing the volume of its lungs when atmospheric carbon dioxide levels increase | back 43 B |
front 44 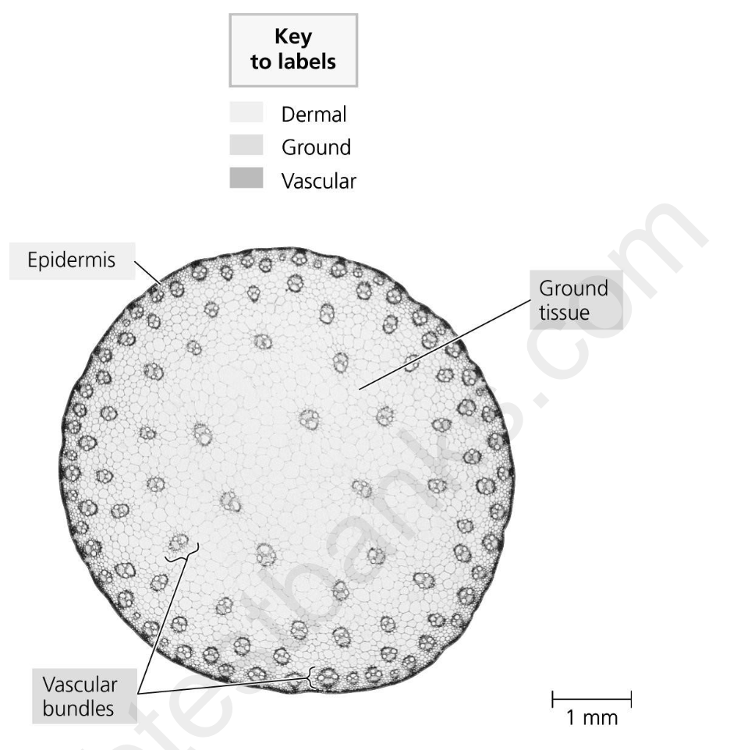 The following question is based on this cross section of a monocot stem. Which of the following is NOT a pattern of vascular bundles evident in this stem? A) smaller vascular bundles toward the outside, larger bundles toward the center B) xylem toward the outside of each bundle, phloem toward the center C) vascular bundles more densely arranged toward the outside, less dense towards the center D) vascular bundles arranged in concentric rings | back 44 B |
front 45 45) Which of the following accurately describes the structure of a leaf? A) stomata can occur on both sides of a leaf B) in a eudicot, spongy mesophyll is on the same side of the leaf as xylem in the vein C) the main veins of leaves have both xylem and phloem, but smaller veins have only xylem or phloem D) palisade mesophyll occurs only in monocot leaves | back 45 A |
front 46 46) Which of the following is a common feature of secondary xylem and cork cells? A) they are both formed from the vascular cambium B) they both form on the outside of secondary phloem C) they are both formed by primary meristems D) they are both composed of dead cells at maturity | back 46 D |
front 47 47) Which of the following are produced by lateral meristems? A) dermal and ground tissues B) buds and branches C) pith and cortex D) wood and cork | back 47 D |
front 48 48) Where is primary growth occurring in an old tree? A) closest to ground level at the base of the tree B) in young branches where leaves are forming C) where the vascular cambium and cork cambium are located D) Nowhere; trees more than a year old have only secondary growth. | back 48 B |
front 49 49) What tissue makes up most of the wood of a tree? A) primary xylem B) secondary xylem C) secondary phloem D) vascular cambium | back 49 B |
front 50 50) A plant has the following characteristics: a taproot system, several growth rings evident in a cross section of the stem, and a layer of bark around the outside. Which of the following best describes the plant? A) herbaceous eudicot B) woody eudicot C) woody monocot D) herbaceous monocot | back 50 B |
front 51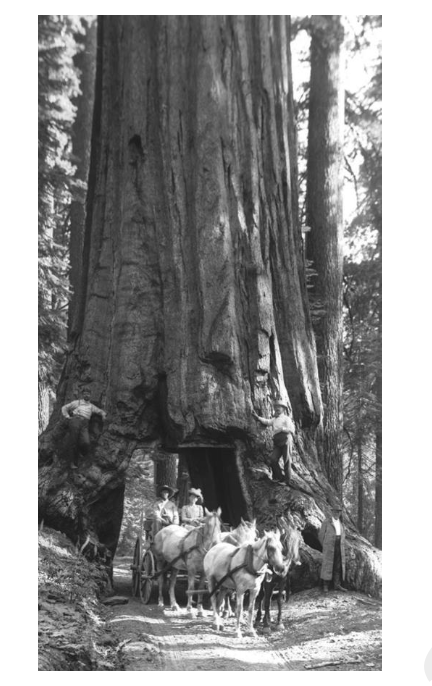  he following question is based on the image below. As this wagon passed from the middle of the Sequoia tree to the outside, what would be the order of tissues it passed through? A) the annual rings, new xylem, vascular cambium, phloem, and bark B) the secondary xylem, cork cambium, phloem, and periderm C) the vascular cambium, oldest xylem, newest xylem, and primary phloem D) the secondary xylem, primary xylem, secondary phloem, primary phloem and vascular cambium | back 51 A |
front 52 Additional vascular tissue produced as secondary growth in a root originates from which cells? A) vascular cambium B) apical meristem C) endodermis D) xylem | back 52 A |
front 53 The bark of a tree trunk includes which of the following tissues? A) heartwood and sapwood B) heartwood and phloem C) primary and secondary phloem D) secondary phloem and layers of periderm | back 53 D |
front 54 The image below is a cross section through a young root tip with a layer of root cap cells surrounding the developing epidermis and interior tissues. The darker epidermal cells are stained to express the homeotic gene GLABRA-2. Which of the following best predicts what will be the appearance of this part of the mature root? A) The epidermis will lack root hairs. B) Only the stained epidermal cells will develop root hairs. C) Only the unstained cells will develop root hairs. D) Every epidermal cell will develop a root hair. | back 54 C |
front 55 55) Many ornamental roses have sepals and multiple showy petals, but lack reproductive parts. Assuming that rose development follows the ABC hypothesis, which gene is most likely to be suppressed? A) the A gene B) the B gene C) the C gene D) both the B and C genes | back 55 C |
front 56 56) When is the polarity of a plant established? A) when the cotyledons form at the shoot end of the embryo B) when the shoot-root axis is established in the embryo C) when the primary root breaks through the seed coat D) when the shoot first breaks through the soil into the light as the seed germinates | back 56 B |
front 57 57) Growth and development of plant parts involves which of the following processes? I) cell division to produce new cells II) enlargement and elongation of cells III) specialization of cells into tissues A) only I B) only II C) only III D) I, II, and III | back 57 D |
front 58 58) An initial cell in a plant apical meristem has a cuboidal shape. Predict the orientation of microtubules beneath the cell membrane if that cell will differentiate into procambium and ultimately a xylem vessel. A) Microtubules are arranged randomly around the cell. B) Parallel microtubules are oriented in the direction the cell will eventually expand. C) Rings of microtubules are oriented in the plane the cell will eventually expand. D) Rings of microtubules are oriented at right angles to the direction the cell will eventually expand. | back 58 D |
front 59 1) Most of the growth of a plant body is the result of ________. A) cell differentiation B) morphogenesis C) cell division D) cell elongation | back 59 D |
front 60 2) The innermost layer of the root cortex is the ________. A) core B) pericycle C) endodermis D) pith | back 60 C |
front 61 3) Heartwood and sapwood consist of ________. A) bark B) periderm C) secondary xylem D) secondary phloem | back 61 C |
front 62 4) The phase change of an apical meristem from the juvenile to the mature vegetative phase is often revealed by ________. A) a change in the shape of the leaves produced B) the initiation of secondary growth C) the formation of lateral roots D) the activation of flower-inducing genes | back 62 A |
front 63 5) The vascular cambium gives rise to ________. A) all xylem B) all phloem C) primary xylem and phloem D) secondary xylem and phloem | back 63 D |
front 64 6) The root pericycle is the site where ________. A) secondary growth originates B) root hairs originate C) lateral roots originate D) the endodermis originates | back 64 C |
front 65 7) Root apical meristems are found ________. A) only in taproots B) only in lateral roots C) only in adventitious roots D) in all roots | back 65 D |
front 66 8) Suppose a flower had normal expression of genes A and C and expression of gene B in all four whorls. Based on the ABC hypothesis, what would be the structure of that flower, starting at the outermost whorl? A) carpel-petal-petal-carpel B) petal-petal-stamen-stamen C) sepal-carpel-carpel-sepal D) sepal-sepal-carpel-carpel | back 66 B |
front 67 9) Which of the following arise(s), directly or indirectly, from meristematic activity? A) secondary xylem B) leaves C) dermal tissue D) all of the above | back 67 D |
front 68 10) A strawberry plant mutant that fails to make stolons would suffer from ________. A) too little mineral absorption B) a tendency to topple over C) too little water absorption D) a reduction in asexual reproduction | back 68 D |