Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 18: Application of Genomics to Medicine and Personalized Health Care
front 1 Pharmacogenomics | back 1 Study of differences between individuals in how they respond to drugs due to allelic variation in genes affecting drug metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity |
front 2 Pharmacokinetics Variations | back 2 the body absorbs, transports, metabolizes, or excretes or their metabolites |
front 3 Pharmacodynamics Variations | back 3 differences in the way the body responds to a drug |
front 4 Cytochrome P-450 | back 4 CYP450 has 56 functional enzymes, different alleles of genes → in absent, decreased, or increased enzyme activity → normal, poor, or ultrafast metabolism |
front 5 ADRs | back 5 adverse drug reactions; one of the top 5 leading causes of death/illness. results in over 100k deaths |
front 6 Pharmacogenetics | back 6 the study of genetic influences on an individual’s response to drugs |
front 7 Are ADRs (Adverse Drug Reactions) preventable? | back 7 Yes; at leat 60% (as of 2008) |
front 8 Three types of metabolizers | back 8 Poor Normal (Extensive) Ultrafast |
front 9 Poor metabolizer | back 9 accumulates drug to toxic levels; overdosing of medication |
front 10 Normal (extensive) metabolizer | back 10 reaches steady-state levels within the therapeutic range (no change) |
front 11 Ultrafast metabolizer | back 11 fails to maintain serum levels within the therapeutic range; underdosing of medication |
front 12 What test can identify the extensive and poor metabolizer phenotype? | back 12 Urinary Metabolic Ratio |
front 13 What is a urinary metabolic ratio? | back 13 a simple test that, after the administration of a probe drug, can identify the extensive metabolizer and the poor metabolizer phenotype |
front 14 How can genetic alterations impact drug metabolism? | back 14 mutations, deletions, or insertions → loss or gain of function in the biochemical systems that metabolize the drug EX) Gene deletion → decrease in enzyme activity → higher concentration doses and/or during a greater length of time (top) → side effects. Gene duplications and gain-of-function polymorphisms → increase the enzymatic activity → lower active drug concentration ➔ no effect. |
front 15 Metabolizer Abbreviations: PM, IM, EM, UM | back 15 Poor Metabolizer, Intermediate Metabolizer (normal), Extensive Metabolizer (normal), Ultrarapid Metabolizer |
front 16 CYP2D6 | back 16 Acts on 25% of all prescription drugs;
|
front 17 Goals of Pharmacogenetics | back 17
|
front 18 Overall Advantage of Pharmacogenetics and Genetics Approach | back 18 Personal genomics is as the means to move from one-size-fits-all to a more individualized approach (precision medicine) to healthcare |
front 19 Advantages of Pharmacogenetics and Genetics Approach | back 19
|
front 20 Gaps between Knowledge and Clinical Applications | back 20 Gaps: limitations on genetic test use, implementation of new testing programs, appropriately interpreting genomic information, educating health care providers Introduction of personal genomics into clinical practice Clinicians: lack of knowledge and self-confidence to make recommendations based on genomics and pharmacogenetic test results (McCullough et al., 2011) |
front 21 Solutions | back 21 Education: at least a 4-8 hr pharmacogenomics course as part of the
education curriculum for medical students, Translational research: the more clinical validity, the more evidence to provide a test with a clear clinical purpose, therefore improve clinical care |
front 22 Genetic Epidemiology | back 22 how genotypes and environmental factors interact to increase or decrease susceptibility to disease |
front 23 Relative Risk Ratio (RRR) | back 23 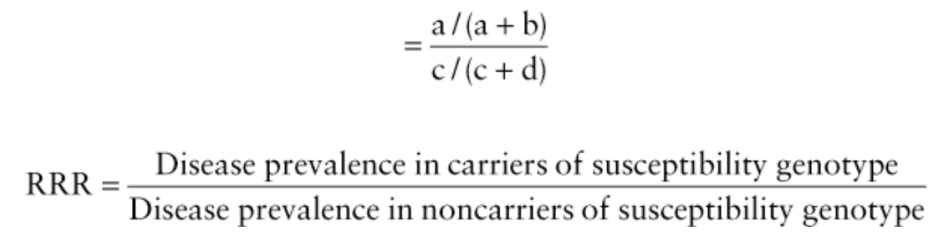 [a/ (a + b)] / [c/(c + d)] = RRR [(affected + present) / total] / [(affected + absent) / total] = RRR |
front 24 Mapping Human Disease Genes by | back 24
|
front 25 Odds Ratio (OR) | back 25 calculates association between disease and genotype |
front 26 Odds Ratio Equation | back 26 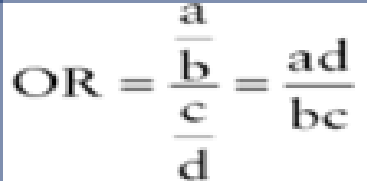 not rlly necessary to know |
front 27 Relative Ratio (RR) | back 27 for cross-sectional or cohort study |
front 28 the further RR or OR diverges from 1... | back 28 the greater is the effect of the genetic variant on the association |
front 29 OR vs RR | back 29 OR is for a case-control study; RR is for a cross-section or cohort study |