Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
microbio lab
front 1 Why don't you make any transfers over your books and paper? | back 1 You may inadvertently contaminate them |
front 2 What is a medium that contains living microbes? | back 2 A culture |
front 3 What do you need to do if you don't understand the instructions? | back 3 Ask the professor I am assuming |
front 4 What do you use to obtain separated microcolonies? | back 4 Streak plate method |
front 5 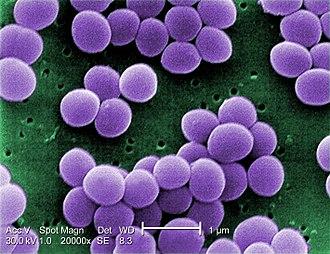 What can you see? | back 5 Gram-positive S.aureus |
front 6 What kind of method is better when you have diluted samples? | back 6 Serial dilution method |
front 7 What are the hanging drop steps in order? | back 7 -Place a small drop of bacterial culture on a coverslip, -Seal the coverslip with petroleum jelly around the edge of a concave slide -Then invert the slide with the droplet hanging in the depression, and observe under a microscope |
front 8 How should you not handle glassware? | back 8 Carry glassware by its neck or side, use one hand to carry glassware, stand or walk on broken glass, put broken glass into a regular waste basket, etc. |
front 9 In what type of bacteria can catalase be found? | back 9 Aerobic bacteria |
front 10 What are the chemicals that develop color as they oxidize? | back 10 Tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine (TMPD) |
front 11 What kind of experiments can you do in the laboratory? | back 11 this is self explanatory |
front 12 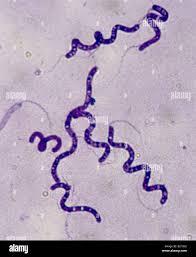 What can you see? | back 12 Gram-positive spirillum |
front 13 What enzyme transforms hydrogen peroxide into water and gaseous oxygen? | back 13 Catalase |
front 14 What kind of method uses 3 streaks? | back 14 T-streak method |
front 15 What is tolerated in the laboratory? | back 15 Self explanatory |
front 16 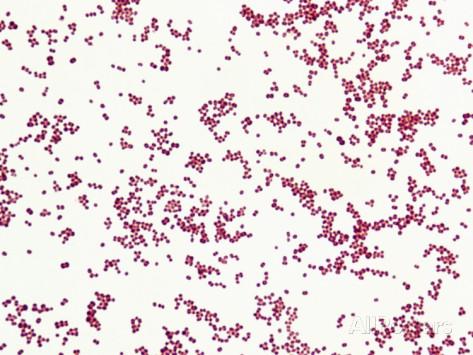 what can you see? | back 16 Gram-negative cocci |
front 17 What is it called when you have a culture with two or more species? | back 17 Mixed culture |
front 18 Which characteristic indicates that you prepare all the materials you need before starting the experiment and put it following the exercise procedure steps? | back 18 Being prepared? |
front 19 What is a substance designed to reduce the number of pathogens on a surface or in liquids? | back 19 Chemical germicides |
front 20  What is this? (in OF) | back 20 control |
front 21  What is this? (in OF) | back 21 Fermentation, E.coli |
front 22  What is this? (in OF) | back 22 control |
front 23 In what type of bacteria can't catalase be found? | back 23 Obligate anaerobic bacteria |
front 24 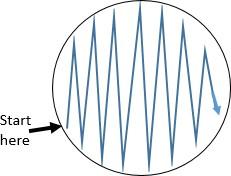 What method is this? | back 24 Zig-zag streak |
front 25 In the oxidase reaction, what is the enzyme that changes the color? | back 25 Cytochrome oxidase |
front 26 What is a substance designed to reduce the number of pathogens in living tissue? | back 26 Antiseptics |
front 27 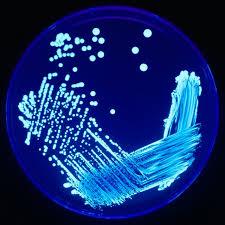 What method is this? | back 27 Quadrant streak |
front 28 If you carry a microscope, what should you not do? | back 28 Do not grasp it by the stage, eyepieces, objective lenses, or other small parts. Always hold it by the arm and base with both hands for proper support. |
front 29 What kind of method uses 4 streaks? | back 29 Quadrant streak |
front 30 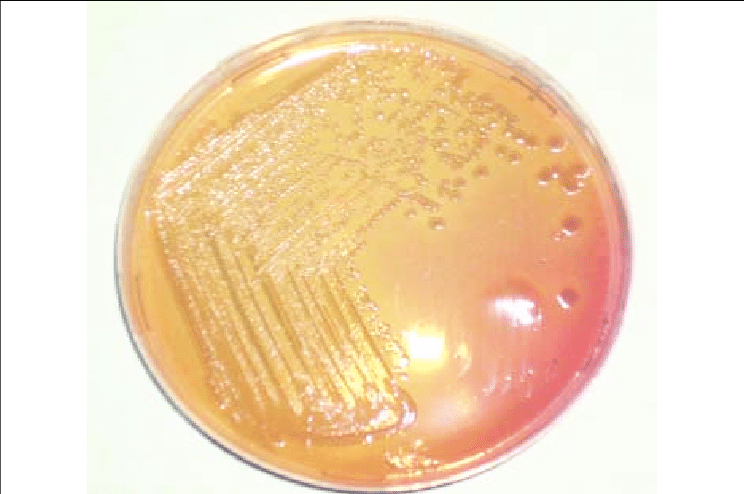 What is this? (in MacConkey) | back 30 Non-lactose fermenting colonies |
front 31 What is the shape of your stain sample? | back 31 How to do a simple stain: 1. Sterilize inoculating loop 2. Obtain your sample and spread it on the slide 3. Allow the sample to air dry for 1 min 4. Fix the sample to the slide (pass over the flame) 5. Flood sample with simple stain (crystal violet, safranin, methylene blue) 6. Let the stain sit for 1 min 7. Rinse with DDH2O 8. Place the coverslip onto the slide 9. Look under the microscope |
front 32 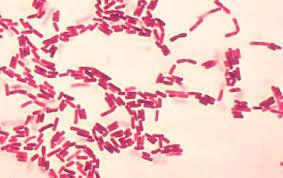 What can you see? | back 32 Gram-negative rods |
front 33 What word do we use for something without contamination? | back 33 Uncontaminated |
front 34 What is a substance designed to reduce the number of pathogens on a surface? | back 34 Disinfectants |
front 35 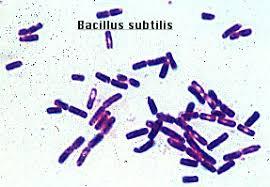 What can you see? | back 35 Gram-positive rods |
front 36 What can you do in the laboratory? | back 36 Self-explanatory |