Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
EXAM 2 BICH: Regulation of PDHC and TCA
front 1 ____undergo pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (reversible phosphorylation II) | back 1 Mammals |
front 2 Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase is allosterically | back 2 -inactivated by pyruvate -activated by NADH, Acetyl CoA |
front 3 The serine residue of E1-PDH phosphorylated blocks | back 3 decarboxylation of pyruvate and halts formation of acetyl-CoA |
front 4 In regulation of pyruvate DH reaction, ______inactivates and _____activates | back 4 -phosphorylation -dephosphorylation |
front 5 The reactivation of pyruvate dehydrogenase requires_____ in reversible____ | back 5 -pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase - phosphorylation II |
front 6 -Allosterically activated by Ca2+(sends strong signal which causes muscle contractions) - Hydrolyzes the phosphorylated serine in E1 - Remains associated as long as NADH/NAD+ and acetyl-CoA ratios are low - High concentrations of NADH or Acetyl-coA inactivate the phosphatase and cause it to dissociate from the complex | back 6 Pyruvate dehydrogenase |
front 7 The cascade of reactions stimulated by insulin binding to its receptors which activates pyruvate DH phosphatase which in turn activates pyruvate DH | back 7 Hormonal control |
front 8 When phosphatase is active, the serine of E1 is phosphorylated and converts | back 8 pyruvate to acetyl coA |
front 9 When phosphatase is inactive, the Pi on Ser of E1 does not allow for pyruvate to | back 9 convert to acetyl CoA |
front 10 Pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase turns on | back 10 + Ca2+ + Insulin |
front 11 Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase turns on ____ and _____, and turns off ___ and ____. | back 11 - Acetyl-CoA and NADH -Ca2+ and ADP |
front 12 The 3 reactions that are regulated in the TCA Cycle | back 12 -citrate synthase - isocitrate dehydrogenase -a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase |
front 13 -ATP, NADH, and succinyl-CoA inhibit -Low energy | back 13 citrate synthase |
front 14 -ATP inhibits, ADP and NAD+ activate | back 14 Isocitrate dehydrogenase |
front 15 -NADH and succinyl-CoA inhibit, AMP activate -High energy signal | back 15 a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase |
front 16 In the TCA cycle, NADH inhibits in: | back 16 PDHC, citrate synthase, a-KGDHC, Isocitrate DH |
front 17 In the TCA cycle, Acetyl-CoA inhibits: | back 17 PDHC |
front 18 In TCA cycle, citrate inhibits: | back 18 citrate synthase, PFK1 |
front 19 In TCA cycle, succinyl CoA inhibits: | back 19 citrate synthase, a-KGDHC |
front 20 In TCA cycle, ATP inhibits/ADP activates: | back 20 isocitrate DH |
front 21 In the TCA cycle, Ca2+ activates: | back 21 Isocitrate DH, PDHC, and a-KGDHC |
front 22 Calcium signals____ ______ and thus production of ATP for fuel | back 22 - muscle contraction |
front 23 PDHC is regulated by: | back 23 -Product inhibition- NADH and Acetyl-CoA -Covalent modification-(phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of E1) |
front 24 The proportional rate to oxygen consumption, NADH reoxidation, and ATP productions are | back 24 tightly coupled |
front 25 What do we see due to the TCA cycle? | back 25 a connection between sugar metabolism and now- fatty acids, steroids, amino acids, nucleotides and prosthetic group |
front 26 The TCA cycle has no need for | back 26 -Amino acids , cholesterol, fatty acids, and glucose |
front 27 Can all 20 common amino acids be made from metabolites derived from the TCA cycle | back 27 YES |
front 28 a-ketoglutarate can make | back 28 purine nucleotides, Glutamate, Arg, and Pro |
front 29 Succinyl CoA can be used to make | back 29 porphyrins (heme hb) |
front 30 Fumarate and oxaloacetate can be used to make several | back 30 amino acids and pyrimidine nucleotides |
front 31 These enzymes catalyze reactions that replenish TCA cycle intermediates | back 31 Anaplerotic reactions |
front 32 What are the 3 filling up reactions in the TCA Cycle? | back 32 -PEP carboxylase - Pyruvate carboxylase - Malic enzyme |
front 33 How does PEP carboxylase aid in the replenishment of intermediates in TCA cycle? | back 33 converts PEP to oxaloacetate |
front 34 How does pyruvate carboxylase aid in the replenishment of intermediates in TCA cycle? | back 34 converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate |
front 35 How does malic enzyme aid in the replenishment of intermediates in TCA cycle? | back 35 coverts pyruvate into malate |
front 36 The ___ is impermeable to almost everything and has transporters | back 36 Inner mitochondrial membrane |
front 37 Pyruvate carboxylase occurs only in the | back 37 mitochondria |
front 38 Because oxaloacetate cannot be transported across the mitochondrial membrane, it is reduced | back 38 to malate |
front 39 Has 2 routes: 1. Aspartate aminotransferase: doesn't require NAD/NADH 2. Malate dehydrogenase: required NAD/NADH thus reducing equivalents can be transported across the IMM | back 39 Malate-Aspartate shuttle |
front 40 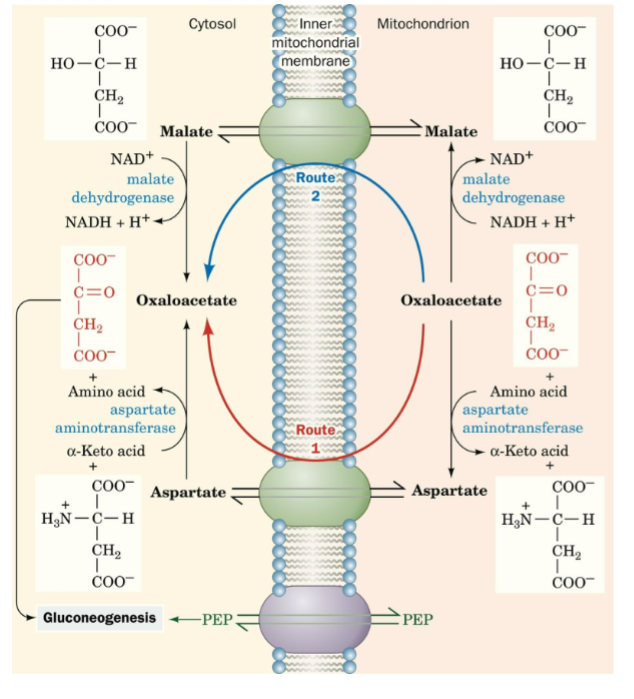 What shuttle is this? | back 40 Malate-Aspartate shuttle |
front 41 What shuttle is this? | back 41 Glcerophosphate shuttle |
front 42 -Electrons from NADH are transferred to FAD via a reaction catalyzed by 3-phosphoglycerol dehydrogenase 1. Ketone converted to OH in reduction as NADH is oxidized 2. OH converted back to ketone as FAD is reduced to FADH2 3. FADH2 part of flavoprotein dehydrogenase that transport 2e to the ETC | back 42 Glycerophosphate shuttle |
front 43 The ____ ______ offers a solution for plants, some bacteria, and algae. | back 43 glyoxylate cycle |
front 44 Since plants can't accomplish efficient photosynthesis, they rely on | back 44 acetate as a carbon source |
front 45 Net-synthesis of carbohydrates and other intermediates from acetate is not possible with TCA cycle | back 45 Acetate based growth |
front 46 What are the short circuiting enzymes? | back 46 Isocitrate lyase and malate synthase |
front 47 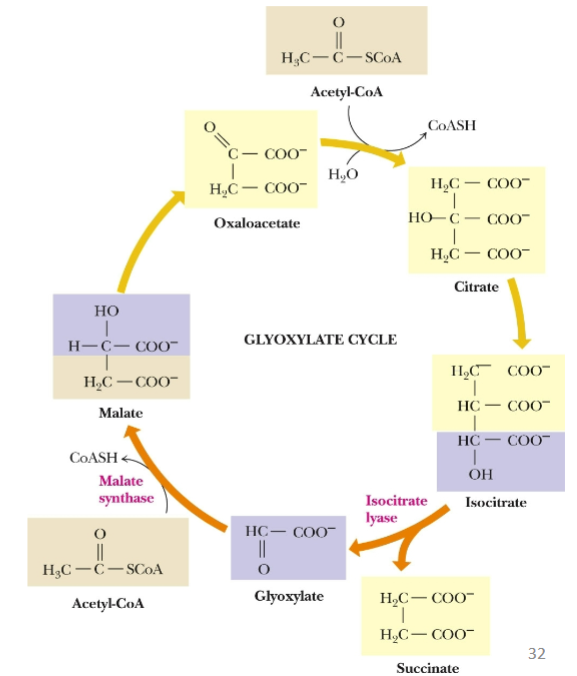 Understand cycle and what is this cycle? | back 47 Glyoxylate cycle |
front 48 Excess glucose and acetyl-CoA can easily be converted | back 48 into fat |
front 49 Excess acetyl-CoA and most fatty acids can not support | back 49 net glucose synthesis |
front 50 Plants and some microbes can convert _______ but not humans | back 50 acetyl CoA-> gluc |