Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Biology ch. 26, 27, 31, 35, 40 Exam Study
front 1 QUIZ 1: Chapters 26, 27, and 35 | back 1 QUIZ 1: Chapters 26, 27, and 35 (back of card) |
front 2 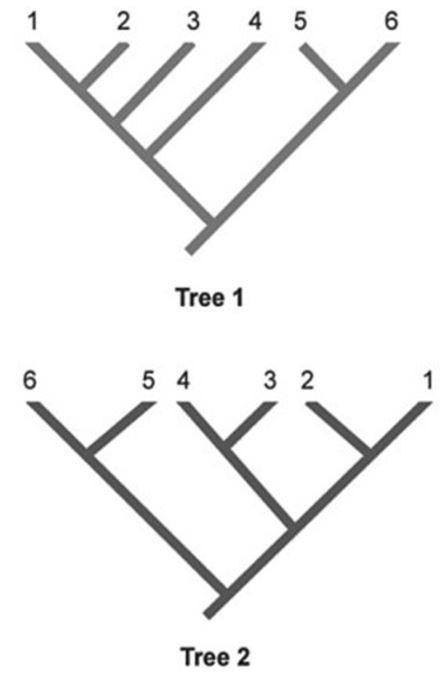 In the phylogenetic trees shown, each number represents a unique species of organisms. Which two species are represented as sister species in Tree 2 but are not represented as sister species in Tree 1? | back 2 3 and 4 |
front 3 If organisms 1, 2, and 3 belong to the same class but to different orders and if organisms 3, 4, and 5 belong to the same order but to different families, which of the following pairs of organisms would be expected to show the greatest degree of morphological homology? | back 3 4 and 5 |
front 4 The term convergent evolution is most applicable to which of the following characteristics? The presence of an opposable thumb in
humans and chimpanzees. | back 4 The presence of an opposable thumb in humans and chimpanzees. |
front 5 Which of the following pairs is the best example of homologous structures? Eyelessness in the Australian mole and
eyelessness in the North American mole. | back 5 Bones in the bat wing and bones in the human forelimb. |
front 6 Some molecular data place the giant panda in the bear family (Ursidae) but place the lesser panda in the raccoon family (Procyonidae). If the molecular data best reflect the evolutionary history of these two groups, then the morphological similarities of these two species is most likely due to which of the following processes? | back 6 Possession of analogous (convergent) traits. |
front 7 Which of the following information would be most useful in creating a phylogenetic tree of a taxon? Morphological data from fossil and
living species. | back 7 Morphological data from fossil and living species. |
front 8 Your professor wants you to construct a phylogenetic tree of a type of plant called orchids. She gives you tissue from seven orchid species and one lily plant. What is the most likely reason she gave you the lily? | back 8 To serve as an outgroup. |
front 9 Which of the following statements best describes the rationale for applying the principle of maximum parsimony in constructing phylogenetic trees? Parsimony allows the researcher to
"root" the tree. | back 9 For trees based on morphology, the most parsimonious tree requires the fewest evolutionary events. |
front 10 Birds and mammals have four limbs. Which of the following statements describes this trait? The trait is a shared ancestral
character. | back 10 The trait is a shared ancestral character. |
front 11 The lakes of northern Minnesota are home to many similar species of damselflies of the genus Enallagma. These species have apparently undergone speciation from ancestral stock since the last glacial retreat about 10 thousand years ago. Sequencing which of the following nucleic acids or proteins would probably be most useful in sorting out evolutionary relationships among these closely related species? Conserved regions of nuclear DNA. | back 11 Mitochondrial DNA. |
front 12 Jams, jellies, preserves, honey, and other foods with high sugar content hardly ever become contaminated by bacteria, even when the food containers are left open at room temperature. Which of the following statements best explains the inability of bacteria to survive in such an environment? They undergo death as a result of water
loss from the cell. | back 12 They undergo death as a result of water loss from the cell. |
front 13 Which of the following statements about flagella provides the best support for the claim that the flagella from eukaryotes and bacteria evolved independently? The flagella of both eukaryotes and
bacteria are made of the same protein. | back 13 The protein structure and the mechanism of movement in eukaryotes flagella are different from those of bacteria flagella. |
front 14 Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic that targets prokaryotic ribosomes, but not eukaryotic ribosomes. Based on an understanding of eukaryotic origins, which of these questions might be a target for research on chloramphenicol from this observation? Can chloramphenicol also be used to
control human diseases that are caused by archaeans? | back 14 If chloramphenicol inhibits prokaryotic ribosomes, should it not also inhibit mitochondrial ribosomes? |
front 15 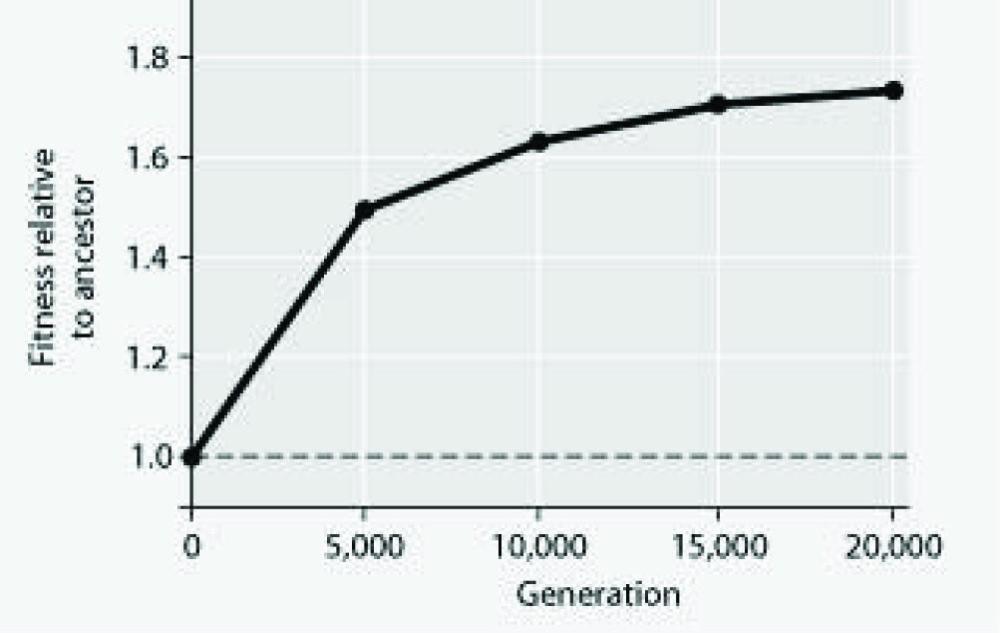 In an eight-year experiment, a population of E. coli, begun from a single cell, was grown in low-glucose conditions. The culture was transferred to fresh growth medium every 24 hours. Periodically, samples were removed from each population and the ability to survive in low-glucose conditions was compared with the original (ancestral) E. coli population. The cells in the cell line grown in low-glucose conditions showed the effects of which of the following processes? Gene flow and genetic
drift. | back 15 Natural selection and mutation. |
front 16 Which of the following statements correctly describes F- cells and F+ cells? Both types of cells can donate F
plasmids to other cells. | back 16 F+ cells function as DNA donors during conjugation and F- cells function as DNA recipients during conjugation. |
front 17 A bacterium has the following characteristics: Which of the following statements about the bacteria is most probably accurate? | back 17 The bacterium is unable donate DNA through conjugation with another cell. |
front 18 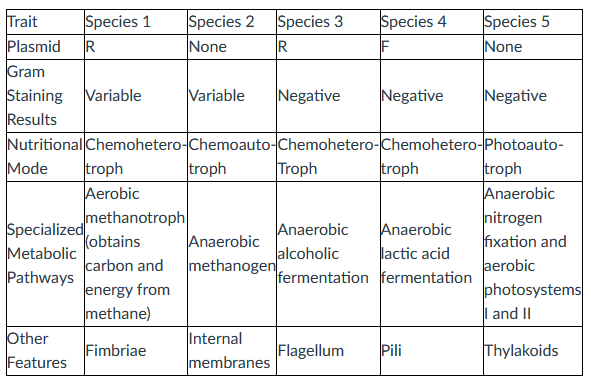 Species 4 is pathogenic if it gains access to the human intestine. Which other species, if it coinhabited a human intestine along with species 4, is most likely to become a recombinant species that is both pathogenic and resistant to some antibiotics? | back 18 Species 3. |
front 19 Which of the following processes leads to genetic recombination by the introduction of viral DNA into a bacterium? Horizontal gene transfer. | back 19 Transduction. |
front 20 Which of the following statements correctly describes both phototrophs and chemotrophs? Both are also autotrophs. | back 20 Chemotrophs obtain energy from chemicals and phototrophs obtain energy from light. |
front 21 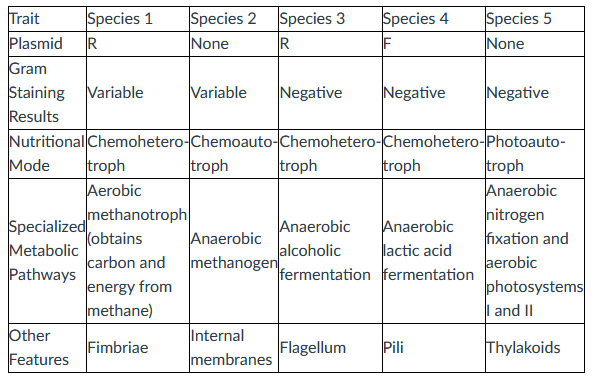 Which species is most likely to be found in sewage treatment plants and in the guts of cattle? | back 21 Species 2. |
front 22 Which of the following plant parts absorbs most of the water and minerals taken up from the soil? Root cap. | back 22 Root hairs. |
front 23 Which of the following structures is a modified horizontal shoot growing along the soil surface? Rhizome | back 23 Stolon |
front 24 Which of the following biological molecules is specific to woody sclerenchyma cells? Cellulose. | back 24 Lignin. |
front 25 Some understory plants in dense tropical rain forests have very large leaves. Which of the following is the most likely selective advantage of these leaves? The higher oxygen concentration on the
forest floor stimulates leaf growth. | back 25 Increased leaf surface area maximizes light absorption for photosynthesis under low light intensity. |
front 26 Which of the following describes an anatomical difference between roots and leaves? Only leaves have phloem and only roots
have xylem. | back 26 A waxy cuticle covers leaves but is absent from roots. |
front 27 Which of the following cell types retains the ability to undergo cell division? A meristem cell near the root
tip. | back 27 A meristem cell near the root tip. |
front 28 Which of the following structures is correctly paired with its function Sclerenchyma–supporting cells with
thick secondary walls. | back 28 Sclerenchyma–supporting cells with thick secondary walls. |
front 29 A student examining leaf cross sections under a microscope finds many loosely packed cells with relatively thin cell walls. The cells have numerous chloroplasts. What type of cells are they? | back 29 Parenchyma. |
front 30 Increasing the number of stomata per unit surface area of a leaf when atmospheric carbon dioxide levels decline is most analogous to which of the following human adaptations? Breathing faster as atmospheric carbon
dioxide levels increase. | back 30 Putting more red blood cells into circulation when atmospheric oxygen levels decline. |
front 31 What tissue makes up most of the wood of a tree? | back 31 Secondary xylem. |
front 32 STUDY QUESTIONS: Chapter 26, 27, and 35 | back 32 STUDY QUESTIONS: Chapter 26, 27, and 35 (back of card) |
front 33 In a comparison of birds and mammals, the condition of having four limbs is: | back 33 A shared ancestral character. |
front 34 To apply parsimony to constructing a phylogenetic tree: | back 34 Choose the tree that represents the fewest evolutionary changes, in either DNA sequences or morphology. |
front 35 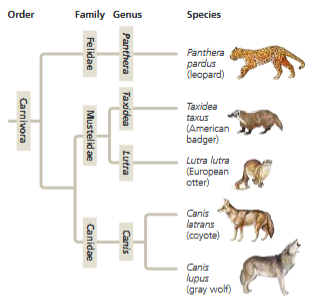 In Figure 26.4, which similarly inclusive taxon is represented as descending from the same common ancestor as Canidae? | back 35 Mustelidae |
front 36 Three living species X, Y, and Z share a common ancestor T, as do extinct species U and V. A grouping that consists of species T, X, Y, and Z (but not U or V) makes up: | back 36 A paraphyletic group. |
front 37 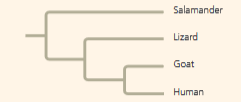 Based on the tree, which statement is correct? Lizards and goats form a sister
group. | back 37 Salamanders are a sister group to the group containing lizards, goats, and humans. |
front 38 If you were using cladistics to build a phylogenetic tree of cats, which of the following would be the best outgroup? Wolf | back 38 Wolf |
front 39 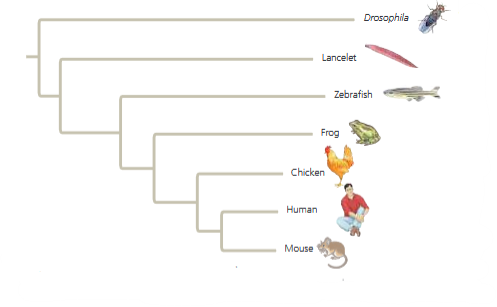 The relative lengths of the frog and mouse branches in the phylogenetic tree in Figure 26.13 indicate that: | back 39 The homolog evolved more slowly in the mouse lineage. |
front 40 A process that cannot produce genetic variation in
bacterial | back 40 Meiosis |
front 41 Photoautotrophs use: | back 41 Light as an energy source and CO2 as a carbon source. |
front 42 Which of the following statements is true? Archaea and bacteria have identical
membrane lipids. | back 42 The cell walls of archaea lack peptidoglycan. |
front 43 Which of the following involves metabolic cooperation
among Binary fission | back 43 Biofilms |
front 44 Which of the following describes a bacterium that lives in
the Commensalist | back 44 Symbiotic pathogen |
front 45 Photosynthesis that releases O2 occurs in Cyanobacteria. | back 45 Cyanobacteria. |
front 46 Most of the growth of a plant body is the result of: | back 46 Cell elongation. |
front 47 The innermost layer of the root cortex is the: | back 47 Endodermis |
front 48 Heartwood and sapwood consist of: | back 48 Secondary xylem. |
front 49 The phase change of an apical meristem from the juvenile to the mature vegetative phase is often revealed by: | back 49 A change in the shape of the leaves produced. |
front 50 The vascular cambium gives rise to: | back 50 Secondary xylem and phloem. |
front 51 The root pericycle is the site where: | back 51 Lateral roots originate. |
front 52 Root apical meristems are found: | back 52 In all roots. |
front 53 Suppose a flower had normal expression of genes A and C and expression of gene B in all four whorls. Based on the ABC hypothesis, what would be the structure of that flower, starting at the outermost whorl? | back 53 Petal-Petal-Stamen-Stamen |
front 54 Which of the following arise(s), directly or indirectly,
from Secondary
xylem. | back 54 All of the above. |
front 55 A strawberry plant mutant that fails to make stolons would suffer from: | back 55 A reduction in asexual reproduction. |
front 56 QUIZ 2: Chapters 31 and 40 | back 56 QUIZ 2: Chapters 31 and 40 (back of card) |
front 57 Fungi have an extremely high surface-to-volume ratio. What is the advantage of this characteristic to an organism that gets most of its nutrition through absorption? | back 57 The high ratio allows for more material to be acquired from the surroundings and transported through the cell membrane. |
front 58 What are the filamentous mats formed by most fungi called? | back 58 Mycelia |
front 59 If all fungi in an environment were to suddenly die, then which group of organisms is most likely to benefit, due to the fact that its fungal competitors have been removed? Flowering plants | back 59 Prokaryotes |
front 60 Which of the following statements describes an adaptive advantage associated with the filamentous nature of fungal mycelia? The ability to form haustoria and
parasitize other organisms. | back 60 An extensive surface area well suited for invasive growth and absorptive nutrition. |
front 61 At which stage of a basidiomycete's life cycle would reproduction be halted if an enzyme that prevented the fusion of hyphae was introduced? | back 61 Plasmogamy. |
front 62 Which of the following statements correctly describes deuteromycetes? They represent the phylum in which all
the fungal components of lichens are classified. | back 62 They are the group of fungi that have, at present, no known sexual stage. |
front 63 Which of the following describes the evolution of multicellularity in fungi and animals? Common ancestry. | back 63 Convergent evolution. |
front 64 Which of the following structures in an ascomycete is haploid? Ascospore | back 64 Ascospore |
front 65 Which of the following types of fungi often live in the digestive tracts of sheep and cattle? Ascomycetes | back 65 Chytrids |
front 66 Which of the following statements describes the relationship between a fungus and a photosynthetic microorganism in a lichen? Neither organism derives any benefit
from the relationship. | back 66 The fungus provides the photosynthetic microorganism a suitable environment for growth. |
front 67 Which of the following options correctly lists three evolutionary adaptations that help some animals directly exchange matter between the cells of their body and the environment? A gastrovascular cavity, a body with
two tissue layers, and a torpedo-like body shape. | back 67 An external respiratory surface, a small body size, and a two-cell-layered body. |
front 68 Which of the following properties are displayed by cardiac muscle cells? Striated appearance and presence of
intercalated disks. | back 68 Striated appearance and presence of intercalated disks. |
front 69 The body's automatic tendency to maintain a constant and optimal internal environment is termed as ________. | back 69 Homeostasis |
front 70 The use of brown fat to generate metabolic heat is mostly limited to small mammals. Which characteristic of small mammals created the selective pressure that favored the use of brown fat to generate metabolic heat? Small mammals cannot grow enough fur to
insulate their bodies. | back 70 Small mammals have a large surface area to volume ratio, which allows rapid heat loss. |
front 71 You are studying a large tropical reptile that has a high and relatively stable body temperature. Which of the following observations is best for determining if the animal is an endotherm or an ectotherm? You know from its high and stable body
temperature that it must be an endotherm. | back 71 You subject this reptile to various temperatures in the lab and find that its body temperature and metabolic rate change with the ambient temperature. You conclude that it is an ectotherm. |
front 72 Which of the following organisms is most likely to have the highest total annual energy expenditure per unit mass? Elephant | back 72 Mouse |
front 73 The BMR of José, an adult human male, is approximately 1,800 kcal/day. Suppose that José ate 2,400 kcal of food in one day and that walking at a slow pace "burns" approximately 150 kcal per hour. How many hours would José have to walk to have a net zero energy gain for the day? | back 73 4 hours. |
front 74  A researcher is setting up an experiment to measure basal metabolic rate in prairie voles (Microtus ochrogaster–a small rodent). Which of the following would be the best set of conditions for the voles immediately before and during the measurement? | back 74 D |
front 75 Blood is best classified as connective tissue because ________. | back 75 its cells are separated from each other by an extracellular matrix |
front 76 Which characteristic is most likely for an epithelium that is specialized for passive diffusion of materials from one fluid-filled compartment to another? A single layer of flattened
cells. | back 76 A single layer of flattened cells. |
front 77 STUDY QUESTIONS: Chapter 31 and 40 | back 77 STUDY QUESTIONS: Chapter 31 and 40 (back of card) |
front 78 All fungi are: | back 78 Heterotrophic. |
front 79 Which of the following cells or structures are associated with asexual reproduction in fungi? Ascospores | back 79 Conidiophores |
front 80 The closest relatives of fungi are thought to be the: | back 80 Animals. |
front 81 The most important adaptive advantage associated with
the | back 81 An extensive surface area well suited for invasive growth and absorptive nutrition. |
front 82 The body tissue that consists largely of material located
outside | back 82 Connective tissue. |
front 83 Which of the following would increase the rate of heat Feathers or
fur. | back 83 Wind blowing across the body surface. |
front 84 Consider the energy budgets for a human, an elephant, a | back 84 elephant; mouse |
front 85 Compared with a smaller cell, a larger cell of the same shape has: | back 85 Less surface area per unit of volume. |
front 86 An animal’s inputs of energy and materials would exceed its outputs: | back 86 If it is growing and increasing its mass. |
front 87 You are studying a large tropical reptile that has a high and relatively stable body temperature. How do you determine whether this animal is an endotherm or an ectotherm? | back 87 You subject this reptile to various temperatures in the lab and find that its body temperature and metabolic rate change with the ambient temperature. You conclude that it is an ectotherm. |
front 88 Which of the following animals uses the largest percentage of its energy budget for homeostatic regulation? Marine jelly (an
invertebrate). | back 88 Desert bird. |
front 89 END Good luck on the exam! | back 89 END (back of card) |