Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exam 4 A&P2
front 1 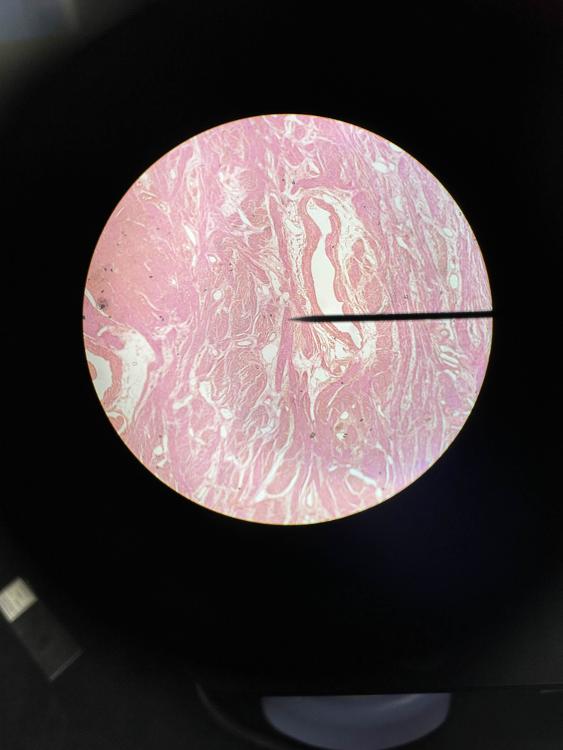 | back 1 uterus (4x) |
front 2 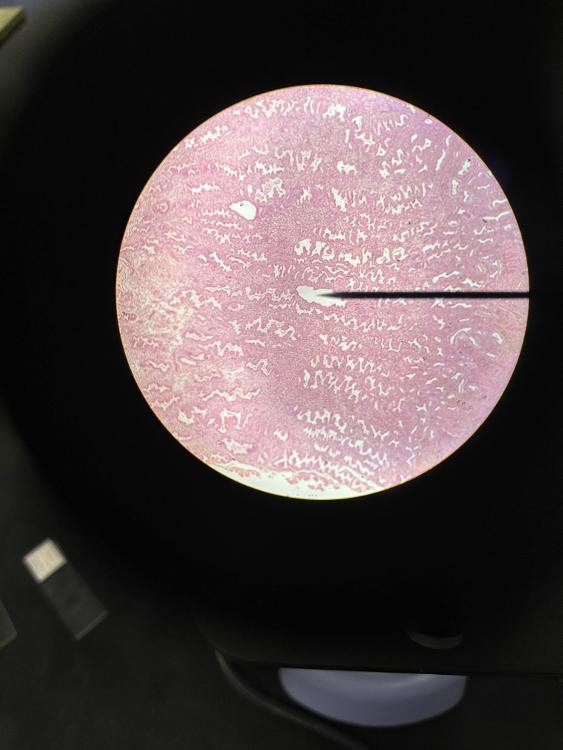 | back 2 uterus (4x) |
front 3 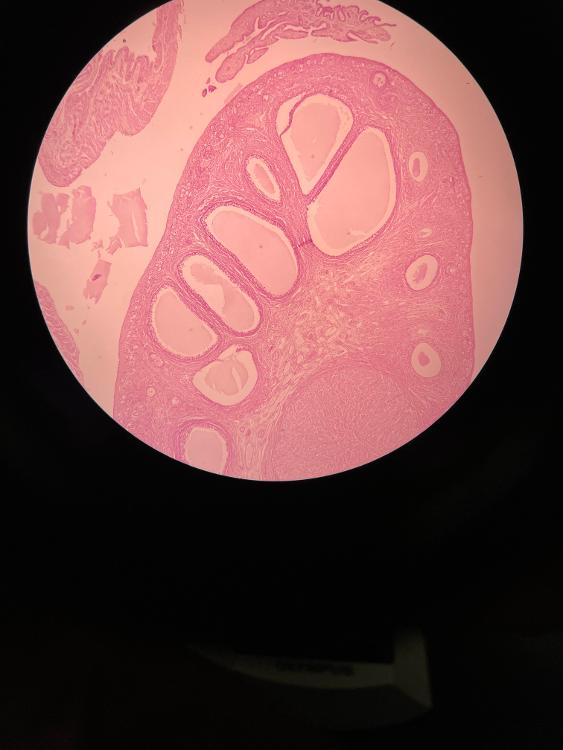 | back 3 ovary (4x) |
front 4 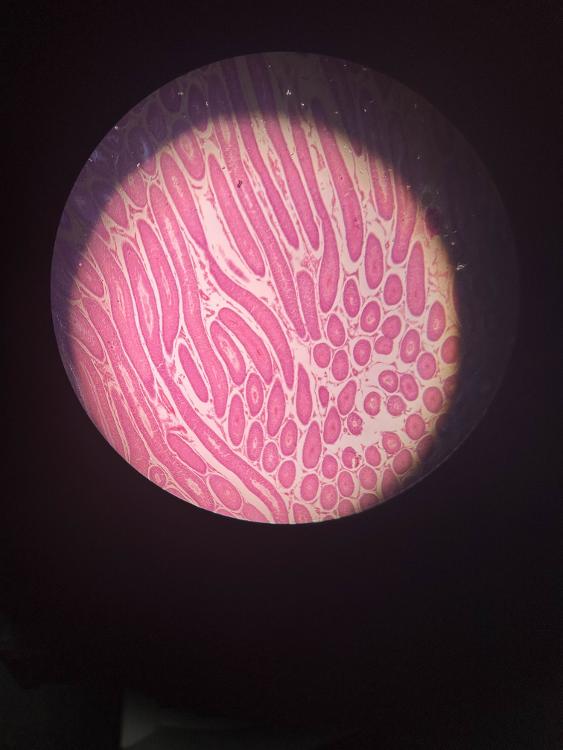 | back 4 testis (4x) |
front 5 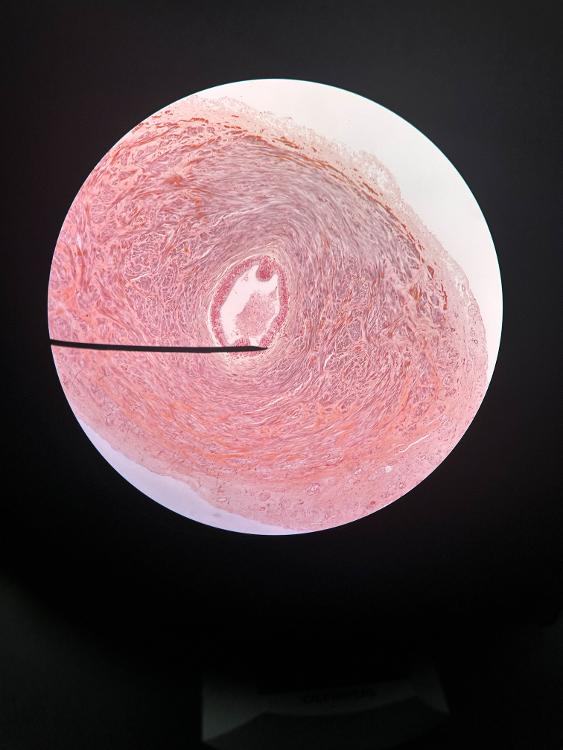 | back 5 ductus deferens (10x) |
front 6 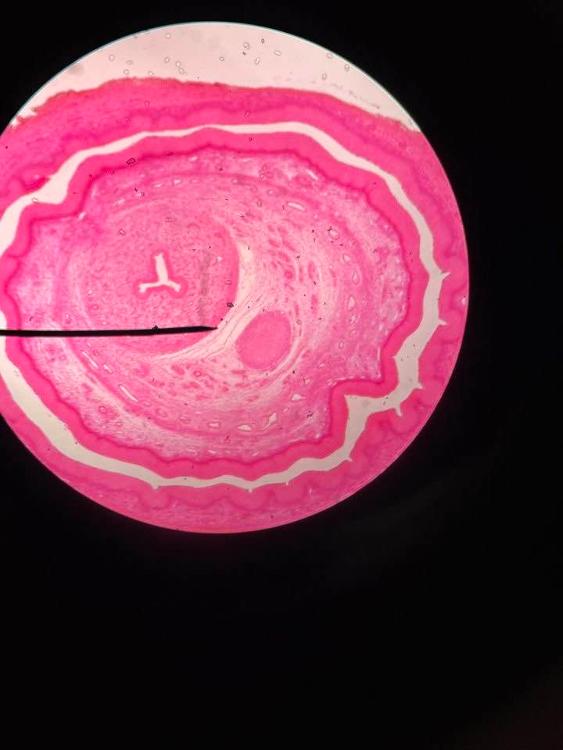 | back 6 penis (4x) |
front 7 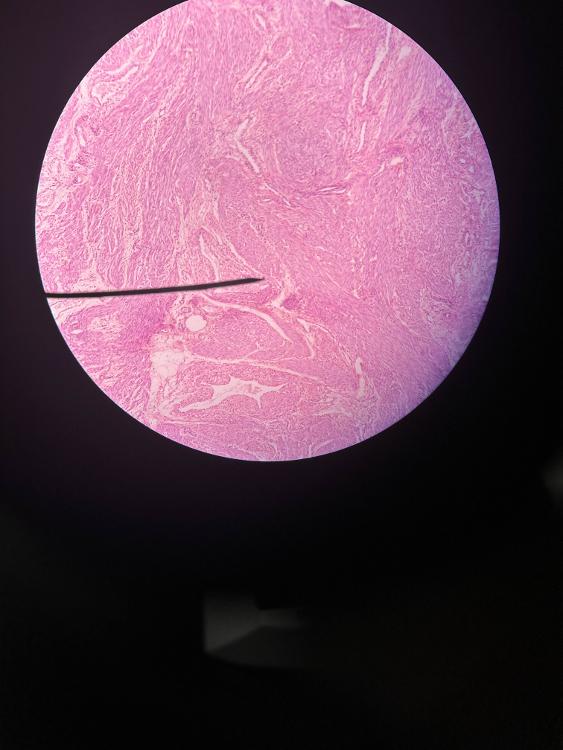 | back 7 uterus (10x) |
front 8 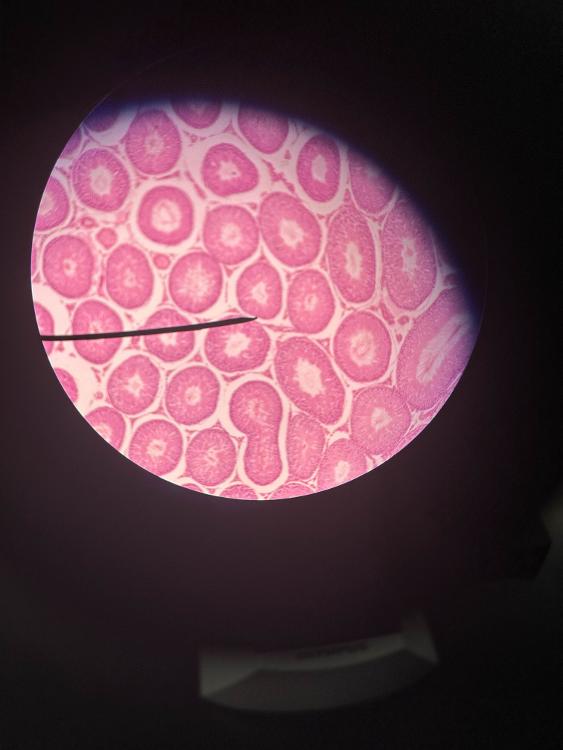 | back 8 testis (10x) |
front 9 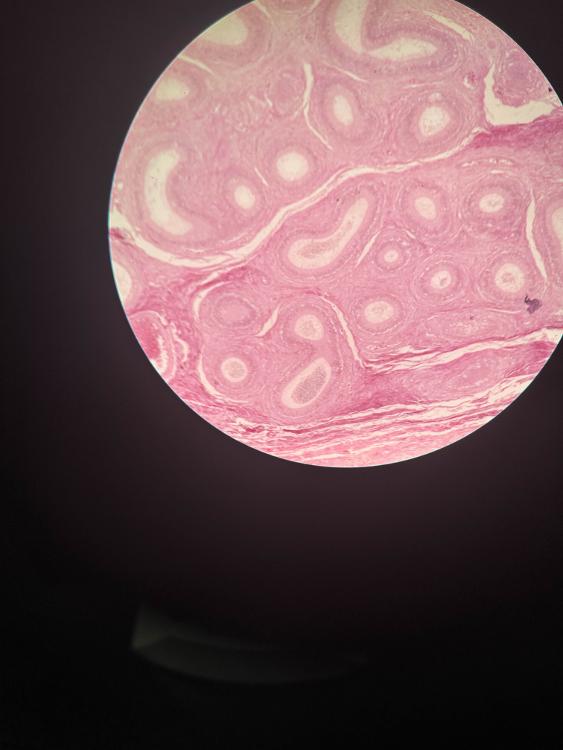 | back 9 epididymis (10x) |
front 10 What are the three primary germ layers (in order) and when are they developed? (what stage) | back 10 Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm. Developed during embryonic stage of development |
front 11 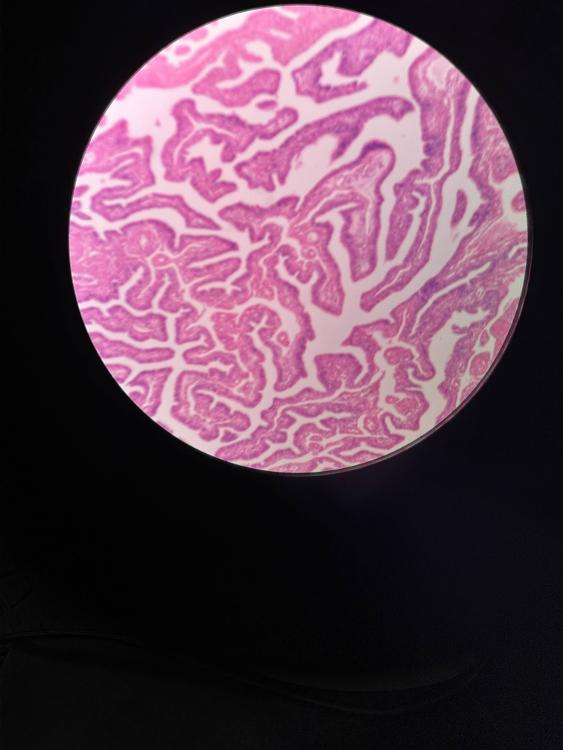 | back 11 uterine tube (10x) |
front 12 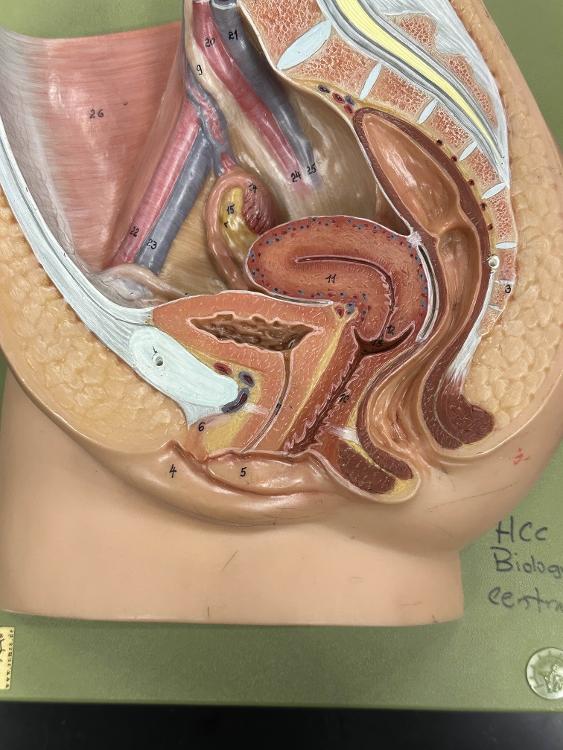 6 | back 12 clitoris |
front 13  11 | back 13 uterus |
front 14  12 | back 14 cervix |
front 15 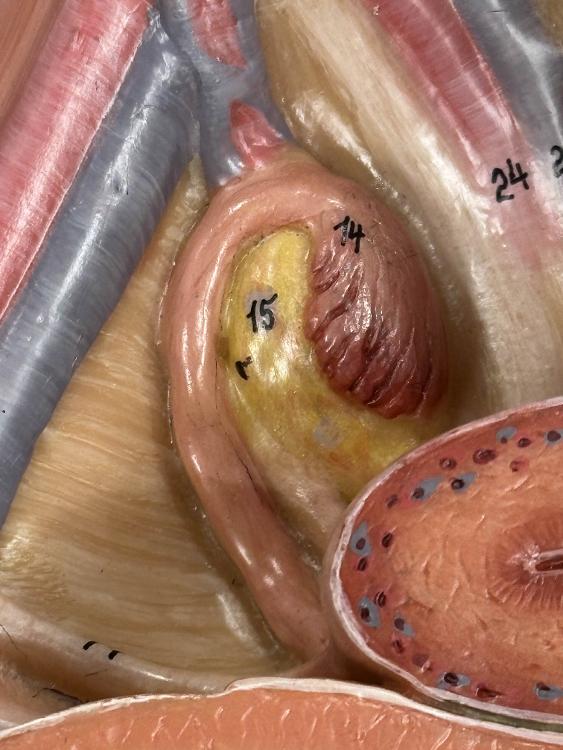 15 | back 15 ovary |
front 16  14 | back 16 uterine tube |
front 17  10 | back 17 vagina |
front 18 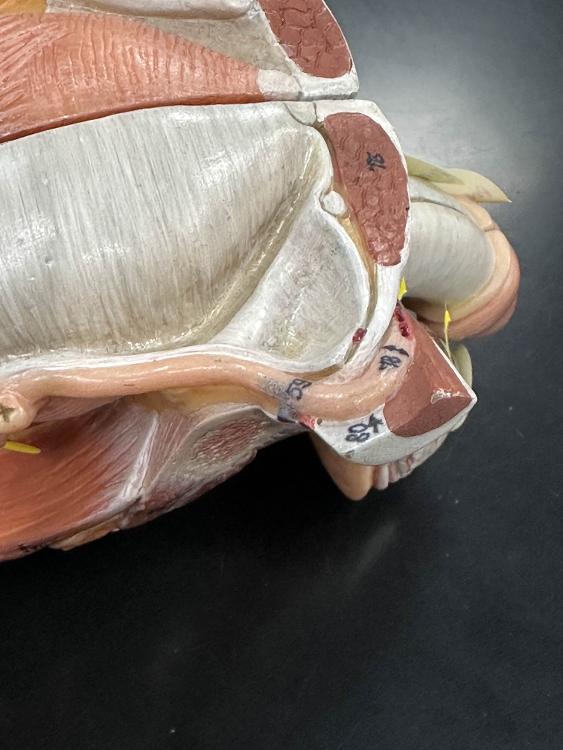 59 | back 18 ductus deference |
front 19 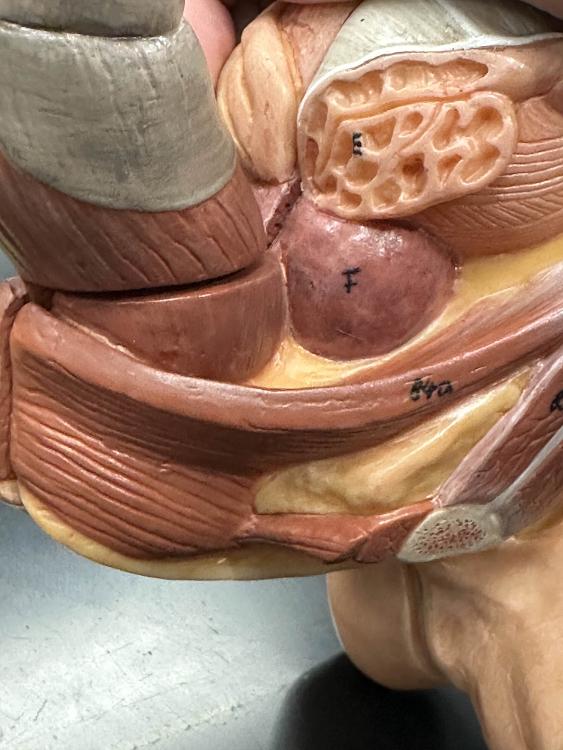 F | back 19 prostate gland |
front 20  E | back 20 seminal vesicles |
front 21 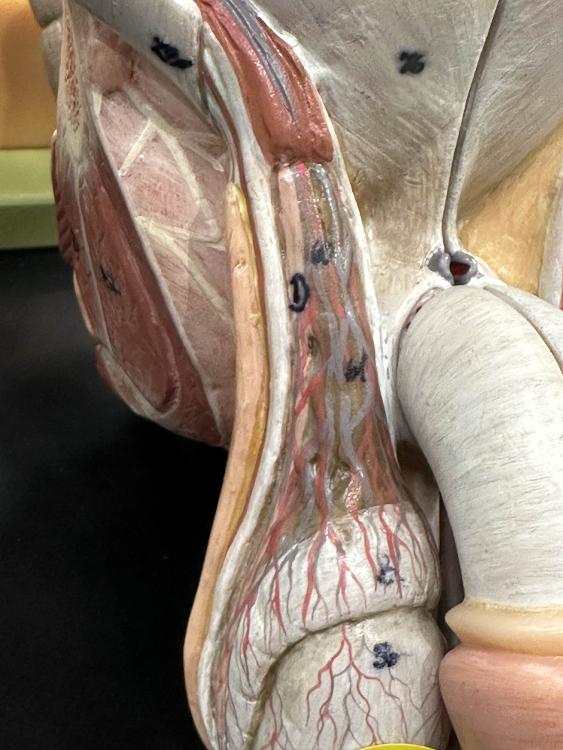 D | back 21 spermatic cord |
front 22 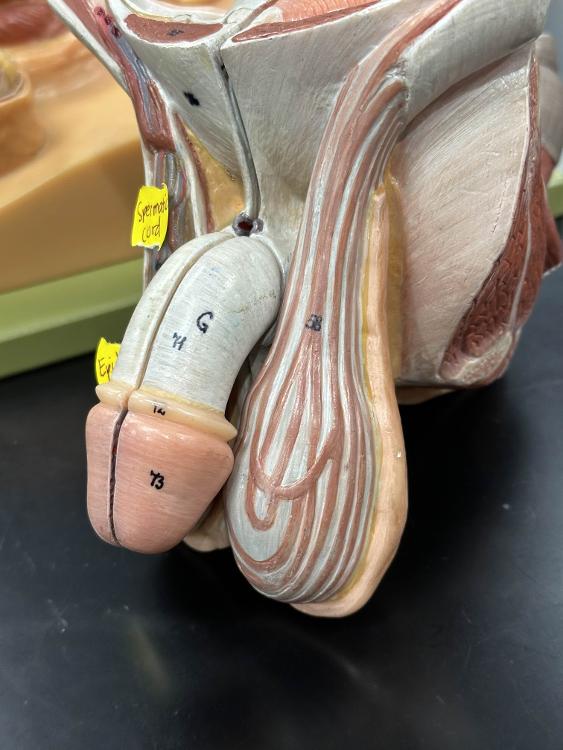 72 | back 22 prepuce |
front 23  G | back 23 penis |
front 24 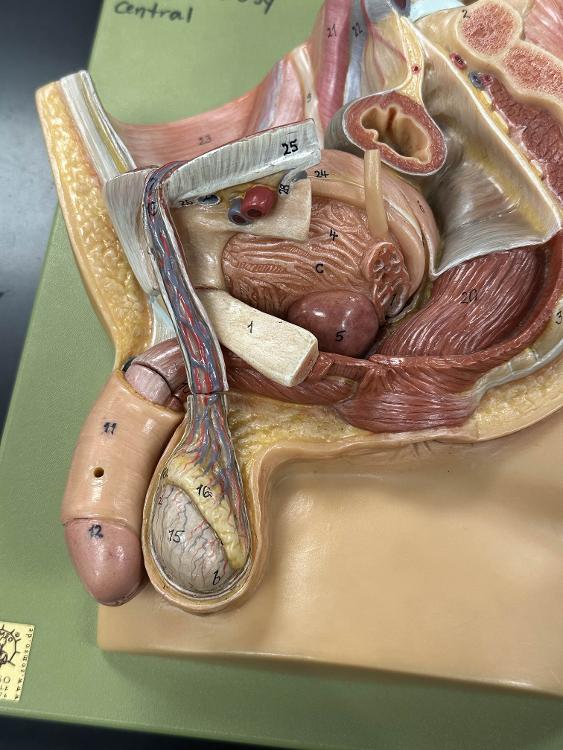 16 | back 24 epididymis |
front 25  15 | back 25 testes |
front 26  11 | back 26 penis |
front 27  B (looks like a c) | back 27 epididymis |
front 28 What is fertilization? | back 28 Process where sperm and ovum combine to form zygote |
front 29 What is meiosis? | back 29 Process of nuclear division in testes and ovaries which produces gametes |
front 30 Function of umbilical cord? | back 30 Connection between placenta and fetus allowing transfer of nutrients, oxygen, and waste between fetal and maternal blood. |
front 31 What is the function of the placenta? | back 31 Site of exchange of nutrients, gases, and wastes between embryonic and maternal blood |
front 32 How many daughter cells are in meiosis? | back 32 4 genetically different daughter cells (haploid) |
front 33 How many stages are in Mitosis? | back 33 4 stages (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) |
front 34 How many daughter cells are in mitosis? | back 34 2 genetically identical daughter cells (diploid) |
front 35 How many chromosomes does a human have? | back 35 46 |
front 36 How many X and Y chromosomes does a male have? | back 36 45 X and 1 Y |
front 37 How many X and Y chromosomes does a female have? | back 37 46 X chromosomes |
front 38 How long is gestation period? | back 38 9 months |
front 39 What are the three primary germ layers (in order) and when are they developed? | back 39 Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm. Developed during embryonic stage of development |
front 40 What are the stages of human development? | back 40 Three stages; pre-embryonic (1-2 wks), embryonic (3rd-8th wks), fetal stages (9th until birth) |