Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Ch.12
front 1 What are the requirements for an enzyme with Michaelis-Menten kinetics? | back 1 • Steady-state assumption: [ES] remains constant (loss |
front 2 What are the 3 ways of interpreting KM | back 2 • Substrate concentration [S] at which at enzyme is at k-1+k2/ k1 |
front 3 What is a turnover number? | back 3 • Turn over number: kcat = Vmax/[E]total |
front 4 What is the catalytic efficiency of an enzyme? | back 4 • Catalytic efficiency: kcat/KM |
front 5 Enzyme kinetics seeks to determine the initial and maximal reaction velocity that enzymes can | back 5 attain and the binding affinities for substrates and inhibitors |
front 6 Michaelis-Menten equation has a ______line on a graph | back 6 non-linear |
front 7 Bisubstrate reactions can occur by _____or______mechanisms or by a _______mechanism | back 7 ordered, random-sequential, Ping-pong |
front 8 1st order reactions display a linear plot of the | back 8 substrate or product concentration, as a function of time |
front 9 Rate law is the mathematical relationship | back 9 between the reaction rate or velocity, and concentration of reactions (linear) |
front 10 The amount of A consumed per unit of time | back 10 rate, or velocity |
front 11 Formula for rate law | back 11 v=k[A]number in front of letter |
front 12 Michaelis-Menten formula: | back 12 vo=Vmax[S]/ Km+[S] |
front 13 Vo is equal to | back 13 the slope |
front 14 At low [S], the rate is proportional | back 14 as in a first-order reaction |
front 15 At high [S], the enzyme reaction approaches | back 15 zero-order kinetics :Vo=Vmax |
front 16 Rate of formation of ES is _____, while rate of dissociation is ___. Rate of product formation is ____ | back 16 k1, k-1, k2 |
front 17 Catalysis is limiting, because the rate is independent of [S](E is saturated | back 17 0th order (when Kmis less than) |
front 18 Rate is dependent on [S], [S] is limiting | back 18 1st order (when Km is greater than) |
front 19 When above Km, it starts to | back 19 plateau due to saturation increasing |
front 20 Vmax=k2[ET] | back 20 no data |
front 21 Km=(k-1+k2)/k1 | back 21 no data |
front 22 Small Km means | back 22 little dissociation (10-6) |
front 23 Larger Km means | back 23 lots of dissociation (10-2) |
front 24 Kcat, the turnover number, is the number of | back 24 substrate molecules converted to product per enzyme molecules, per unit of time, when E is saturated with substrate |
front 25 Catalytic efficiency formula: | back 25 kcat/Km |
front 26 kcat/Km is approaching | back 26 1.0x109 |
front 27 At temperatures are above 50o to 60oC, | back 27 enzymes typically decline in activity |
front 28 The two classes of single-displacement: | back 28 random and ordered |
front 29 Random single displacement where either | back 29 substrate may bind first, followed by the other substrate |
front 30 Ordered single displacement where a | back 30 leading substrate binds first, followed by the other substrate |
front 31 Double displacement (Ping-Pong) reactions | back 31 involves a covalent intermediate |
front 32 In single displacement, high concentrations the | back 32 y-intercept is lower |
front 33 Random, single-displacement reaction is formed rapidly and reversibly when | back 33 enzyme is added to a reaction mixture containing A,B,P, and Q |
front 34 Ordered, single-displacement reaction leading substrate (A) must | back 34 bind first, followed by B. And for the products, P and Q |
front 35 Double-displacement has a formation | back 35 of a covalently modified enzyme intermediate, E' |
front 36 Reversible inhibitor may bind | back 36 at the active site or at some other site |
front 37 Four types of reversible enzyme inhibitors: | back 37 -competitive -noncompetitive -mixed noncompetitive -uncompetitive |
front 38 Competitive inhibition | back 38 only time where inhibitor can be competed by the substrates |
front 39 Increases the apparent Km but | back 39 no effect on Vmax |
front 40 Noncompetitive inhibitor | back 40 decreases Vmax with no change in Km |
front 41 Mixed noncompetitive alters | back 41 both Km and Vmax |
front 42 Uncompetitive inhibition alters | back 42 both Km and Vmax but with same slope Km/Vmax |
front 43 Uncompetetive inhibition only observed | back 43 in enzyme having two or more substrates |
front 44 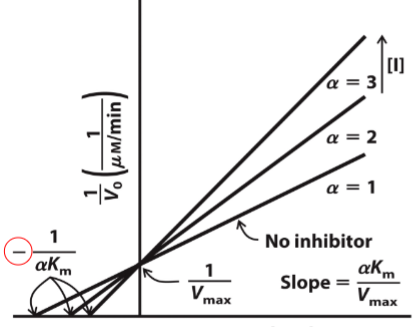 What type of reversible inhibitor is this? | back 44 Competitive Inhibition |
front 45 Competitive inhibition______apparent Km but______on Vmax | back 45 increases, no effect |
front 46 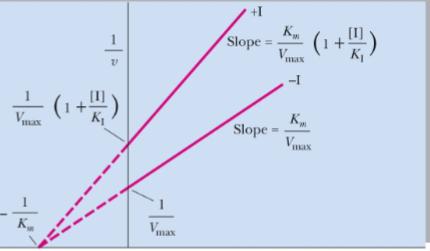 What type of reversible inhibitor is this? | back 46 Pure noncompetitive inhibition |
front 47 Pure noncompetitive inhibition____Vmax with ____in Km | back 47 decreases, no change |
front 48 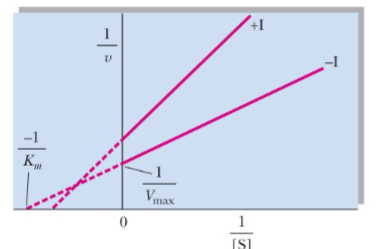 What type of reversible inhibitor is this? | back 48 Mixed noncompetitive inhibition |
front 49 Mixed noncompetitive inhibition alters Km and Vmax by _____ | back 49 decreasing |
front 50 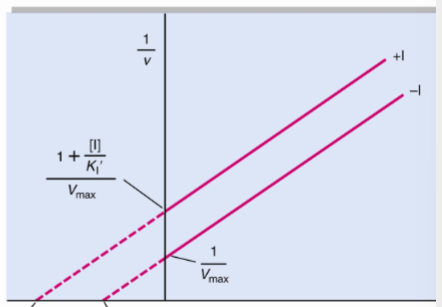 What type of reversible inhibitor is this? | back 50 Uncompetitive inhibition |
front 51 Uncompetitive inhibition alters both Km and Vmax but have ______ | back 51 the same slope, Km/Vmax |