Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exam 3 CHEM 315
front 1 What are the five types of Chromatographic separation? | back 1 -Adsorption chromatography -Partition chromatography -Ion Exchange chromatography -Size exclusion chromatography - Affinity Chromatography |
front 2 Solute equilibrates between mobile phase and surface of stationary phase | back 2 Adsorption Chromatography |
front 3 Solute equilibrates between mobile phase and film of liquid attached to stationary phase | back 3 Partition chromatography |
front 4 Ions in mobile phase are attracted to counterions covalently attached to stationary phase | back 4 Ion exchange chromatography |
front 5 Different-sized solutes penetrate pores in the stationary phase to different extents. The largest solutes are eluded first | back 5 Molecular (size) exclusion chromatography |
front 6 Molecular exclusion chromatography separates by size, so the large molecules______, and the solid stationary phase has a_____gel | back 6 elude first, porous |
front 7 What is the mobile phase? | back 7 -the solvent moving through the column - a liquid or gas |
front 8 What is the stationary phase? | back 8 -the one that stays in place inside the column - a viscous liquid chemically bonded to the inside of a capillary tube or packed column |
front 9 In Ion exchange chromatography, what eludes first in an anion exchange chromatography? | back 9 The positively charged molecules will elude first because the stationary phase attracts the negatively charged molecules. |
front 10 In Ion exchange chromatography, what eludes first in an cation exchange chromatography? | back 10 The negatively charged molecules will elude first because the stationary phase attracts positively charged molecules. |
front 11 Retention time, tr is the | back 11 elapsed time between injection and arrival |
front 12 Retention volume, Vr, is the volume of | back 12 mobile phase required to elute a particular solute from the column |
front 13 Gaussian chromatography states that if the peaks are farther apart, | back 13 the better the separation |
front 14 Gaussian chromatography states that the longer the peak resides in a column, | back 14 the broader the band width |
front 15 A resolution____ than 1.5 is highly desireable | back 15 greater |
front 16 The narrower the peaks are, the____the separation, and the ___the resolution | back 16 better, higher |
front 17 How does the column length affect the resolution? | back 17 increasing the column length allows for more separation time, and increases retention time and run time |
front 18 How does temperature affect resolution? | back 18 raising the temperature in GC decreases the retention time by reducing the partition coefficient, allowing for faster elution. Higher temps can also reduce resolution and cause peaks to overlap |
front 19 how does coating thickness affect resolution? | back 19 A thicker stationary phase will increase the retention time by providing more interaction time for analytes, enhancing the separation. Too thick can lead to excessive broadening and reduced efficiency |
front 20 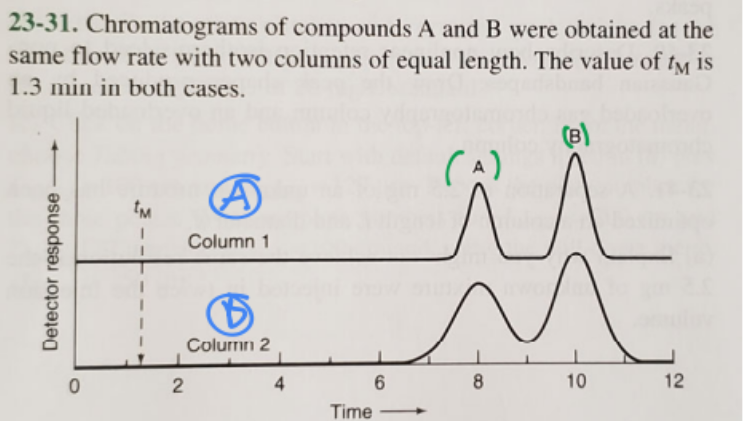 Which column has a larger plate number? | back 20 A(blue) |
front 21 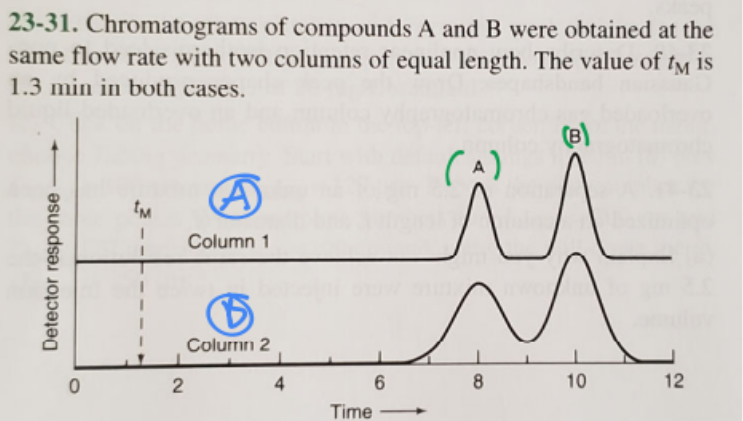 Which column has a larger plate height? | back 21 B (blue) |
front 22 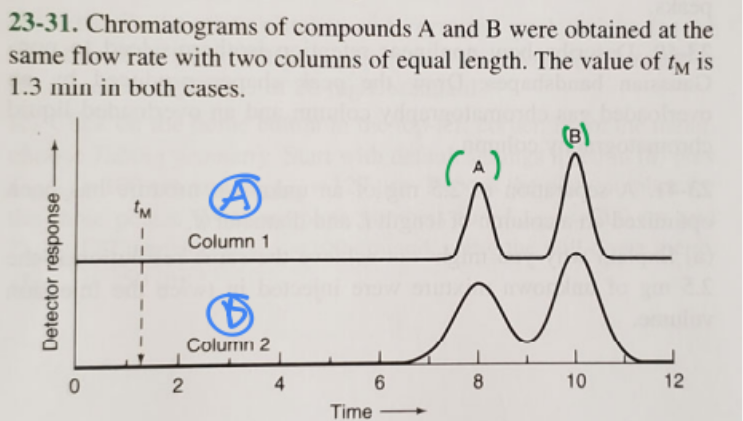 1. Which column gives higher resolution? 2. Which column gives a greater separation factor? 3. Which compound has a higher retention factor? | back 22 1. A (blue) 2. A (blue) 3. B (green) |
front 23 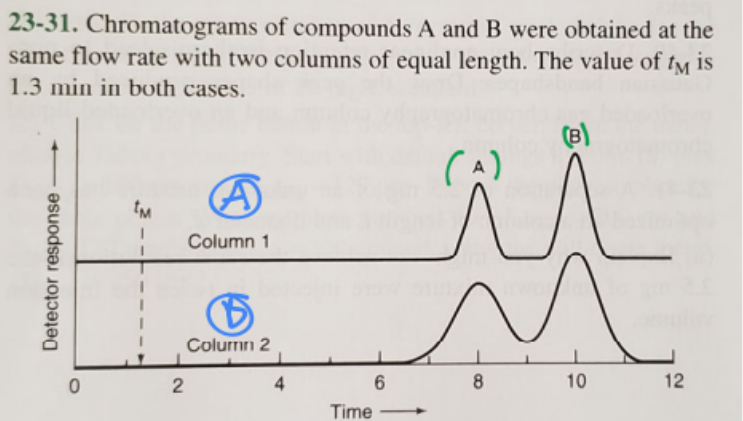 1. Which compound has a greater distribution constant? | back 23 B (green) |
front 24 In Normal Phase HPLC, the polar column allows for polar analytes to have | back 24 longer retention times, so non-polar molecules eludes first |
front 25 In Reverse Phase HPLC, the non-polar column allows for non-polar analytes to have | back 25 longer retention times, so polar molecules elude first |
front 26 What does each letter stand for? H=A+(B/ux)+Cux ____ plate height ____Eddy diffusion (multiple path) ____longitudinal diffusion ____ linear flow rate of mobile phase _____resistance mass transfer in stationary and mobile phases | back 26 H , A, B, ux, C |
front 27 A study of interaction between matter and radiation | back 27 Spectroscopy |
front 28 Technique that uses light to measure chemical concentrations | back 28 spectrophotometry |
front 29 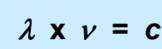 What does each symbol stand for? | back 29 lambda: wavelength (nm) V: frequency (sm-1) c: speed of light (3.0x108m/s) |
front 30 Electronic transition occurs when | back 30 molecules absorb UV or visible light, causing electrons to move to higher electronic energy levels |
front 31 Vibrational transition occurs in the | back 31 infrared region, causing them to vibrate |
front 32 Rotational transition occurs in the microwave region causing | back 32 molecules to rotate |
front 33  Label the following picture of measuring absorbance: | back 33 1. light sources 2. wavelength selector (monochromator) 3. sample 4. Light detector |
front 34 Absorption spectrophotometer measures | back 34 how much light is absorbed by a sample at specific wavelengths |
front 35 Emission spectrometer measures | back 35 how much light emitted by a sample after it has been excited |
front 36 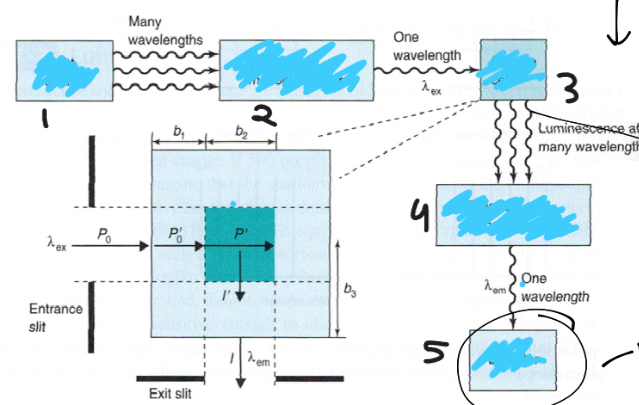 Label the following for measuring emission: | back 36 1. light source 2. excitation monochromator 3. sample cell 4. emission monochromator 5. detector |
front 37 Beers law: A=ε⋅b⋅C, what do each letters signify? | back 37 A= absorbance b= path length of the sample cuvette c=concentration of solution |
front 38 You can find concentration by relating these 2 equations: A=ε⋅b⋅C and Y=mx+b. What symbols work hand in hand? | back 38 y= A m=ε x=b b=C |
front 39 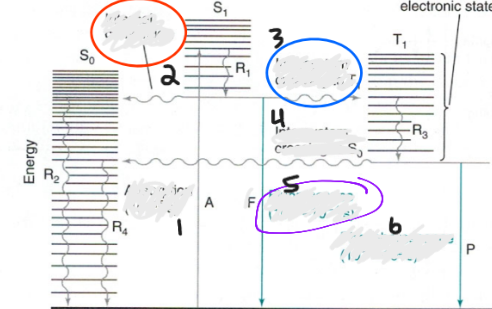 Label Jablonski Diagram: | back 39 1. absorption (1015s) 2. Internal conversion 3. intersystem crossing to T 4. INtersystem crossing to So 5. Fluorescence (10-8-10-4 s) 6. Phosphorescence (10-4-102 s) |
front 40 Has shorter emission time, brighter emission, emission of photon during internal converion, and only glows when UV light hits it | back 40 Fluorescence |
front 41 longer emission time, dimmer emission, emission of photon during intersystem crossing, and can be charged with UV light | back 41 Phosphorescence |
front 42 Internal conversion is a nonradioactive transition between states with the | back 42 same spin |
front 43 Intersystem crossing is a nonradioactive transition between states with | back 43 different spins |
front 44 The process by which an atom or molecule loses electrons Na → Na+ + e− | back 44 Oxidation |
front 45 The process by which an atom or molecule gains electrons. Cl2 + 2e− → 2Cl− | back 45 Reduction |
front 46 This is the substance that gains electrons ( gets reduced)
| back 46 oxidizing agent |
front 47 This is the substance that loses electrons ( gets oxidized)
| back 47 reducing agent |
front 48 Galvanic cells are spontaneous and | back 48 external energy is not required |
front 49 In a reaction equation, the left is the____ and the right is the____ | back 49 anode, cathode |
front 50 The anode gets______ and the cathode gets ____ | back 50 oxidized, reduced |
front 51 If E>0, it is a _____reaction, and if E<0, it is a _____reaction | back 51 spontaneous, non-spontaneous |