Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
ochem lab final
front 1 Where should the tip of the thermometer be placed in a microscale distillation set up? | back 1 At or slightly below the side arm of the distillation head. |
front 2 What are the concerns presented by overheating a distillation to a dry flask? | back 2 - the empty glassware might heat quickly, igniting vapors from the distillation - the remaining solid residue might contain explosive peroxides |
front 3 When performing the acid-catalyzed dehydration of an alcohol, the yield of product can be increased by ___________________ during the reaction. | back 3 distilling off the product |
front 4 The dehydration is ______________, and removing the product from _________________ reduces the ___________ reaction. | back 4 reversible, the reaction flask, hydration |
front 5 Why does the dehydration of an alcohol more often use concentrated sulfuric acid, H2SO4, as the acid catalyst rather than dilute hydrochloric acid, HCl? | back 5 - The presence of the chloride ion could result in a competing substitution - The additional water solvent from a dilute solution could reverse the dehydration. |
front 6 Which changes can be made to a chemical reaction in order to increase the rate constant? | back 6 Add a catalyst, increase the temperature |
front 7 Suppose you are performing a titration, at the beginning of the titration you read the titrant volume as 2.03 mL. After running the titration and reaching the endpoint, you read the titrant volume as 20.03 mL. What volume, in ML, of titrant was required for the titration | back 7 18.0 mL |
front 8 For a reaction rate based on one reactant, identify the type of graph that will give a linear plot in each case. first-order reaction __________________ zero order reaction __________________ second order reaction ______________ | back 8 In[reactant] versus time [reactant] versus time 1/[recatant] versus time |
front 9 Concnetration data is commonly monitored duringa reaction to determine the order with respect to a reactant. Consider the types of observations listed, and determine which order is likely for that reactant. Assume all other factors are held constant. The reaction rate is constant regardless of the amount of reactant in solution. ______________________ The reaction rate increases in direct proportion to the concentration of the reactant in solution. _________________ An increase in the concentration of the reactant in solution causes the reaction rate to increase exponentially. | back 9 zero order, first order, second order |
front 10 The term SN1 describes a reaction that is a(n) __________________ involving _______________________________________ | back 10 nucleophilic substitution, one molecule in the rate determining step |
front 11 If the dehydration reaction of an alcohol is successful, what changes would be seen in the IR spectrum fro the product compared to the starting material? | back 11 - The disappearance of an O-H band from the starting material - The disappearance of a C-O band from the starting material -The addition of a C-C double bond band in the product |
front 12 In the presence of acid and heat, ______________________ will undergo a more effective dehydration reaction because it is a _____________ alcohol and the ________ in the intermediate of the mechanism will be more stable. | back 12 cyclohexanol, secondary, cation |
front 13 Describe the complete role of the acid catalyst in the dehydration of an alcohol. | back 13 The acid protonates the hydroxyl group and then the conjugate base deprotonates an adjacent carbon |
front 14 How can a catalyst be recognized in a mechanism? | back 14 The catalyst is used and then regenerated in a later step |
front 15 The dehydration of a secondary alcohol, like cyclohexanol, is a mechanism that occurs ____________________. First, the alcohol is protonated to _______________________________, creating ___________ intermediate. Then, a _________________ is removed, moving the electrons from that bond to make a __________________ | back 15 in two steps, leave as a water molecule, a cation, hydrogen ion, carbon-carbon double |
front 16 Why is potassium hydroxide preferred over sodium hydroxide in organic reactions? | back 16 Potassium hydroxide is more soluble in organic alcohols |
front 17 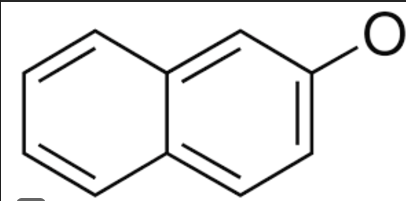 Identify the best description of the role each species play in the SN2 synthesis of nerolin I- ______________________ KOH ____________________ I-CH2CH3 ___________________ (two rings w/ one O-) _____________ | back 17 leaving group, base, electrophile, nucleophile |
front 18 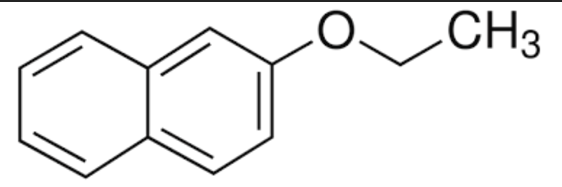 Identify the best description of the role each species play in the SN2 synthesis of nerolin _____________________ | back 18 product |
front 19 Consider the SN2 reaction of an alcohol with an alkyl halide in the presence of base. The ______ should be added to the alcohol first to _____________ the alcohol and allow it to attack the ______________ | back 19 base, deprotonate, alkyl halide |
front 20 An SN2 reaction is a type of ______________________ in which the nucleophile attacks the electrophile ____________________ a leaving group leaves. The rate of the reaction depends on the concentration of _______________ | back 20 substitution reaction, at the same time, both reactants |
front 21 When working in a fume hood, what is the best position of the hood sash? | back 21 As low as possible no more than halfway up |
front 22 When working in the fume hood, it is important to make an effort to minimize __________. Only keep items in the fume hood if they are being used for ________________. Do not _______ chemicals in the fume hood unless instructed to do so. | back 22 clutter, the current experiment, store |
front 23 If crystal growth does not start on its own after the solution in the flask returns to room temperature, identify the best way to promote its process. | back 23 Add a bit of solid as a seed crystal, scratch the bottom of the flask gently with a stirring rod. |
front 24 When should you start timing the reflux for the procedure? | back 24 when the reflux ring stabilizes in the condenser |
front 25 When it is time to end a reflux, first _______________________ and then turn off the heat. ____________________________ until the system has cooled. | back 25 lower the heat source, leave the condenser water on |
front 26 The biggest concern of working with hydrocarbons in lab is that many of them are _____________ Therefore, hydrocarbons should be handled _____________ to contain any associated vapors with that hazard | back 26 flammable, in the hood |
front 27 Bayer's test, also known as the permanganate test, shows the presence of _______________ a positive bayers test appears as _____________ a negative bayers test appears as ______________ | back 27 alkenes, a brown precipitate, a purple solution |
front 28 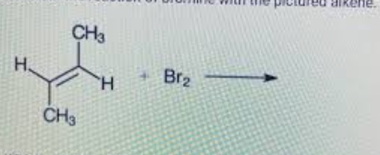 Consider the reaction of bromine with the pictured alkene Which structure shows the correct bonding for the product? | back 28 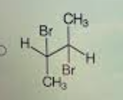 |
front 29 The bromine test shows the presence of ____________ A positive bromine test appears as a _____________ A negative bromine test as ____________________ | back 29 alkenes, a colorless solution, an orange solution |
front 30 In general, when hydrocarbons like oil are added to water, the two liquids ______________ because hydrocarbons are ____________ and water is ___________ | back 30 do not mix, non polar, polar |
front 31 In general, when a hydrocarbon is added to water, the hydrocarbon will _________ the water because hydrocarbons are _______ than water | back 31 float above, less dense |
front 32 A hydrocarbon is saturated if _________________________ are present. _______________ are saturated hydrocarbons A hydrocarbon is unsaturated if _____________________ are present. _________________ are unsaturated hydrocarbons | back 32 only single bonds Alkanes any multiple bonds Alkenes |
front 33 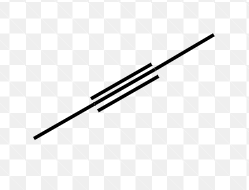 Identify the type of hydrocarbon represented by each structure | back 33 Alkyne (unsaturated) |
front 34 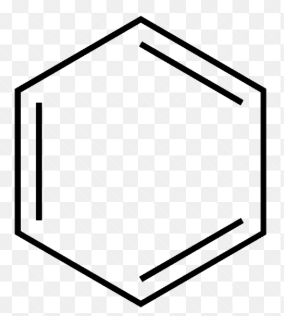 Identify the type of hydrocarbon represented by each structure | back 34 Aromatic (unsaturated) |
front 35  Identify the type of hydrocarbon represented by each structure | back 35 Alkane (saturated) |