Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
CHEM 23: Stoichiometric Calculations: The Workhorse of the Analyst
front 1 stoichiometry | back 1 the ratios in which chemicals react, from which we apply appropriate conversion factors to arrive at the desired calculated results |
front 2 definition of avogadro's number | back 2 tells the number of particles in 1 mole (or mol) of a substance. |
front 3 avogadro's number | back 3 6.022x1023 |
front 4 atomic weight | back 4 is the weight of a specified no. of atoms in that element |
front 5 molecular weight | back 5 the sum of the atomic weights of the atoms that make up a compound |
front 6 Find the molecular weight of HCl | back 6 (1.0080)+(35.45) = 36.458 g/mol (insert surname) |
front 7 formula weight | back 7 sum of atomic weights but for ionic compounds |
front 8 Find the formula weight of NaOH | back 8 (22.990) + (12.011) + (1.0080) = 40 g/mol (insert surname) |
front 9 equivalent weight | back 9 the mass of one equivalent, that is the mass of a given substance which will combine with or displace a fixed quantity of another substance |
front 10 formula of equivalent weight | back 10 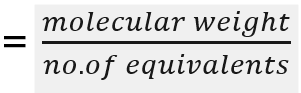 |
front 11 percent by mass | back 11 is the ratio of the mass of a solute to the mass of the solution multiplied by 100 percent |
front 12 formula of percent by mass | back 12 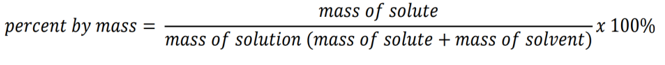 |
front 13 A sample of 0.894 grams (g) of potassium chloride (KCl) is dissolved in 54.8 grams of water. What is the percent by mass of KCl in the solution? | back 13 1.61% |
front 14 percent by volume | back 14 a unit of concentration used to express the amount of solute in a solution as a percentage of the volume of the solution. |
front 15 formula of percent by volume | back 15 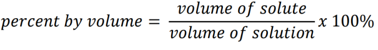 |
front 16 In a solution, there is 122.4 mL solvent and 5.24 ml solute present. Find the percent by volume. | back 16 4.11% |
front 17 mole | back 17 amount or sample of a chemical substance that contains as many constitutive particles as there are atoms in 12 grams = carbon – 12 (12g C-12 = 1mol) |
front 18 formula of mole | back 18 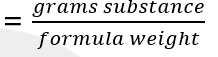 |
front 19 molarity | back 19 one-molar solution is defined as one that contains one mole of substance in each liter of solution |
front 20 formula of molarity | back 20 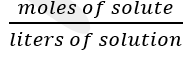 |
front 21 normality | back 21 one normal solution contains one equivalent per liter |
front 22 formula of normality | back 22 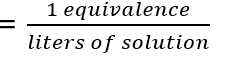 |
front 23 dilution | back 23 for preparation of a smaller concentration |
front 24 formula of dilution | back 24 C1V1=C2V2 |
front 25 parts per million | back 25 represents the number of parts of a substance per million parts of the solution |
front 26 formula of parts per million | back 26 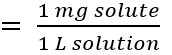 |
front 27 A solution has a concentration of 1.24 g/L. What is its concentration in ppm? | back 27 1240 ppm |