Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P II Test 4
front 1 Which of the following respiratory structures is more commonly known as the "throat"?
| back 1 b. Pharynx |
front 2 What is the amount of air that can be exhaled with the greatest possible exhalation after the deepest inhalation called?
| back 2 b. vital capacity |
front 3 What is the most powerful respiratory stimulant in a healthy person?
| back 3 c. blood carbon dioxide level |
front 4 Which of the following are the two main functions of the larynx.
| back 4 a. To provide a patent airway; to act as a switching mechanism to route air and food into the proper channels. |
front 5 The _________________ is also known as the "guardian of the airways".
| back 5 b. epiglottis |
front 6 The smallest subdivisions of the lung visible with the naked eye are the _____________, which appear to be connected by black carbon in smokers.
| back 6 c. lobules |
front 7 What is the amount of air that can be exhaled with the greatest possible exhalation after the deepest inhalation called?
| back 7 a. vital capacity |
front 8 The descending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable to both solutes and water. T/F | back 8 False |
front 9 Chemicals that enhance urinary output are called _______________.
| back 9 c. diuretics |
front 10 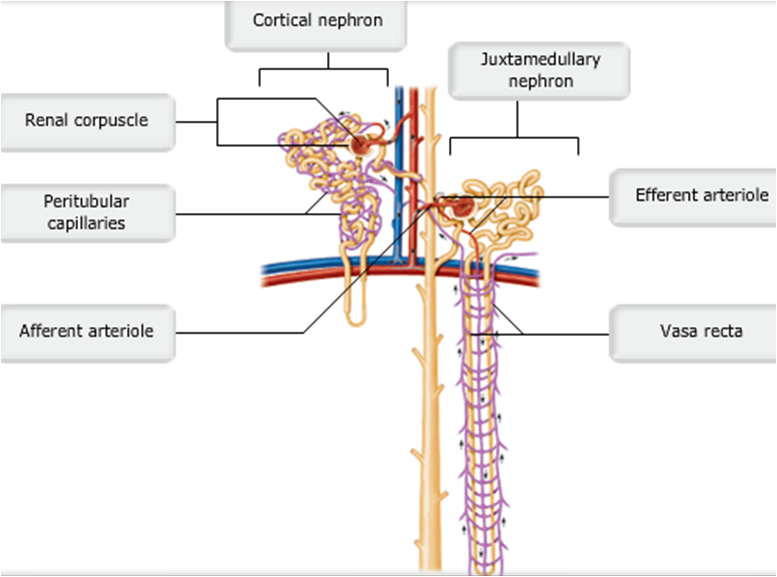 Cortical and Juxtamedullary Nephrons | back 10 pic |
front 11 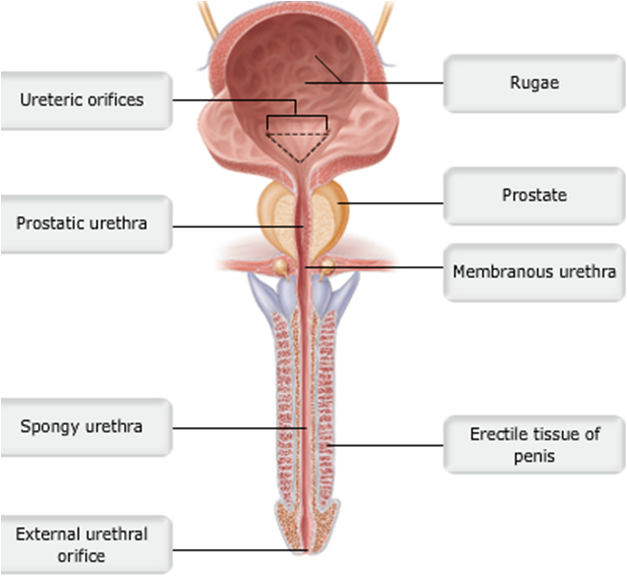 Male Urethra | back 11 pic |
front 12 Which of the following is not one of the things that must happen for micturition to occur?
| back 12 a. The extrusor muscle must relax |
front 13 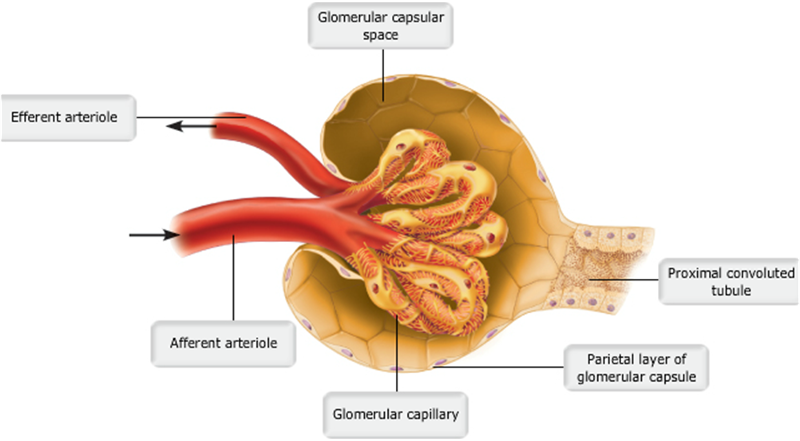 | back 13 no data |
front 14 Most solutes that are reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule use which of the following pathways?
| back 14 a. transcellular
|
front 15 During reabsorption of water in the proximal convoluted tubule, what causes water to diffuse from the lumen into the interstitial space?
| back 15 b. an increase in the osmolarity of the interstitium
|
front 16 The decreased intracellular concentration of sodium in tubular cells during active transport is caused by which of the following mechanisms?
| back 16 c. the sodium-potassium ATPase pump in the basolateral membrane
|
front 17 The active transport of which ion out of proximal convoluted tubule cells causes the reabsorption of both water and solutes?
| back 17 a. sodium
|
front 18 Which of the following transporters in the luminal membrane results in secretion?
| back 18 d. Na+-H+ countertransport
|
front 19 What is the limiting factor for the reabsorption of most actively transported solutes in the proximal tubule?
| back 19 a. number of transport carriers in the luminal membrane
|
front 20 Which of the following substances is not normally found in filtrate?
| back 20 a. blood cells and large particles
|
front 21 What is the primary driving force (pressure) that produces glomerular filtration?
| back 21 b. hydrostatic pressure of blood (blood pressure)
|
front 22 Which of the following would only be found in the glomerular filtrate if the glomerular membrane were damaged?
| back 22 c. protein
|
front 23 If the osmotic pressure in the glomerular capillaries increased from 28 mm Hg to 35 mm Hg, would net filtration increase or decrease?
| back 23 c. net filtration would decrease
|
front 24 Calculate the net filtration pressure if capillary hydrostatic pressure is 60 mm Hg, capillary osmotic pressure is 25 mm Hg, and capsular hydrostatic pressure is 10 mm Hg.
| back 24 d. 25 mm Hg
|
front 25 The _____________ collect(s) urine, which drains continuously from the papillae; the urine is then emptied into the ______________.
| back 25 d. calyces; renal pelvis |
front 26 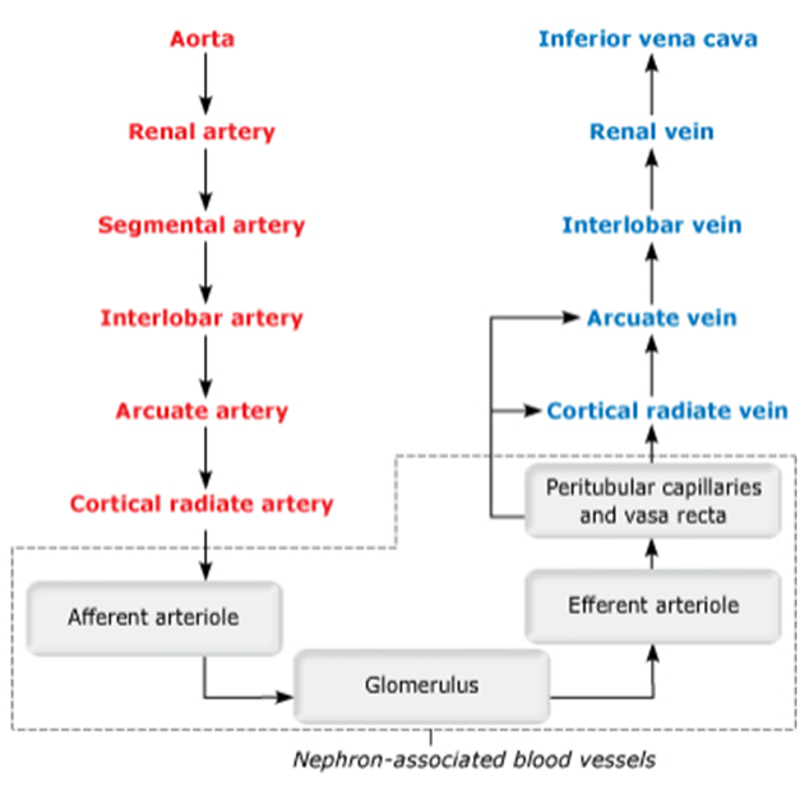 Blood flow path through renal bv | back 26 no data |
front 27 Approximately 80% of the energy used for active transport is devoted to the reabsorption of _______________.
| back 27 b. sodium |
front 28 What is the largest component of urine by weight, other than water?
| back 28 c. urea |
front 29 Despite the fact that the kidney's intrinsic controls work to maintain a constant GFR, in some situations the body's extrinsic controls will work to override these intrinsic controls in order to maintain systemic blood pressure. T/F | back 29 True |
front 30 In which part of the kidney is reabsorption (1) dependent upon the body's needs at the time, and (2) regulated by hormones?
| back 30 a. Distal convoluted tubule |
front 31 Which of the following is not a function of the kidneys?
| back 31 b. Producing the hormones melanin and oxytocin |
front 32 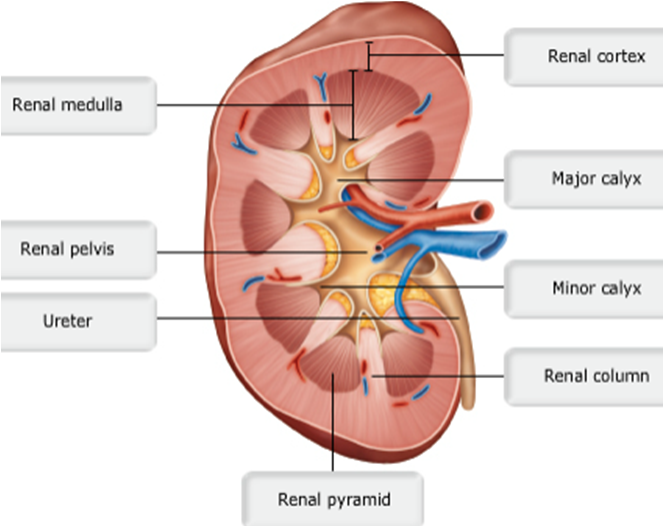 | back 32 no data |
front 33 Which of the following best describes glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
| back 33 d. the volume of filtrate created by the kidneys per minute
|
front 34 GFR regulation mechanisms primarily affect which of the following?
| back 34 c. glomerular hydrostatic pressure (HPg)
|
front 35 Which of the following are mechanisms of intrinsic control of glomerular filtration (renal autoregulation)?
| back 35 c. myogenic mechanism and tubuloglomerular feedback
|
front 36 Macula densa cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) regulate GFR through which intrinsic mechanism?
| back 36 c. tubuloglomerular feedback
|
front 37 The myogenic mechanism of renal autoregulation primarily involves smooth muscle in which blood vessels?
| back 37 d. afferent arterioles
|
front 38 What does a high concentration of NaCl in the renal tubule at the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) most likely indicate?
| back 38 b. insufficient NaCl reabsorption due to high GFR
|
front 39 Through the tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism, how would an increase in filtrate NaCl concentration affect afferent arteriole diameter?
| back 39 b. Afferent arteriole diameter would decrease.
|
front 40 Granular cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) regulate GFR through which mechanism?
| back 40 a. renin-angiotensin mechanism
|
front 41 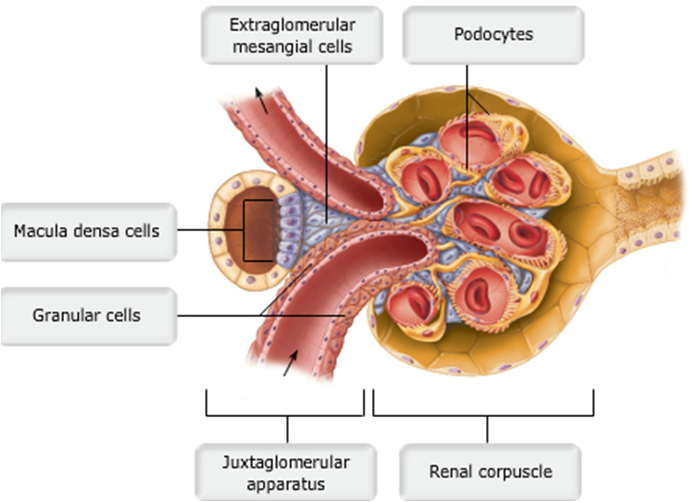 Juxtaglomerular complex of a nephron | back 41 no data |
front 42 The _______ keeps the urethra closed when urine is not being passed from the bladder, and prevents leaking between voiding.
| back 42 a. internal urethral sphincter |
front 43 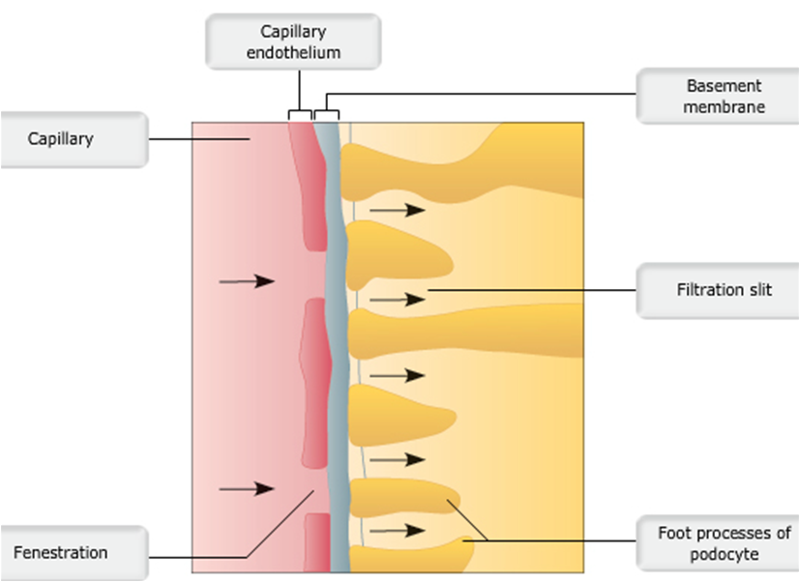 Layers of filtration membrane | back 43 no data |
front 44 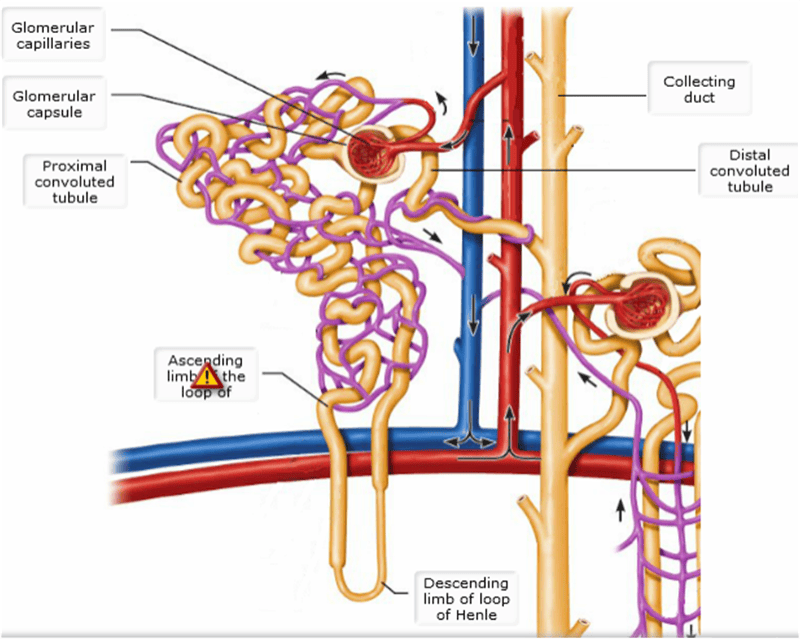 Cortical & juxtamedullary nephrons detailed | back 44 pic |
front 45 Where does most solute reabsorption occur in the nephron?
| back 45 a. Proximal convoluted tubule |
front 46 The _________ is an outer layer of dense fibrous connective tissue that anchors the kidney and the adrenal gland to surrounding structures. The _________ prevents infections in surrounding regions from spreading to the kidneys.
| back 46 b. renal fascia; fibrous capsule |
front 47 Under normal conditions, the large renal arteries deliver one-fourth of the total cardiac output (about 1200 ml) to the kidneys each minute. T/F | back 47 True |
front 48 Glomerular hydrostatic pressure (HPg) is the chief force pushing water and solutes out of the blood and across the filtration membrane. T/F | back 48 True |
front 49 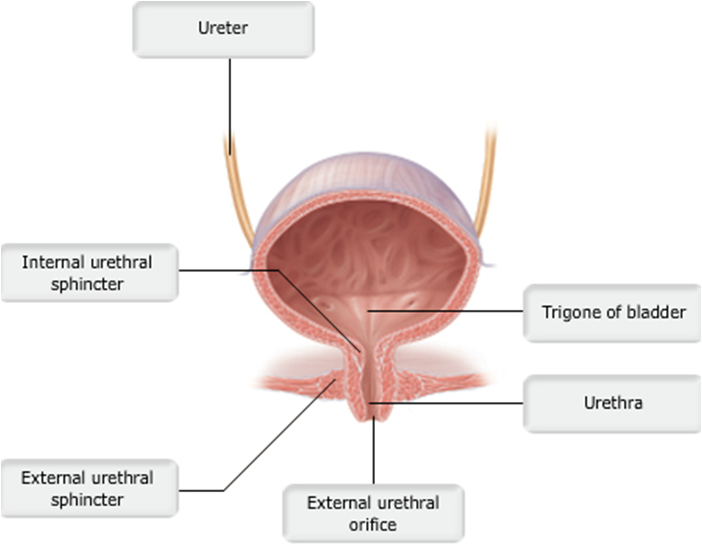 Urinary bladder (female) | back 49 pic |
front 50 Each nephron consists of a _______________, which is a tuft of capillaries, and a ___________.
| back 50 d. glomerulus; renal tubule |
front 51 Which of the following congenital abnormalities of the urinary system is found in male infants only?
| back 51 a. Hypospadias |
front 52 Under normal conditions, the proximal convoluted tubule reabsorbs all of the glucose, lactate, and amino acids in the filtrate and 65% of the Na+ and water. T/F | back 52 True |
front 53 22 During inhalation,
| back 53 e. the diaphragm and rib muscles contract.
|
front 54 22 From which structures do oxygen molecules move from the lungs to the blood?
| back 54 e. Alveoli |
front 55 22 Which statement is correct?
| back 55 d. In the blood, oxygen is bound to hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells.
|
front 56 After blood becomes oxygenated,
| back 56 b. it returns to the heart, and is then pumped to body cells. |
front 57 Hemoglobin
| back 57 c. is a protein that can bind four molecules of oxygen. |
front 58  Position of the kidneys against the posterior body wall | back 58 pic |
front 59 m1 functional residual capacity | back 59 volume of air in lungs after normal tidal expiration |
front 60 m1 inspiratory reserve | back 60 volume that can be forced in after a tidal inhalation |
front 61 m1 tidal volume | back 61 about 500 ml |
front 62 m1 total lung capacity | back 62 about 6000 ml in an average male |
front 63 m1 vital capacity | back 63 maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after maximum inhalation |
front 64 Air moves into the lungs because __________. | back 64 the gas pressure in the lungs becomes lower than the outside pressure as the diaphragm contracts
|
front 65 Alveolar ventilation rate is __________. | back 65 the movement of air into and out of the alveoli during a particular time
|
front 66 Hemoglobin has a tendency to release oxygen where __________. | back 66 pH is more acidic
|
front 67 In the alveoli, the partial pressure of oxygen is __________. | back 67 about 104 mm Hg
|
front 68 Most of the carbon dioxide transported by the blood is __________. | back 68 converted to bicarbonate ions and transported in plasma
|
front 69 The elastic cartilage that shields the opening to the larynx during swallowing is the __________. | back 69 epiglottis |
front 70 The movement of air into and out of the lungs is called __________. | back 70 pulmonary ventilation |
front 71 Involuntary hyperventilation during an anxiety attack can cause the person to become faint because of __________. | back 71 lowered CO2 levels in the blood and consequent constriction of cerebral blood vessels |
front 72 Which of the following terms describes the increase in depth and force of breathing that occurs during vigorous exercise? | back 72 hyperpnea |
front 73 Approximately 20% of carbon dioxide is transported in the blood as __________. | back 73 carbaminohemoglobin |
front 74 Which of the following controls the respiratory rate? | back 74 medulla |
front 75 Which of the following is NOT a function of the trachealis muscle? | back 75 IT DOES NOT:
|
front 76 An example of an enzyme located in the lung capillary membrane that acts on material in the blood is __________. | back 76 angiotensin converting enzyme |
front 77 Which of the following conditions would NOT cause atelectasis? | back 77 WOULD NOT CAUSE: loss of lung elasticity
|
front 78 Airway resistance is insignificant in relationship to gas flow because __________. | back 78 the airways branch more as they get smaller, resulting in a huge total cross-sectional area |
front 79 The transpulmonary pressure is the difference between the __________ and the __________ pressure. | back 79 intrapulmonary; intrapleural |
front 80 Which of the following conditions would NOT decrease the total respiratory compliance | back 80 WOULD NOT: increase in lung compliance
|
front 81 Which of the following nonrespiratory movements would ventilate all of the alveoli? | back 81 yawning |
front 82 The dorsal respiratory group __________. | back 82 Is located dorsally at the root of cranial nerve IX
|
front 83 The pontine respiratory group is responsible for all of the following functions, EXCEPT __________. | back 83 stimulating the contraction of the diaphragm |
front 84 Which of the following would NOT be found in a "blue bloater" | back 84 weight loss |
front 85 How is Na+ reabsorbed | back 85 by active transport using ATP |
front 86 Micturition is __________. | back 86 a sacral reflex in infants
|
front 87 The most important factor affecting the glomerular filtration rate is __________. | back 87 net filtration pressure
|
front 88 When the concentration of ADH increases, __________. | back 88 less urine is produced |
front 89 Which process results in increased blood pressure in response to hormone release? | back 89 renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism |
front 90 Arrange the following structures in the correct sequence in which urine passes through them to the external environment: (1) ureter, (2) renal pelvis, (3) calyx, (4) urinary bladder, (5) urethra. | back 90 3, 2, 1, 4, 5 |
front 91 If the efferent arteriole constricts while the afferent arteriole remains unchanged, the glomerular filtration rate __________. | back 91 increases
|
front 92 The renal hilum lies on the __________ surface of the kidney. | back 92 medial |
front 93 Renal ptosis may lead to __________. | back 93 hydronephrosis due to urine backup |
front 94 All of the following are layers of the filtration membrane in the glomerular membrane, EXCEPT the __________. | back 94 renal capsule |
front 95 Which of the following is NOT part of the filtration membrane? | back 95 extraglomerular mesangial cells |
front 96 All of the following functions are carried out in the renal tubules, EXCEPT __________. | back 96 FILTRATION |
front 97 All of the following would stimulate the release of renin from granular cells, EXCEPT __________. | back 97 inhibition by the macula densa cells |
front 98 The energy needed for secondary active transport is provided by the __________. | back 98 concentration gradient established by Na |
front 99 Which of the following is the countercurrent multiplier in the kidney? | back 99 the loop of Henle of a juxtamedullary nephron |
front 100 Urea transport into the medullary collecting duct is enhanced by __________. | back 100 ADH |
front 101 Which of the following substances is the standard substance used to measure the GFR? | back 101 inulin |
front 102 Which of the following is NOT associated with primary nocturnal enuresis? | back 102 females over the age of 60 years |