Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P chapter 9
front 1 In nursemaids elbow the radial head is dislocated from the _________.
| back 1 annular ligament |
front 2 anterior longitudinal ligament is
| back 2 a wide fibrous band that connects the anterior surfaces of the adjacent vertebral bodies |
front 3 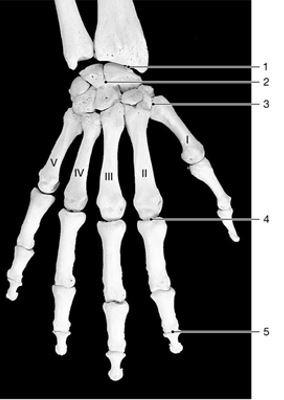 identify the type of joint at label "4"
| back 3 condylar |
front 4 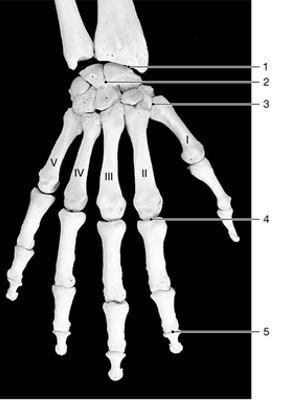 identify the type of joint at label "5"
| back 4 hinge |
front 5 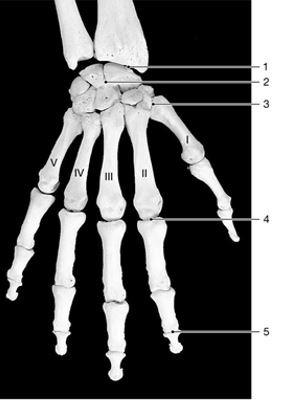 identify the type of joint at label "1"
| back 5 condylar |
front 6  identify the type of joint at label "2"
| back 6 gliding |
front 7  identify the type of joint at label "3"
| back 7 saddle |
front 8 _______ is a type of angular movement that increases the angle between bones.
| back 8 extension |
front 9 which of the following explains the occurrence of a hip fracture rather than a hip dislocation?
| back 9 stress gets transferred from head of femur to diaphysis via the thin neck |
front 10 The joints that connect the four fingers with the metacarpal bones are
| back 10 condylar joints |
front 11 The atlantoaxial joint is an example of a ________ joint.
| back 11 pivot |
front 12 Which of the following occurs when the articular cartilage is damaged?
| back 12 all of the answers are correct |
front 13 Which of the following is not a member of the rotator cuff?
| back 13 teres major |
front 14 The shoulder joint, or ________ joint, permits the greatest range of motion of any joint.
| back 14 glenohumeral |
front 15 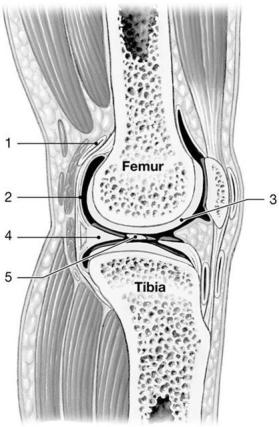 Identify the structure labeled "5"
| back 15 intracapsular ligament |
front 16  Identify the structure labeled "2"
| back 16 synovial membrane |
front 17  Identify the structure labeled "4"
| back 17 joint capsule |
front 18 An example of a synchondrosis is the articulation of the _________.
| back 18 ribs with the sternum |
front 19 The movement of rotating a limb outward is called ___________ rotation.
| back 19 lateral |
front 20 The supraspinous ligament is
| back 20 a longitudinal fibrous band that is attached to the tips of spinous processes from C7 to the sacrum |
front 21 The joint between the forearm bones and the wrist is a ________ joint.
| back 21 condylar |