Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&p 2 Test 4 Digestive System
front 1 The primary dentition consists of _____ teeth. | back 1 20 |
front 2 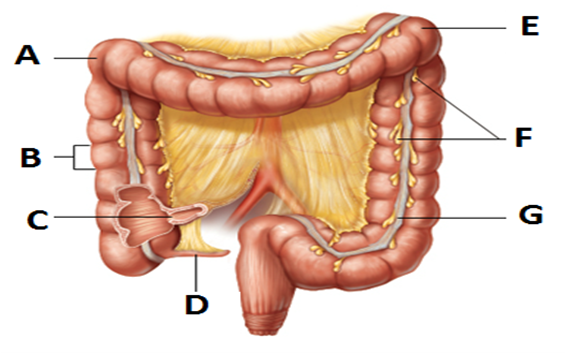 Gross Anatomy of large intestine | back 2 a. right colic (hepatic) flexure
|
front 3 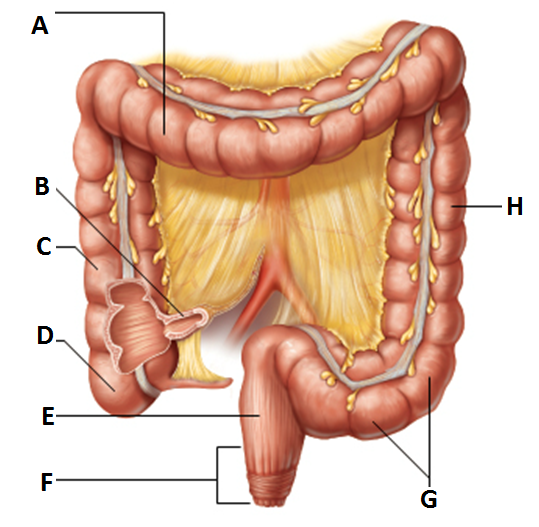 Gross Anatomy of large intestine | back 3 a. Transverse colon
|
front 4 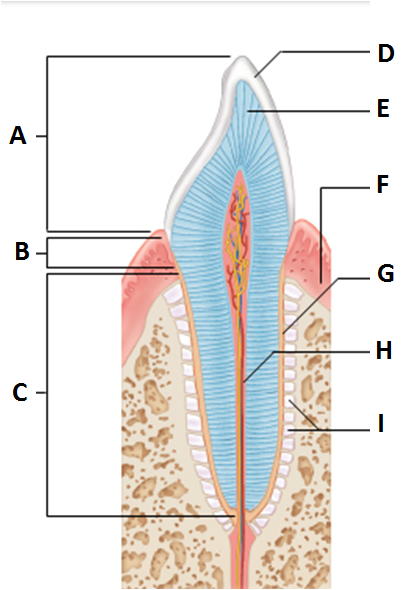 Anatomy of a tooth | back 4 a. Crown
|
front 5 Absorbed lipids are transported from intestinal epithelial cells to the lymphatic system in what form?
| back 5 d. in the form of chylomicrons |
front 6 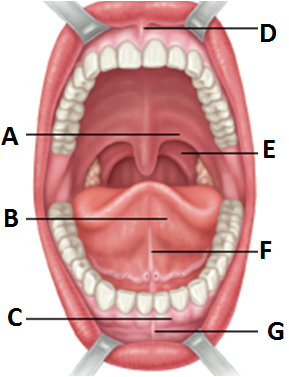 Anterior view of mouth | back 6 a. Palatoglossal arch
|
front 7 The primary function of the large intestine is: | back 7 defecation |
front 8 Which digestive process normally occurs only in the mouth?
| back 8 d. ingestion |
front 9 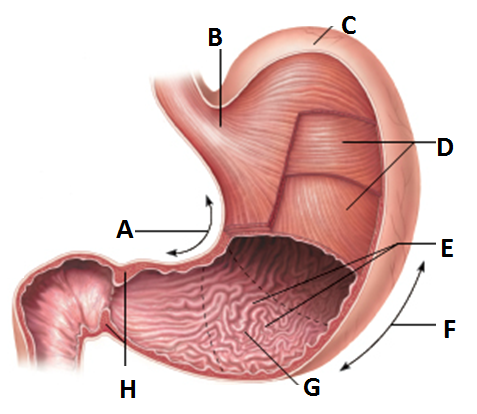 Anatomy of the stomach | back 9 a. Lesser curvature
|
front 10 Proteins are digested into: | back 10 Amino acids |
front 11 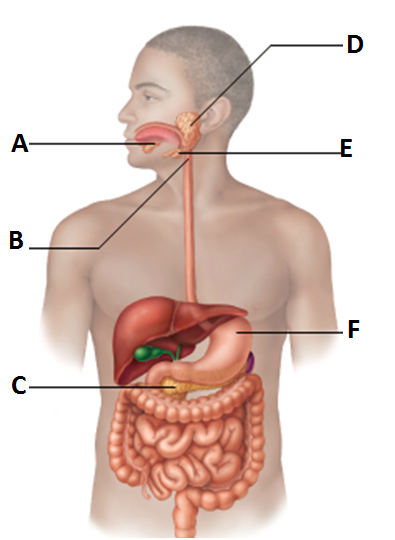 Alimentary canal & *accessory organs | back 11 a. Sublingual gland
|
front 12 Saliva does not:
| back 12 d. aid in the chemical digestion of proteins. |
front 13 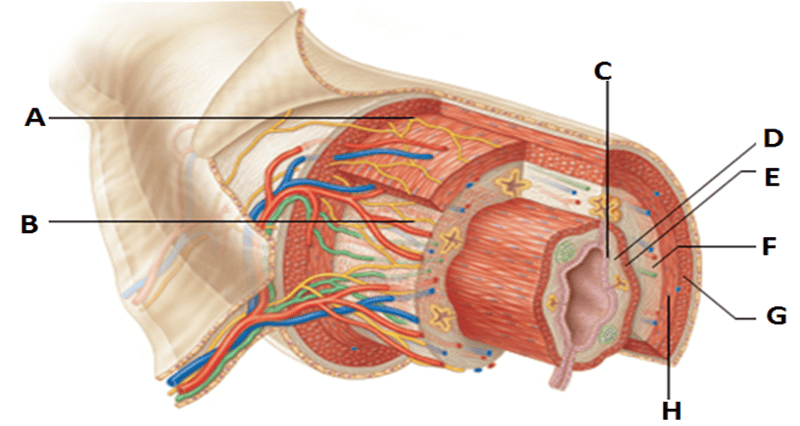 Alimentary canal-basic structure | back 13 a. Myenteric nerve plexus
|
front 14 pci | back 14 no data |
front 15 Which part of the digestive system is the major location for absorption of the end products of digestion?
| back 15 d. small intestine |
front 16 How are fats absorbed into the blood?
| back 16 d. in the form of chylomicrons |
front 17 Which organ of the digestive tract is the body's major digestive organ? | back 17 small intestines |
front 18 Which of the following are mismatched?
| back 18 d. protease: lipid digestion |
front 19 Which enzymes are responsible for the final chemical breakdown of carbohydrates, amino acids, and nucleic acids?
| back 19 c. brush border enzymes |
front 20 ______ can result if food passes too slowly through the large intestine.
| back 20 c. Constipation |
front 21 The _______ circulation includes all of the arteries that serve the digestive organs.
| back 21 c. splanchnic |
front 22 The liver is able to regenerate even after 50% of its original mass is lost. T/F | back 22 True |
front 23 Pic layers of stomach wall | back 23 no data |
front 24 PIC Alimentary canal 2 | back 24 no data |
front 25 A function of the large intestine is to:
| back 25 c. absorb water. |
front 26 Which part of the digestive system is the major location for absorption of the end products of digestion?
| back 26 c. small intestine |
front 27 What is the function of the bacterial flora that inhabit the large intestine?
| back 27 b. Bacterial flora synthesize B-complex vitamins and some of the vitamin K needed by the liver. |
front 28 In the ________ of gastric secretion, chyme is moved into the duodenum.
| back 28 b. intestinal phase |
front 29 The innermost tissue layer of the alimentary canal is the __________.
| back 29 d. mucosa |
front 30 PIC Gastric pits and gastric glands | back 30 no data |
front 31 PIC Mesenteries of the abdom. digestive organs | back 31 no data |
front 32 Bacteria that reside in the large intestine make vitamin K. T/F | back 32 T |
front 33 The major means of propelling food through the digestive tract is ___________.
| back 33 b. peristalsis
|
front 34 Bile is produced by the:
| back 34 c. liver. |
front 35 Which vitamins are made by the bacteria in the large intestine? | back 35 B complex and K |
front 36 PIC The 4 layers of the alimentary canal | back 36 no data |
front 37 The _______ is the serous membrane that lines the body wall.
| back 37 b. parietal peritoneum |
front 38 Which of the following is not a structural modification of the small intestine to increase surface area?
| back 38 c. Rugae |
front 39 Which of the following processes occurs only in the large intestine?
| back 39 d. defecation |
front 40 The major means of propelling food through the digestive tract is __________. | back 40 peristalsis |
front 41 Proteins are digested into ______.
| back 41 d. Amino acids |
front 42 Blood drained from the stomach is more alkaline (basic) than blood that serves the stomach. T/F | back 42 True! |
front 43 The_________ is the last segment of the small intestine.
| back 43 d. ileum |
front 44 What role of the stomach is essential to life?
| back 44 c. production of intrinsic factor |
front 45 Which of the following is a water-soluble vitamin?
| back 45 d. Vita C |
front 46 What is the major digestive function of the pancreas?
| back 46 d. production of digestive enzymes |
front 47 Which of the following is not a characteristic of the stomach?
| back 47 a. The stomach releases enzymes to digest carbohydrates. |
front 48 Which histological layer of the digestive tract is composed primarily of epithelial tissue?
| back 48 c. mucosa |
front 49 Which of the following is considered to be an accessory organ of the digestive system?
| back 49 c. Gallbladder |
front 50 Enzymatic breakdown of which of the following compounds doesn’t begin until it reaches the stomach?
| back 50 a. proteins |
front 51 Which of the following enzymes is important for breaking down protein?
| back 51 a. pepsin
|
front 52 Which of the following enzymes is important for the digestion of fat?
| back 52 c. pancreatic lipase
|
front 53 In the small intestine, which of the following enzymes breaks down maltose?
| back 53 b. glucoamylase
|
front 54 The breakdown products of which of the following are absorbed into lacteals?
| back 54 b. fats
|
front 55 The pancreas secretes:
| back 55 a. procarboxypeptidase. |
front 56 The nervous system does not regulate digestive activity. t/f | back 56 false |
front 57 The _______ guards the entry of food into the stomach.
| back 57 a. cardiac sphincter |