Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Procedures
front 1 Which of the following radiologic procedures requires that a contrast medium be injected into the renal pelvis via a catheter placed within the ureter? Retrograde urography Nephrotomography IVU | back 1 Retrograde urography |
front 2 Which of the following statements is (are) correct regarding the parietoacanthial projection (Waters' method) of the skull? 1. The head is rested on the extended chin. 2. The orbitomeatal line (OML) is perpendicular to the (IR). 3. The maxillary antra should be projected above the petrosa. | back 2 1. the head is rested on the extended chin, 3. the maxillary antra should be projected above the petrosa. |
front 3 In the RPO position of the cervical spine, which anatomy is demonstrated: (1) Left intervertebral foramina (2) Right pedicles (3) Right intervertebral foramina (4) Left pedicles | back 3 1. Left intervertebral foramina, 4. Left pedicles |
front 4 The bilateral AP "frog leg" position of the femoral neck places the patient in a supine position with the femora: 1- adducted 40 degrees from the horizontal 2- abducted 25 degrees from the vertical 3- abducted 40 degrees from the vertical | back 4 3- abducted 40 degrees from the vertical |
front 5 To demonstrate the first two cervical vertebrae in the AP recumbent projection, the patient is positioned so that: 1- A line between the maxillary occlusal plane and the mastoid tip is vertical. 2- The acanthiomeatal line is vertical 3- A line between the mentum and the mastoid tip is vertical. | back 5 1- A line between the maxillary occlusal plane and the mastoid tip is vertical. |
front 6 The ideal position for demonstrating polyps and ulcers of the pylorus, duodenal bulb, and C-loop of the duodenum: PA Right Lateral LPO RAO | back 6 RAO |
front 7 Single contrast BE studies are likely to demonstrate: 1- anatomy/tonus 2- mucosa 3- intraluminal lesions | back 7 1- anatomy/tonus |
front 8 For the average patient, the CR for a lateral projection of a barium-filled stomach should enter: 1- midway between the mid-coronal line and the anterior abdominal surface 2- Perpendicular to the level of L2 3- at the mid-coronal line at the level of the level of the iliac crest | back 8 1- midway between the mid-coronal line and the anterior abdominal surface |
front 9 The junction of articulation between the lambdoidal suture and the squamosal suture exists between what bones? At the junction of the temporal, parietal, and occipital At the junction of the occipital, frontal, and temporal | back 9 At the junction of the temporal, parietal, and occipital |
front 10 Which of the following projections of the hand places the thumb in an oblique position? PA oblique, external rotation PA Lateral in extension | back 10 PA oblique, external rotation |
front 11 Blunting of the costophrenic angles seen on a PA projection of the chest can be an indication of: 1- Ascites 2- Emphysema 3- Pleural Effusion | back 11 3- Pleural Effusion |
front 12 Some common mild side effects of intravenous administration of water-soluble iodinated contrast agents include: 1. Flushed feeling 2. Bitter taste 3. Urticaria | back 12 1. Flushed feeling, 2. Bitter taste |
front 13 To obtain an exact axial projection of the clavicle, place the patient 1- supine and angle the central ray 15° cephalad. 2- in a lordotic position and direct the central ray at right angles to the coronal plane of the clavicle. 3- supine and angle the central ray 30° caudally. | back 13 2- in a lordotic position and direct the central ray at right angles to the coronal plane of the clavicle. |
front 14 A patient is usually required to drink barium sulfate suspension to demonstrate which of the following structures? 1. Esophagus 2. Pylorus 3. Ilium | back 14 1. Esophagus 2. Pylorus 3. Ilium |
front 15 Which surface of the forearm must be adjacent to the IR to obtain a lateral projection of the fourth digit/finger with optimal recorded detail? Medial | back 15 Medial |
front 16 To position a patient for a Danelius-Miller axiolateral cross-table projection of the hip: The knee and the hip of the unaffected leg are flexed and elevated. | back 16 The knee and the hip of the unaffected leg are flexed and elevated. |
front 17 Which of the following structures is (are) located in the right upper quadrant (RUQ)? 1. Spleen 2. Gallbladder 3. Hepatic flexure | back 17 2. Gallbladder, 3. Hepatic flexure |
front 18 To radiograph an infant for suspected free air within the abdominal cavity, which of the following projections of the abdomen will demonstrate the condition with the least patient exposure? Left lateral decubitus without grid | back 18 Left lateral decubitus without grid |
front 19 Which of the following statements is (are) true regarding the PA axial projection (Caldwell) of the cranium? 1. The central ray is directed caudally to the OML. 2. The petrous pyramids are projected into the lower third of the orbits 3. The frontal sinuses are visualized | back 19 1. The central ray is directed caudally to the OML. 2. The petrous pyramids are projected into the lower third of the orbits 3. The frontal sinuses are visualized |
front 20 Which of the following is a major advantage of the double-contrast UGI examination over the single-contrast UGI? Small lesions on the mucosa are better demonstrated | back 20 Small lesions on the mucosa are better demonstrated |
front 21 The tarsometatarsal joins have Ginglymus ( Hinge) movements? False | back 21 False |
front 22 Which of the following positions will most effectively move the gallbladder away from the vertebrae in an asthenic patient? LAO | back 22 LAO |
front 23 The innominate bone is located in the pelvis | back 23 pelvis |
front 24 What is the position of the stomach in a hypersthenic patient High and Horizontal | back 24 High and Horizontal |
front 25 Which of the following positions/projections is most likely to offer the best visualization of the pulmonary apices? AP axial lordotic | back 25 AP axial lordotic |
front 26 Spondylolysis is the dissolution of a vertebra, such as from aplasia True | back 26 True |
front 27 Which of the following are the most common routine projection/position (s) for demonstration of the sternum? Right anterior oblique and lateral | back 27 Right anterior oblique and lateral |
front 28 A patient presents with a potential intertrochanteric hip fracture. After the technologist has taken an initial AP projection, which of the following is the best way to proceed? Use a cross-table lateral projection, with the central ray directed perpendicular to the femoral neck | back 28 Use a cross-table lateral projection, with the central ray directed perpendicular to the femoral neck |
front 29 Although they are both classified as synovial joints, the hip joint is ______ while sacroiliac joints are ______. diarthrotic; amphiarthrotic | back 29 diarthrotic; amphiarthrotic |
front 30 Which of the following conditions would require an increase in exposure factors? 1. Congestive Heart Failure 2. Pleural Effusion 3. Emphysema | back 30 1. Congestive Heart Failure, 2. Pleural Effusion |
front 31 Which of the following sinus groups is best demonstrated with the patient positioned for a parietoacanthial projection (Waters method) with the CR directed through the patient's open mouth? Sphenoidal | back 31 Sphenoidal |
front 32 In what order should the following studies be conducted? 1. Barium Enema 2. Intravenous urogram 3. UGI | back 32 2,1,3 |
front 33 Which of the following positions would demonstrate the right lumbar zygapophyseal articulations closest to the IR? RPO | back 33 RPO |
front 34 Correct preparation for a patient scheduled for an UGI series is most likely to be NPO after midnight | back 34 NPO after midnight |
front 35 In which of the following conditions is a double-contrast BE essential for the demonstration of the condition? 1. Polyps 2. Colitis 3. Diverticulosis | back 35 1. Polyps, 2. Colitis |
front 36 With the patient in PA position and the OML and The CR perpendicular to the IR, the resulting image will demonstrate the petrous pyramids. completely within the orbits | back 36 completely within the orbits |
front 37 Fractures that can be due to trauma, osteoporosis, or metastatic disease could be 1- Stress Fractures 3- Compression Fractures | back 37 1- Stress Fractures 3- Compression Fractures |
front 38 The liver is in the Upper Right Quadrant | back 38 Upper Right Quadrant |
front 39 All of the following bones are associated with condyles except the Fibula | back 39 Fibula |
front 40 Visualization of the nasal bones is best demonstrated with a Lateral Projection of both sides Parietoacanthial Projection, Waters Method | back 40 Lateral Projection of both sides Parietoacanthial Projection, Waters Method |
front 41 Shoulder arthrography is performed to : 1. evaluate humeral luxation 2. demonstrate complete or partial rotator cuff tear 3. evaluate the glenoid labrum | back 41 2. demonstrate complete or partial rotator cuff tear, 3. evaluate the glenoid labrum |
front 42 Which of the following precautions should be observed when radiographing a patient who has sustained a traumatic injury to the hip? 1. When a fracture is suspected, any required manipulation of the affected extremity must be performed by a physician. 2. The axiolateral projection should be avoided. 3. To evaluate the entire region, the pelvis typically is included in the initial examination. | back 42 1. When a fracture is suspected, any required manipulation of the affected extremity must be performed by a physician, 3. To evaluate the entire region, the pelvis typically is included in the initial examination. |
front 43 Which is the portion of the alimentary canal where digestion and the absorption of the food occur? Small Intestine | back 43 Small Intestine |
front 44 Where is the center of the IR positioned for the AP abdominal radiograph done in the Upright position? 2 inches above iliac crests | back 44 2 inches above iliac crests |
front 45 A 6-year-old patient aspirated a coin. Which bronchus would the coin most likely enter and why? The right because it is more vertical | back 45 The right because it is more vertical |
front 46 Which position will best demonstrate the lumbar intervertebral foramina? Lateral Position Lumbar Projection | back 46 Lateral Position Lumbar Projection |
front 47 Contrast agents that can be used during excretory urography include all of the following except: Barium Sulfate | back 47 Barium Sulfate |
front 48 Which of the following radiographic procedures uses an intrathecal route of introducing a drug or contrast medium? Myleogram | back 48 Myleogram |
front 49 A substance or method used to cleanse the large bowel prior to a barium enema is called 1. a cathartic 2. a cleansing enema 3. a purgative | back 49 1. a cathartic 2. a cleansing enema 3. a purgative |
front 50 Which of the following conditions is characterized by "flattening" of the hemidiaphragms? Emphysema | back 50 Emphysema |
front 51 The articular facets of L5-S1 are best demonstrated in a/an: 30° oblique | back 51 30° oblique |
front 52 What part of the "Scotty dog," seen in a correctly positioned oblique lumbar spine, represents the lumbar transverse process? Nose | back 52 Nose |
front 53 Elements of correct positioning for PA projection of the chest include: 1. weight evenly distributed on feet 2. elevation of the chin 3. shoulders elevated and rolled forward | back 53 1 and 2 only |
front 54 Which position of the shoulder demonstrates the lesser tubercle in profile medially? Internal rotation | back 54 Internal rotation |
front 55 When performing the AP projection of the scapula, The central ray should be directed toward a point 2 inches __________ to the Coracoid process Inferior | back 55 Inferior |
front 56 Which of the following examinations involves the introduction of a radiopaque contrast medium through a uterine cannula? Hysterosalpingogram | back 56 Hysterosalpingogram |
front 57 Correct preparation for a patient scheduled for a lower GI series is most likely to be cathartics and cleansing enemas | back 57 cathartics and cleansing enemas |
front 58 Which of the following is/are effective in reducing exposure to sensitive tissues for frontal views during scoliosis examinations? 1. Use of PA position 2. Use of breast shields 3. Use of compensating filtration | back 58 1. Use of PA position 2. Use of breast shields 3. Use of compensating filtration |
front 59 Which of the following examinations most likely would be performed to diagnose Wilms' tumor? IVU | back 59 IVU |
front 60 Which of the following is a functional study used to demonstrate the degree of AP motion present in the cervical spine? Flexion and extension laterals | back 60 Flexion and extension laterals |
front 61 In a lateral projection of the nasal bones, the CR is directed half inch distal to the nasion | back 61 half inch distal to the nasion |
front 62 Deoxygenated blood from the head and thorax is returned to the heart by the superior vena cava | back 62 superior vena cava |
front 63 What projection of the calcaneus is obtained with the leg extended, the plantar surface of the foot vertical and perpendicular to the IR, and the CR directed 40 degrees cephalad? Axial plantodorsal projection | back 63 Axial plantodorsal projection |
front 64 With a patient in the PA position and the OML perpendicular to the table, a 15 degree-20 degree caudal angulation would place the petrous ridges in the lower third of the orbit. To achieve the same result in an infant or a small child, it is necessary for the radiographer to modify the angulation to 10 degree-15 degree caudal | back 64 10 degree-15 degree caudal |
front 65 A patient unable to extend his or her arm is seated at the end of the x-ray table, elbow flexed 90 degrees. The CR is directed 45 degrees medially. Which of the following structures will be demonstrated best? 1. Radial head 2. Capitulum 3. Coronoid Process | back 65 1 and 2 only |
front 66 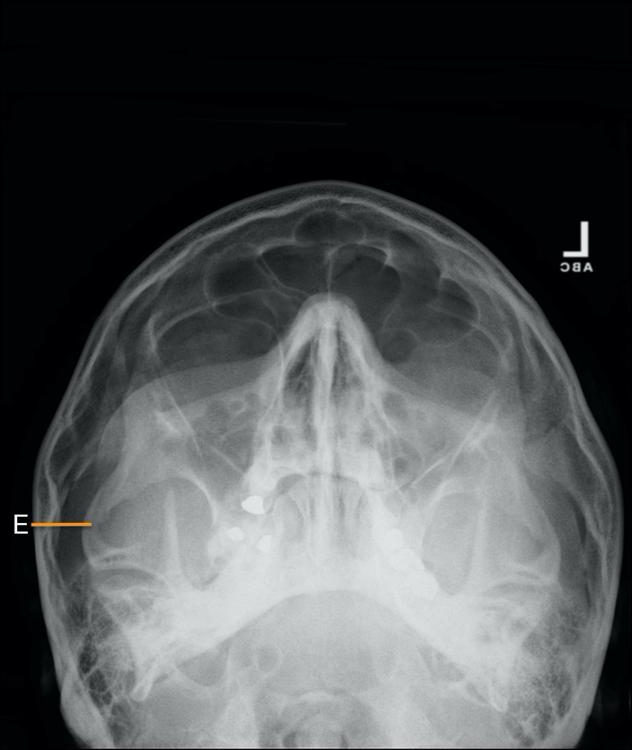 Identify the structure that is identify by letter E:
| back 66
|
front 67 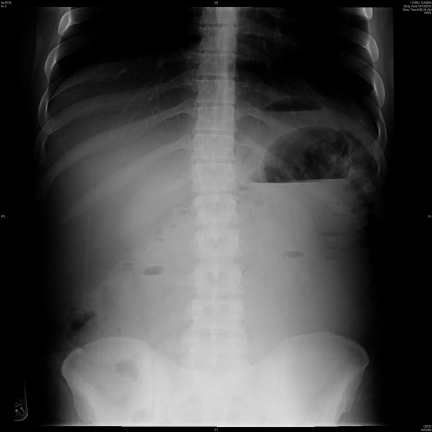 What is the patient position utilized in this radiograph?
| back 67
|
front 68 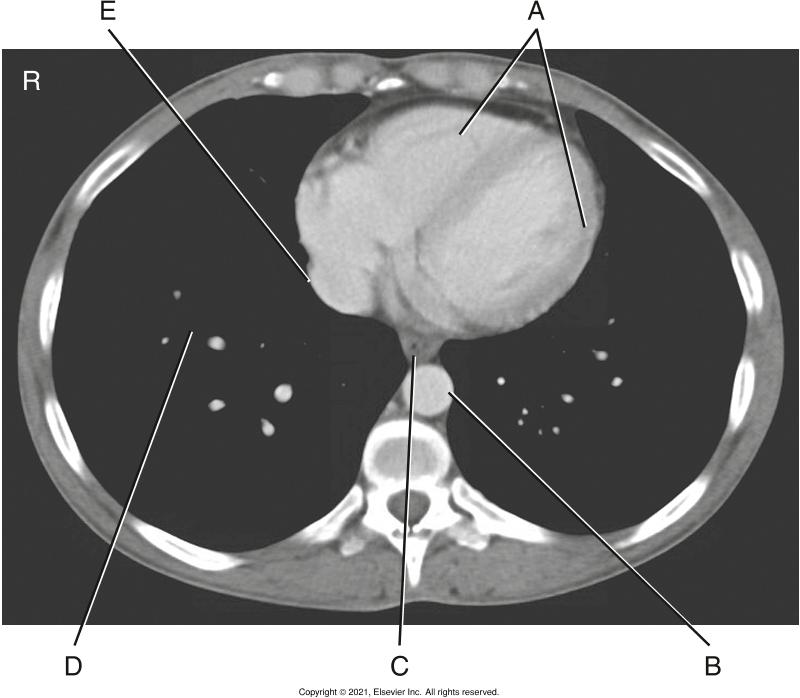 In the image below letter B is the?
| back 68 Descending aorta |
front 69  Identify the structure that is mark as an letter A
| back 69 Air-filled trachea and larynx |
front 70 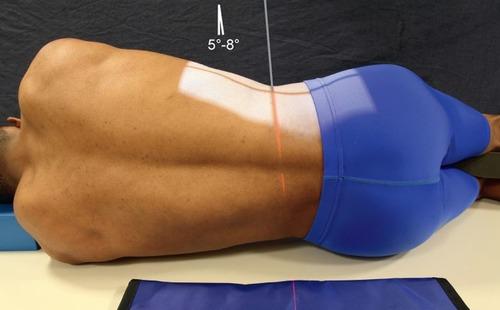 Which of the positions illustrated in Figures A will best demonstrate the lumbar intervertebral foramina? 1- Lateral position lumbar projection 2- Left Anterior Oblique Position 3- Left Posterior Oblique Position | back 70 1- Lateral position lumbar projection |