Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
BIOLOGY 1307 Final Exam Review
front 1 Protocells are fluid filled with a surrounding membrane and contain DNA. | back 1 False |
front 2 The first genetic material on early Earth was most likely | back 2 RNA. |
front 3 Which of the following is an accurate characteristic of bacterial cell walls? | back 3 They prevent cells from shrinking in hypertonic environments. |
front 4 Gram-positive bacteria have which characteristics? | back 4 Thick peptidoglycan layer and stain darkly |
front 5 What structure protects Bacillus anthracis to survive in extreme environments like those without nutrients for decades? | back 5 Endospores |
front 6 Bacteria are able to adhere to substrates and to other individuals by using fimbrae. | back 6 True |
front 7 Which statement about the genomes of prokaryotes is correct? | back 7 Prokaryotic genomes are composed of circular DNA. |
front 8 Which of the following describes an organism that obtains energy from light? | back 8 phototroph |
front 9 Why can prokaryotic population numbers be magnitudes larger than populations of multicellular eukaryotes? | back 9 Prokaryotes are small, reproduce by binary fission, and often have short generation times. |
front 10 Suppose bacteria are grown on a petri dish that contains nutrient agar and the antibiotic ampicillin. After observing the bacteria growth on the plate for two days, you notice that only some of the bacteria have survived. What is a plausible explanation for your observations? | back 10 The bacteria that survived were transformed with a plasmid that contains the resistance gene for ampicillin. |
front 11 What is one key difference between transformation and conjugation? | back 11 Transformation is uptake of DNA from the environment and conjugation is exchange DNA between prokaryotes. |
front 12 The main difference between endotoxins and exotoxins is that endotoxins are released when the bacterium dies, whereas exotoxins are proteins that are secreted by living bacteria. | back 12 True |
front 13 The interactions of prokaryotes with humans are | back 13 both negative and positive. |
front 14 Which of these observations gives the most support to the endosymbiotic theory for the origin of eukaryotic cells? | back 14 the similarity between the ribosomes of prokaryotes and the ribosomes within mitochondria and chloroplasts |
front 15 Sponges are most accurately described as | back 15 filter feeders. |
front 16 Ribozymes are DNA molecules that can catalyze reactions | back 16 False |
front 17 Some members of this group have an "excavated" feeding groove on one side of the cell body | back 17 Excavata |
front 18 Comparisons of choanoflagellate and animal genome sequences tell us that key steps in the transition to multicellularity in animals | back 18 involved new ways of using proteins or parts of proteins that were encoded by genes |
front 19 Phytoplankton blooms are caused by | back 19 an abundance of nitrogen and phosphorus found in fertilizer run-off |
front 20 Green algae differ from land plants in that some green algae | back 20 are unicellular. |
front 21 Of the four supergroups of eukaryotes, which one contains red algae, green algae, and all land plants? | back 21 Archeplastida |
front 22 The first multicellular organisms were collections of connected cells with a vast amount of differentiation | back 22 False |
front 23 Which of the following are correctly described as a primary producers? | back 23 Diatoms, dinoflagellates, multicellular algae, and other protists |
front 24 The life cycle of the malarial parasite, Plasmodium, includes | back 24 two stages of development: in mosquitos and humans |
front 25 Sponges are most accurately described as | back 25 filter feeders. |
front 26 The most ancient branch point in animal phylogeny is that between having | back 26 true tissues and no tissues. |
front 27 Of the four supergroups of eukaryotes, which one contains red algae, green algae, and all land plants? | back 27 Archeplastida |
front 28 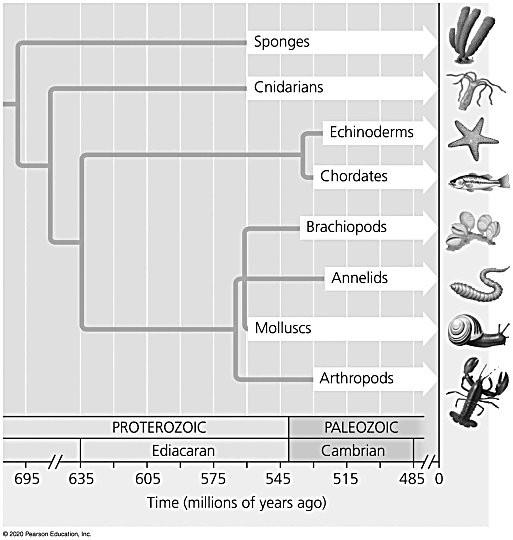 Using the figure above, what is the minimum age of the common ancestor of Sponges and Cnidarians? | back 28 695 million years |
front 29 Bilateral symmetry has only one imaginary slice divides the animal into two mirror-image halves | back 29 True |
front 30 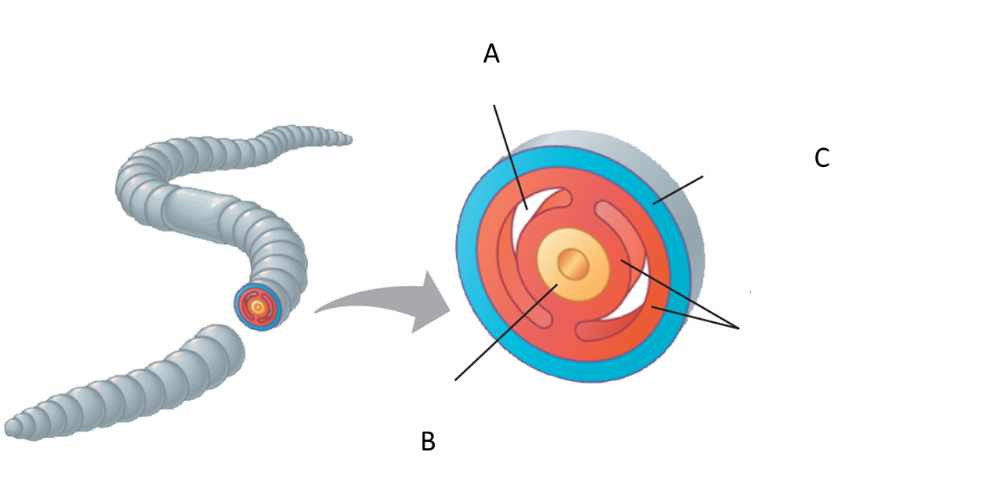 In the figure above, what tissue type does B refer to? | back 30 Endoderm |
front 31 The body of the mollusk has three main parts: ____________________. | back 31 Visceral mass, foot, and mantle |
front 32 The chorion of amniotes functions to provide | back 32 gas exchange |
front 33 Marsupials are | back 33 are born early and complete development nursing from a nipple |
front 34 Upright posture, bipedal locomotion, and complex tool usage traits associated with | back 34 Homo sapiens |
front 35 Xylem, a vascular tissue, performs transport of food. | back 35 False |
front 36 Which tissue is responsible for plant growth? | back 36 meristem |
front 37 Lateral branches, thorns, or flowers on the shoot and vertical roots on the rhizome produce from the | back 37 axillary bud. |
front 38 Mature cork cells deposit a waxy substance called ________ in cell walls. | back 38 suberin |
front 39 Arrange the following steps of cell differentiation during plant
growth (in length) in the correct sequence. | back 39 ii, i, iv, iii |
front 40 If a plant is infected with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, what is the most probable effect on the plant? | back 40 It will likely grow faster than an uninfected plant. |
front 41 ________ is to xylem as ________ is to phloem. | back 41 Vessel element; sieve-tube member |
front 42 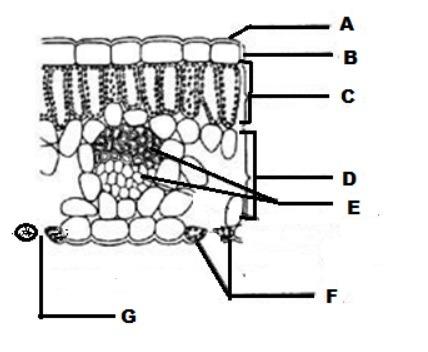 What does 'F' represent? | back 42 Guard Cells |
front 43 Which of the following is considered an organic fertilizer? | back 43 manure |
front 44 Phloem transport is described as being from source to sink. Which of
the following would most accurately complete this statement about
phloem transport as applied to most plants in the late spring? | back 44 sugars; leaf; apical meristem |
front 45 Epiphytes are plants that live in poor soil and digest insects to obtain nitrogen | back 45 False |
front 46 The water and minerals in the xylem vessels transported by | back 46 bulk flow. |
front 47 The cuticle on the surface of epidermis of leaves is an adaptation for plants to conserve | back 47 water |
front 48 The dominant chemical in phloem sap is (are) | back 48 sucrose. |
front 49 The cork cambium replaces which of the following tissues during the plant growth? | back 49 epidermis |
front 50 The rise (upward mobility/transportation) of xylem sap by the cohesion-tension mechanism begins at the | back 50 leaves |
front 51 Arrange the following stages in the life cycle of an angiosperm in a correct sequence. i.gametophyte development ii.double fertilization iii.pollination iv.seed development | back 51 i, iii, ii, iv |
front 52 The products of asexual reproduction in plants are | back 52 clones, and they do not require the fusion of egg and sperm. |
front 53 The function of the cotyledon is to _______ | back 53 nourish the growing seedling. |
front 54 Microsporangia in flowering plants are located in the | back 54 stamen |
front 55 The union of a sperm cell with ________ of the female gametophyte is referred as double fertilization. | back 55 two polar nuclei |
front 56 Which of the following is a multiple fruit? | back 56 pineapple |
front 57 Increased success of offspring in a stable environment is considered an advantage of asexual reproduction in plants. | back 57 True |
front 58 The ripening of fruit and the dropping of leaves and fruit are principally controlled by | back 58 ethylene |
front 59 Why do coleoptiles grow toward light? | back 59 Auxin moves away from the light to the shady side. |
front 60 Auxins play a role in ____________. | back 60 cell elongation |
front 61 Young leaves and developing seeds are the prime sites for ________ synthesis. | back 61 gibberellin |
front 62 A long-day plant will flower only when | back 62 nights are shorter than a certain critical value. |
front 63 If a short-day plant has a critical night length of 15 hours, then which of the following 24-hour cycles will prevent flowering? | back 63 8 hours light/8 hours dark/light flash/8 hours dark |
front 64 Trichomes on certain plant species are a ________ to prevent excessive herbivory. | back 64 physical defense |
front 65 The radicle is the food storage for growing seedling. | back 65 False |
front 66 If a plant requires pollination by bees, what adaptation would be best? | back 66 Production of nectar |
front 67 During the lifecycle of an angiosperm, what type of reproduction takes place during the vegetative phase? | back 67 Asexual |
front 68 Incomplete flowers lack one or more sexual organs. | back 68 True |
front 69 A short-day plant will flower only when | back 69 nights are longer than a certain critical value. |
front 70 What is the circulatory fluid called in arthropods with open circulatory systems? | back 70 hemolymph |
front 71 If a person loses a large amount of water in a short period of time, she may die from dehydration. ADH can help reduce water loss through its interaction with its target cells in the | back 71 kidney |
front 72 A collection of tissues functioning together is an | back 72 organ |
front 73 The pulmonary circuit in mammals involved the flow of blood from the ______ to the ______. | back 73 heart; lungs |
front 74 An example of a homeostatic response is | back 74 an increase in body temperature that results from involuntary shivering. |
front 75 Which of the following develops the greatest pressure on the blood in the mammalian aorta? | back 75 systole of the left ventricle |
front 76 Sparrows (a small bird species) secrete uric acid as their form of nitrogenous waste because uric acid | back 76 requires little water for nitrogenous waste disposal, thus reducing water waste. |
front 77 An example of an organism that has only behavioral controls over its body temperature is the | back 77 rosy boa (a snake). |
front 78 The steroid hormone aldosterone affects only a small number of cells in the body because | back 78 only its target cells contain aldosterone receptors. |
front 79 How do marine fish perform osmoregulation? | back 79 through drinking water and eating food |
front 80 In animals, nitrogenous wastes are produced mostly from the catabolism of | back 80 proteins and nucleic acids. |
front 81 Abnormally reduced somatic growth (dwarfism) can be a consequence of decreased hormone secretion from the | back 81 anterior pituitary gland. |
front 82 Coordinating body functions via release of chemical signals into the vascular system is accomplished by | back 82 the endocrine system. |
front 83 What type of muscle tissue is found lining the walls of many internal organs such as blood vessels and the digestive tract? | back 83 smooth muscle |
front 84 Positive feedback differs from negative feedback in that | back 84 the positive feedback's responses amplify the response rather than inhibiting it. |
front 85 The function of platelets is to ___________. | back 85 blood clotting |
front 86 Innate immunity | back 86 is activated immediately upon infection. |
front 87 The set of blood vessels with the slowest velocity of blood flow is | back 87 the capillaries. |
front 88 Engulfing-phagocytic cells of innate immunity include all of the following except | back 88 natural killer cells. |
front 89 Adaptive immunity depends on | back 89 pathogen-specific recognition. |
front 90 B cells have antigen receptors that bind to antigens that are either freely dissolved or present on the surface of invading/foreign cells. T cells have antigen receptors that | back 90 bind to antigen fragments presented on major histocompatibility complexes by host cells. |
front 91 Antigens are | back 91 foreign molecules that trigger the generation of antibodies. |
front 92 Immunological memory accounts for | back 92 the ancient observation that someone who had recovered from the plague could safely care for those newly diseased. |
front 93 HIV is such a devastating virus because ____________. | back 93 it destroys helper T cells (CD4) |
front 94 Antibodies function to bind and kill pathogens | back 94 False |
front 95 For the successful development of a vaccine to be used against a pathogen, it is necessary that | back 95 the surface antigens of the pathogen do not change. |
front 96 A key part of the humoral immune response is | back 96 the production of antibodies by plasma cells. |
front 97 Activation of cytotoxic T cells requires binding to a MHC receptor on an antigen presenting cell. | back 97 True |
front 98 Naturally acquired passive immunity results from the | back 98 transfer of antibodies in breast milk. |
front 99 An example of a pathogen that undergoes rapid changes resulting in antigenic variation is | back 99 the influenza virus, which expresses alternative envelope proteins. |
front 100 Activation of helper T cells by an antigen will directly activate | back 100 B cells and cytotoxic T cells only. |
front 101 Asexual reproduction results in greater reproductive success than does sexual reproduction when | back 101 a species is in stable and favorable environments. |
front 102 Environmental cues that influence the timing of reproduction usually directly affect hormone levels. | back 102 True |
front 103 Which of the following patterns of reproduction are found only among invertebrate animals? | back 103 fission and budding |
front 104 External fertilization often yields more offspring than does internal fertilization. However, internal fertilization offers the advantage that | back 104 the smaller number of offspring produced often receive a greater amount of parental investment. |
front 105 Chemical signals released into the environment that coordinate potential reproductive partners are called | back 105 pheromones. |
front 106 Among human males, both semen and urine normally travel along the | back 106 urethra. |
front 107 The moment of orgasm is characterized by | back 107 rhythmic contraction of many parts of the reproductive system. |
front 108 If a man is born with a blockage in his vas deferens, he may experience | back 108 low sperm count. |
front 109 The primary function of the corpus luteum is to | back 109 maintain progesterone and estrogen synthesis after ovulation has occurred. |
front 110 The vulva consists of the following structures. Please select all that apply | back 110 Labia majora and minora, Hymen, Clitoris |
front 111 These hormone levels surge during ovulation. | back 111 FSH and LH |
front 112 This male accessory gland secretes a clear mucus that neutralizes acidity in the urethra. | back 112 Bulbourethral gland |
front 113 The hypothalamic hormone that triggers the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). | back 113 False |
front 114 If gastrulation was blocked by an environmental toxin, then | back 114 embryonic germ layers would not form. |
front 115 During fertilization, the acrosomal contents | back 115 digest the protective jelly coat on the surface of the egg. |
front 116 Fertilization normally | back 116 reinstates diploidy. |
front 117 The vertebrate nervous system develops from the | back 117 ectoderm |
front 118 Most of the neurons in the human brain are | back 118 interneurons |
front 119 The cell body of a neuron contains | back 119 the nucleus and most organelles. |
front 120 Efferent neurons send information to the CNS. | back 120 False |
front 121 In a simple synapse, neurotransmitter chemicals are released by | back 121 the presynaptic membrane. |
front 122 For a neuron with an initial membrane potential at -70 mV, an increase in the movement of potassium ions out of the cytoplasm would result in the | back 122 hyperpolarization of the neuron. |
front 123 The "threshold" potential of a membrane is the | back 123 minimum depolarization needed to operate the voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels. |
front 124 Action potentials move along axons | back 124 more rapidly in myelinated than in nonmyelinated axons. |
front 125 ________ occurs when several inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) arrive at the axon hillock rapidly in sequence from a single dendritic location. | back 125 Temporal summation |
front 126 Receptors for neurotransmitters are of primary functional importance in assuring one-way synaptic transmission because they are mostly found on the | back 126 postsynaptic dendritic membrane. |
front 127 A lobster without a statocyst would not be able to | back 127 know which way is up and which is down. |
front 128 Raccoons are most active from dusk until dawn. What kinds of cells would you expect to find in the retina of a raccoon? | back 128 many more rods than cones |
front 129 After earning an A in your biology course, your instructor gives you a firm handshake. You can feel the deep pressure of the handshake, and it is so strong it even starts to hurt a little. What type(s) of receptor was (were) activated by the handshake? | back 129 mechanoreceptors and nociceptors |
front 130 What type of neuron would be abundant in the white matter in the brain and the white matter in the spinal cord? | back 130 myelinated axons |
front 131 The system that modulates excitation and inhibition of the smooth and cardiac muscles of the digestive, cardiovascular, and excretory systems is the | back 131 autonomic nervous system. |
front 132 Preparation for the "rest and digest" response includes activation of the ________ nervous system. | back 132 parasympathetic |
front 133 Afferent neuronal systems include the | back 133 sensory systems. |
front 134 This frontal lobe area is active when speech is generated | back 134 Broca's area |
front 135 The bottlenose dolphin breathes air but can sleep in the ocean because it | back 135 alternates which half of its brain is asleep and which half is awake. |
front 136 These glial cells are responsible for laying down the myelin sheaths in the central nervous system | back 136 Oligodendrocytes |
front 137 These glial cells are responsible for circulating cerebral spinal fluid. | back 137 Ependymal cells |
front 138 What does troponin bind to during excitation of muscle contraction? | back 138 calcium ions |
front 139 The "motor unit" in vertebrate skeletal muscle refers to | back 139 one motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers on which it has synapses. |
front 140 Muscle cells are stimulated by neurotransmitters released from the synaptic terminals of | back 140 motor neuron axons. |
front 141 Which of the following is the correct sequence that describes the excitation and contraction of a skeletal muscle fiber? 1. Tropomyosin moves and uncovers the cross-bridge binding
sites. | back 141 5 → 3 → 2 → 1 → 4 |
front 142 The hydrostatic skeleton of the earthworm allows it to move around in its environment by using peristaltic contractions of its circular and longitudinal muscles. | back 142 True |
front 143 Animal communication involves what type(s) of sensory information? | back 143 visual, auditory, olfactory, and tactile |
front 144 Chimpanzees indicate to each other that there are threats nearby by raising their arms in the air. What type of communication signal is this? | back 144 visual |
front 145 Salmon are hatched in freshwater streams, and then they migrate to the ocean. When an adult salmon is ready to mate, it returns to the exact stream where it hatched. What term best applies to this behavior? | back 145 imprinting |
front 146 While on a field expedition in Ethiopia, you come across a group of baboons. After watching them for several days, you notice that one male baboon frequently mates with many different females. You also don't see any other males in the group. What type of mating system best describes these baboons? | back 146 polygyny |
front 147 How do altruistic behaviors arise through natural selection? | back 147 Altruism increases the likelihood that some of its genes will be passed on to the next generation. |
front 148 In which form of locomotion is friction the greatest impediment to moving? | back 148 swimming |
front 149 Cross fostering places the young from one species in the care of adults from another species | back 149 True |
front 150 A stickleback fish will attack a fish model as long as the model has red coloring. What animal behavior idea is manifested by this observation? | back 150 sign stimulus |