Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
DNA Rep Ch 11 Connect Assignment
front 1 Two daughter molecules of DNA are the product of which process? Multiple choice question. Reverse transcription Transcription Translation DNA replication Transduction | back 1 DNA replication |
front 2 How many strands of DNA are there in a double helix? Multiple choice question. 4 2 3 1 | back 2 2 |
front 3 What are the individual building blocks of a strand of DNA called? Multiple choice question. Bases Amino acids Nucleotides Riboses | back 3 Nucleotides |
front 4 The names of the bases found in DNA nucleotides are: ____, ____, ____, and ____. | back 4 adenine or a cytosine or c thymine or t guanine or g |
front 5 The two strands of DNA in a double helix associate with one another due to ____ bonding between opposite bases in the helix and due to the nucleotides stacking on top of one another to form a ladder-like structure. | back 5 hydrogen |
front 6 Parental DNA strands are used as templates to produce daughter DNA strands during the process called ____ ____. | back 6 DNA replication |
front 7 When two strands of DNA associate to form a double helix, the bases on opposite strands of DNA interact via hydrogen bonds. Different numbers of hydrogen bonds form between the different base-pairs: there are ____ hydrogen bonds between adenine and ____, and between cytosine and ____ there are ____ hydrogen bonds. | back 7 2; thymine; guanine; 3 |
front 8 In the DNA double helix, there are ____ strands of DNA. | back 8 2 or double |
front 9 Select all that apply Which of the following are analogous to the antiparallel arrangement of strands of DNA in a double helix? Multiple select question. Two pencils laid next to one another pointing in opposite directions A single set of train tracks Two pencils laid end to end (eraser to tip, eraser to tip) A two lane, two way highway with a divider/median | back 9 Two pencils laid next to one another pointing in opposite directions A two lane, two way highway with a divider/median |
front 10 Individual strands of DNA are composed of building blocks called | back 10 nucleotides |
front 11 In a DNA double helix, one strand of DNA runs 5' to 3' and the other strand runs 3' to 5'. Because the two strands are arranged like this and never cross one another, the two strands are said to be | back 11 antiparallel |
front 12 Select all that apply What are the types of bases found in DNA? Multiple select question. Thymine Cytosine Guanine Adenine Ribose Uracil Deoxyribose | back 12 Thymine Cytosine Guanine Adenine |
front 13 Select all that apply How are the two strands of DNA held together in a double helix? Multiple select question. Ionic bonds between opposite bases Stacking of the bases on top of one another Phosphodiester bonds between opposite bases Hydrogen bonds between opposite bases | back 13 Stacking of the bases on top of one another Hydrogen bonds between opposite bases |
front 14 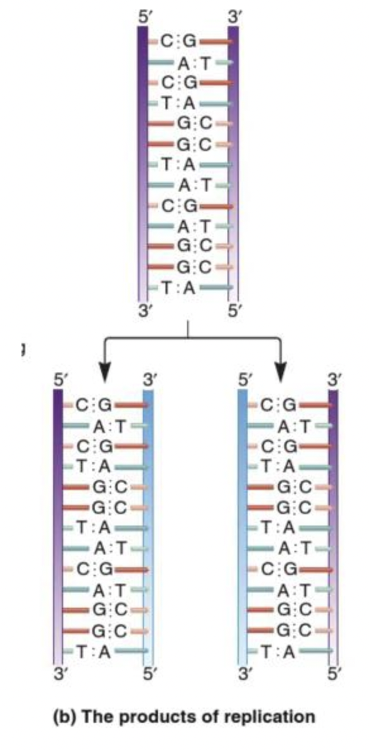 What is the name given to the strand of DNA that contains the information to make the new strand of DNA during DNA replication? Multiple choice question. The conserved strand The template strand The complementary strand The daughter strand | back 14 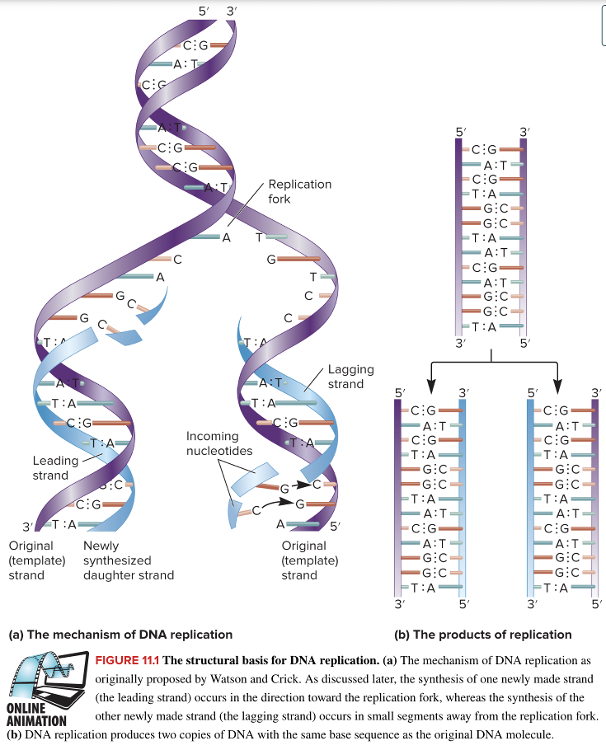 The template strand |
front 15 Select all that apply Which of the following demonstrate correct base pairing? Multiple select question. C - G with 2 hydrogen bonds A - T with 2 hydrogen bonds C - G with 3 hydrogen bonds A - T with 3 hydrogen bonds | back 15 A - T with 2 hydrogen bonds C - G with 3 hydrogen bonds |
front 16  What is the name of the new strand of DNA that is produced during DNA replication? Multiple choice question. The coding strand The daughter strand The template strand The parental strand | back 16  The daughter strand |
front 17 Escalators usually come in pairs; one moves people upwards between floors and one moves people downward between floors. Given that one goes in one direction and the other goes in the other direction, and they don't cross over one another, this is an example of something that is ______. Multiple choice question. antiparallel confluent redundant parallel complimentary | back 17 antiparallel |
front 18 Match the three proposed models of DNA replication with the correct description. Dispersive Conservative Semiconservative The daughter molecules of DNA consist of one strand of parental DNA and one complementary strand of newly formed DNA. Both strands of parental DNA remain together following replication and the daughter molecule consists of only newly synthesized DNA strands. Pieces of parental DNA and newly synthesized DNA are interspersed throughout both daughter strands in the newly formed molecule. | back 18
|
front 19 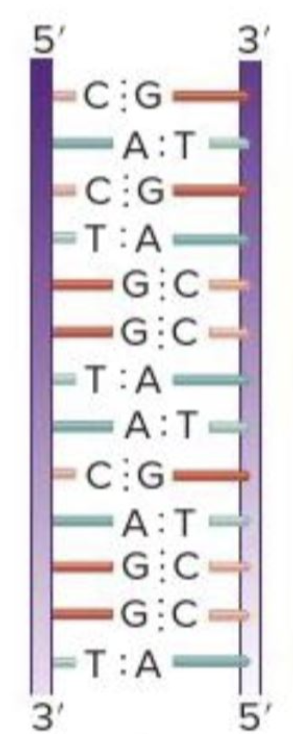 As shown in the figure, the two strands of the DNA double helix run in opposite directions: one runs 5' to 3' and the other runs 3' to 5'. Also, the two strands never cross one another. This arrangement of the two strands of DNA in a double helix as described as | back 19  antiparallel |
front 20 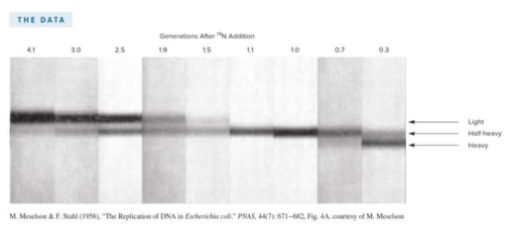 In the Meselson and Stahl experiment, E.coli was first grown in medium containing 15N compounds such that all N in the DNA contained 15N. The cells were then grown in medium containing 14N for various periods of time. The bacterial lysate was then separated by CsCl centrifugation. The experiment yielded the data in the image shown. This experiment suggested that DNA replication is | back 20  semiconservative |
front 21 The figure shows data from Meselson and Stahl's experiment to determine the mechanism of DNA replication. After one generation, which model(s) for DNA replication does the data support? Multiple choice question. Only the dispersive model Both semiconservative and dispersive models Only the conservative model Only the semiconservative model Both semiconservative and conservative models Both conservative and dispersive models | back 21 Both semiconservative and dispersive models |
front 22  The strand of DNA that contains the information used to make a new strand of DNA during DNA replication is called the ____ strand. | back 22  template |
front 23 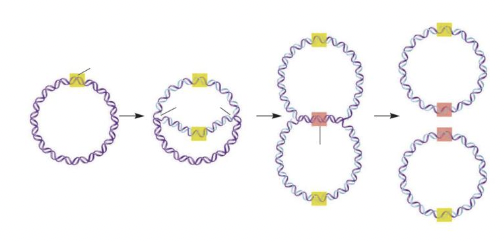 The area highlighted in yellow, where DNA replication begins, is called the ____ ____ ____. | back 23 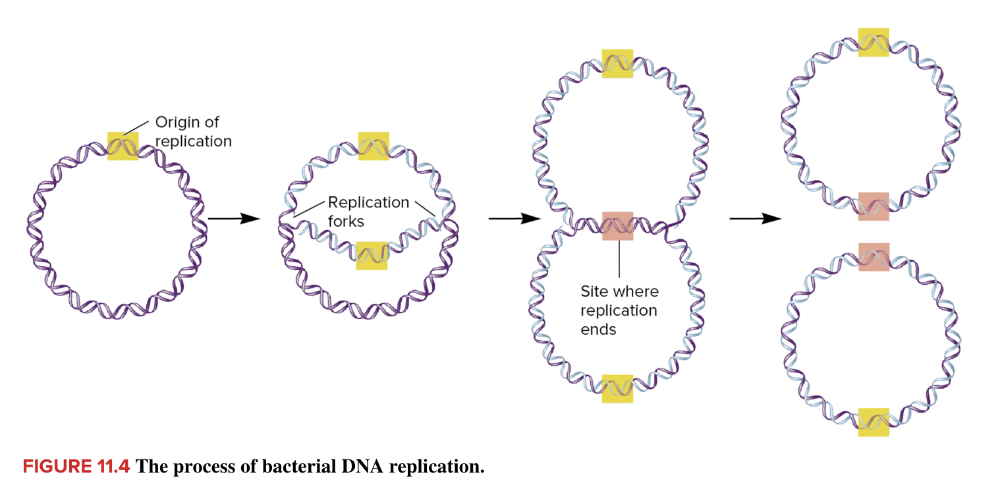 origin of replication |
front 24  The strand of DNA that is produced during DNA replication is generally called the ____ strand. | back 24  daughter |
front 25 Because DNA replication proceeds in both directions from a single origin of replication, it is said to be ____ replication. | back 25  bidirectional |
front 26 Match the three proposed types of replication with the correct figure. Instructions A B C Semiconservative model Dispersive model Conservative model | back 26 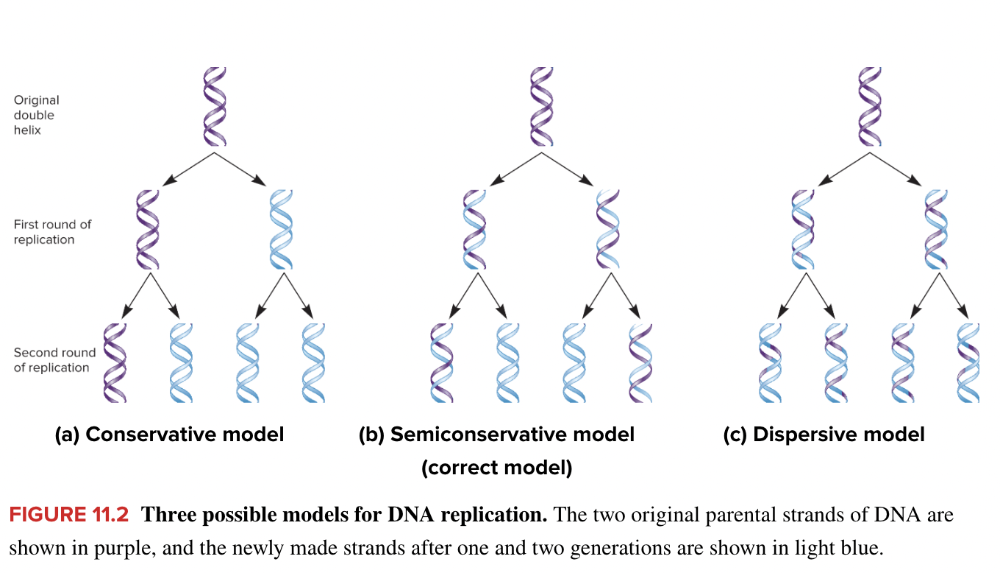
|
front 27 The sites where the parental template strands of DNA separate during replication are called the ____ ____. | back 27 replication fork |
front 28 List the steps of Meselson and Stahl's experiment, which provided evidence of semiconservative DNA replication, in the correct sequence. Lyse the cells and separate the lysate in a CsCl gradient. Add 14N to the growth medium and incubate for various lengths of time such that all newly formed DNA will contain 14N. Grow E. coli in the presence of 15N for many generations such that all of the N in the DNA is labeled with 15N. Centrifuge the gradients such that all DNA molecules reach their equilibrium densities. Observe the DNA under UV light. | back 28 1) Grow E.coli in the presence of 15N for many generations such that
all of the N in the DNA is labeled with 15N. |
front 29 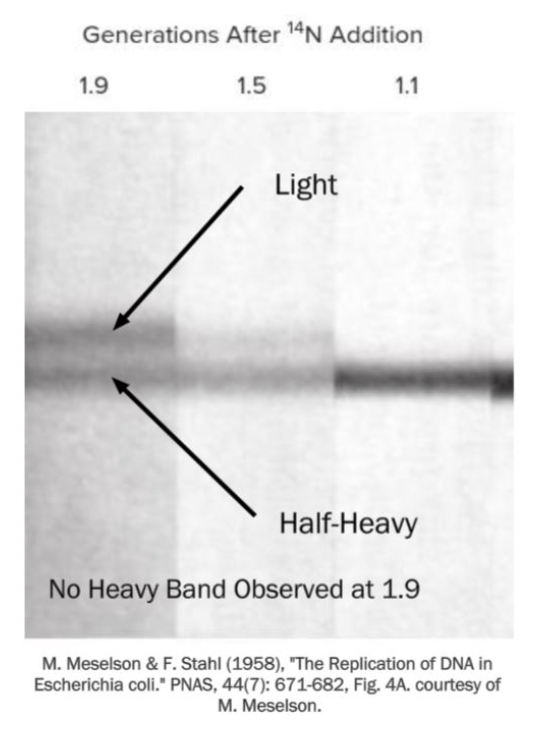 The figure shows data from Meselson and Stahl's experiment to determine the mechanism of DNA replication. After 1.9 generations, which model(s) for DNA replication does the data support? Multiple choice question. Both the conservative and dispersive models Only the conservative model Only the dispersive model Only the semiconservative model Both the semiconservative and dispersive models | back 29 Only the semiconservative model |
front 30 DNA replication begins at a site called the ____ of ____. | back 30 origin of replication |
front 31 The three types of DNA sequences located within the oriC complex are the ____ rich region, ____ box sequence and the ____ methylation site. | back 31 AT DNAa GATC |
front 32 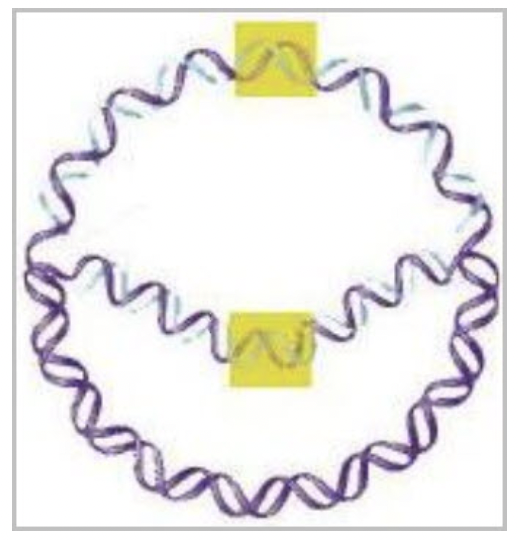 As shown in the image, bacterial DNA replication occurs ____ from a single origin of replication. | back 32  bidirectionally |
front 33 For E. coli, what occurs prior to helicase binding and creating two replication forks? Multiple choice question. DnaA proteins bind to sequences in the five DnaA boxes Initiation factors bind to the promoter mRNA binds to the ribosome DNA polymerase binds to the template strand | back 33 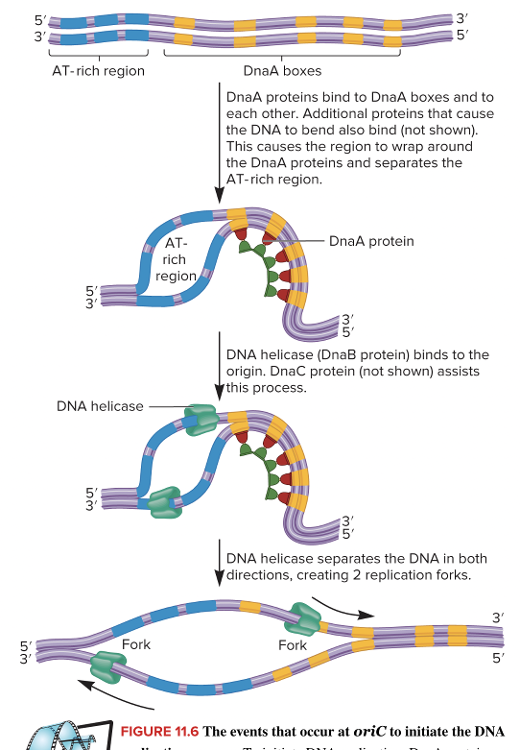 DnaA proteins bind to sequences in the five DnaA boxes |
front 34 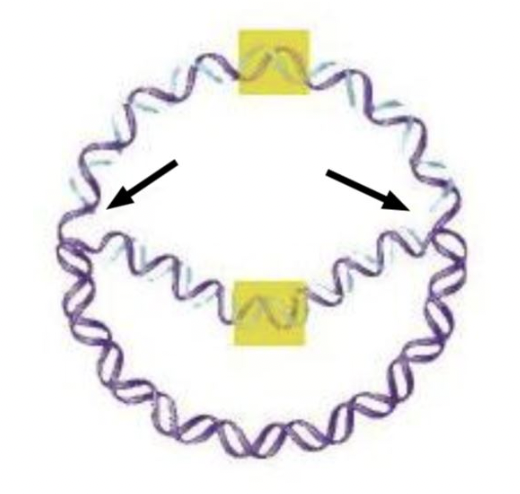 The areas at the tips of the arrows in this replicating molecule of DNA are called the ____ ____. | back 34  replication forks |
front 35 DNA helicase ______. Multiple choice question. joins two Okasaki fragments together separates double-stranded DNA into two single strands removes positive supercoils that accumulate ahead of the replication fork creates negative supercoils in DNA molecules | back 35 separates double-stranded DNA into two single strands |
front 36 The name of the enzyme that methylates the GATC methylation site within the oriC is | back 36 DAM |
front 37 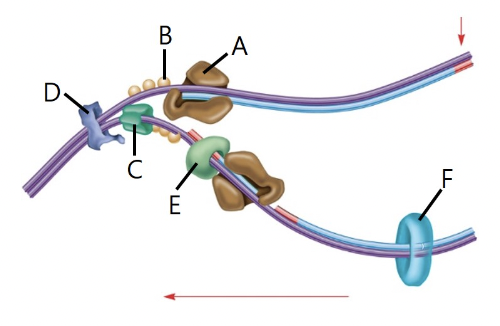 Identify the proteins shown in the image that are involved in E. coli DNA replication. A B C D E F DNA ligase DNA polymerase III Topoisomerase II Single stranded binding protein Primase DNA helicase | back 37 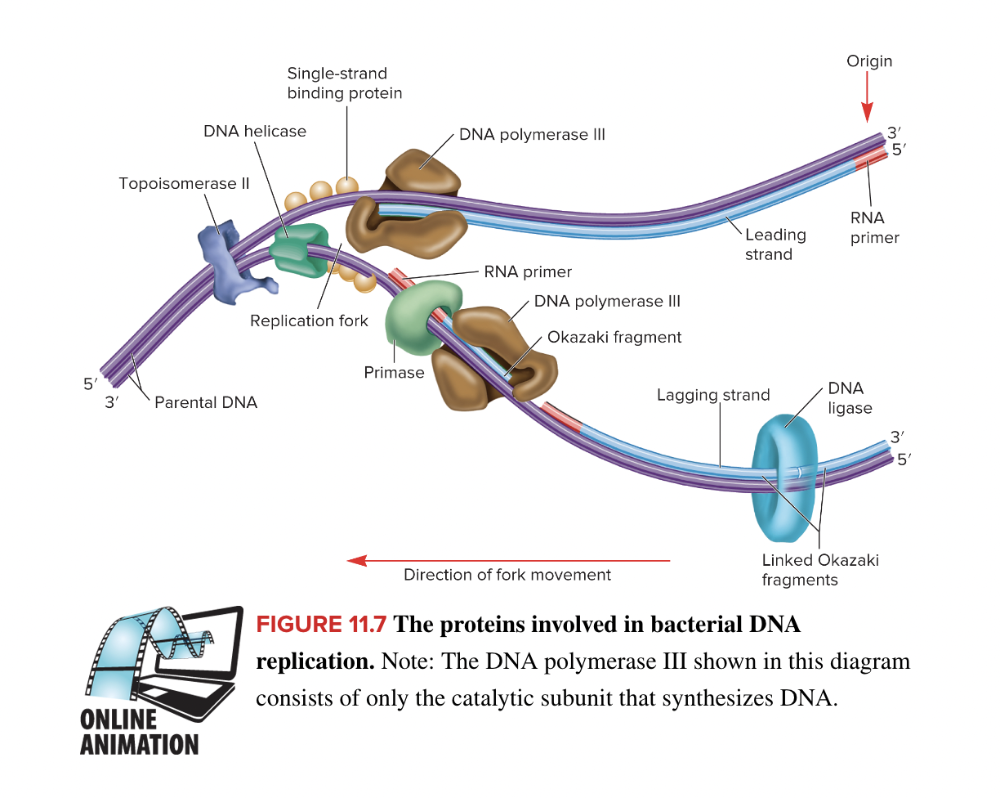
|
front 38 Select all that apply Select the three types of DNA sequences located within the oriC complex. Multiple select question. Promoter DnaA box sequence AT-rich region Replication fork GATC methylation site | back 38 DnaA box sequence AT-rich region GATC methylation site |
front 39 List the events that occur at oriC to initiate DNA replication, putting the first step at the top. DNA helicase proteins bind to the origin HU, IHF and other DNA binding proteins cause the DNA to wrap around the DnaA complex DNA helicase separates the DNA in both directions creating two replication forks DnaA protein binds to the DnaA box sequence The double-stranded DNA molecule separates at the AT-rich region | back 39  Answer in the picture. |
front 40 The role of topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) in replication is to ______. Multiple choice question. synthesize the RNA primer synthesize new DNA stabilize the replication fork break hydrogen bonds between complementary bases remove positive supercoiling in the DNA | back 40 remove positive supercoiling in the DNA |
front 41 The enzyme that converts a double-stranded DNA region into two single strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the strands is called DNA ____. | back 41 helicase |
front 42 Proteins that function to stabilize the replication fork by preventing the reformation of the double strand are called ______. Multiple choice question. helicases GATC methylation sites single strand binding proteins DNA polymerases topoisomerases | back 42 single strand binding proteins |
front 43 During DNA replication, what is the role of the GATC methylation site within the oriC? Multiple choice question. Promote termination of replication Recruit DNA helicase to bind Regulate DNA replication initiation Alleviate positive supercoiling | back 43 Regulate DNA replication initiation |
front 44 The enzyme that synthesizes the short molecules of RNA, called RNA primers, is called ____. | back 44 primase |
front 45 Match the following proteins with the function they serve in E. coli DNA replication. Primase DNA polymerase III DNA polymerase I DNA ligase Tus Synthesizes RNA primers Covalently attaches adjacent Okazaki fragments Removes RNA primers and fills the gaps with DNA Binds to ter sequences, preventing the advancement of the replication fork Synthesizes DNA of both leading and lagging strand | back 45
|
front 46 Which newly synthesized DNA molecule has multiple primers? Multiple choice question. Lagging strand Leading strand | back 46 Lagging strand |
front 47 The name of the enzyme that travels in front of helicase to remove positive supercoiling in the DNA is called ____ ____. | back 47 DNA gyrase or topoisomerase II |
front 48 What is the function of DNA polymerase? Multiple choice question. Synthesis of RNA primers Stabilization of the replication fork Synthesis of DNA on both the leading and lagging strands Reduction of positive supercoiling in the DNA | back 48 Synthesis of DNA on both the leading and lagging strands |
front 49 Identify the role of single-strand binding proteins. Multiple choice question. Stabilize the replication fork by preventing the reformation of the double strand Break hydrogen bonds between complementary bases Synthesize the RNA primer Remove positive supercoiling in the DNA Synthesize the new DNA molecule | back 49 Stabilize the replication fork by preventing the reformation of the double strand |
front 50 The short molecules of RNA that start the DNA replication process are called ____ ____. | back 50 RNA primers |
front 51 Select all that apply Identify the three DNA polymerases found in E. coli that play a role in the replication of damaged DNA and DNA repair. Multiple select question. DNA polymerase II DNA polymerase III DNA polymerase V DNA polymerase I DNA polymerase IV | back 51 DNA polymerase II DNA polymerase V DNA polymerase IV |
front 52 Which newly synthesized DNA molecule has a single primer? Multiple choice question. Lagging strand Leading strand | back 52 Leading strand |
front 53 Which DNA polymerase involved in E. coli DNA replication consists of 10 subunits? Multiple choice question. DNA polymerase IV DNA polymerase III DNA polymerase I DNA polymerase II | back 53 DNA polymerase III |
front 54 List the functions of key proteins involved with bacterial DNA replication | back 54 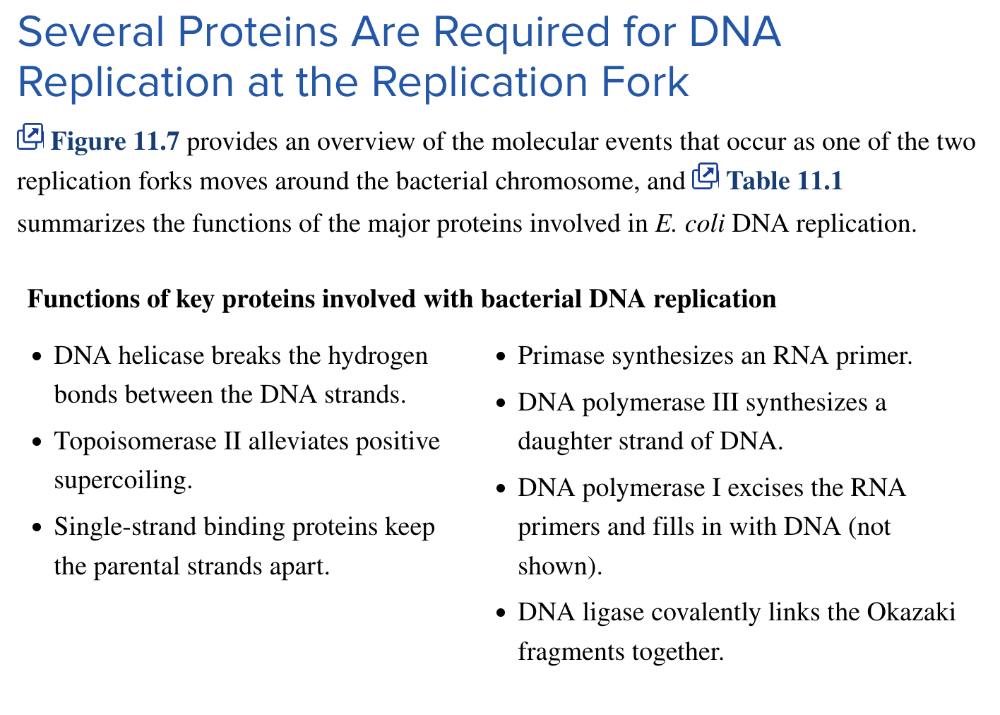 Answer in the picture. |
front 55 Which enzyme synthesizes the DNA of both the leading and lagging strand? Multiple choice question. DNA polymerase RNA primase Helicase DNA gyrase | back 55 DNA polymerase |
front 56 DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides in the ____ to ____ direction. | back 56 5' to 3' |
front 57 Proteins that function to stabilize the replication fork by preventing the reformation of the double strand are called ______. Multiple choice question. GATC methylation sites topoisomerases DNA polymerases single strand binding proteins helicases | back 57 single strand binding proteins |
front 58 During DNA replication, synthesis of the ____ strand is continuous while synthesis of the ____ strand is discontinuous. | back 58 leading; lagging |
front 59 Select all that apply Identify the two DNA polymerases found in E. coli that play a role in normal DNA replication. Multiple select question. DNA polymerase IV DNA polymerase II DNA polymerase III DNA polymerase V DNA polymerase I | back 59 DNA polymerase III DNA polymerase I |
front 60 Match the following proteins involved in E. coli DNA replication with the correct function. DnaA proteins DnaC proteins DnaB (helicase) Topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) Single stranded binding proteins Removes positive supercoiling ahead of the replication forks Bind to DnaA box proteins within the oriC to initiate DNA replication Separates double-stranded DNA Aid DnaA in the recruitment of helicase to the origin Bind to single-stranded DNA and prevent it from re-forming a double-stranded structure | back 60
|
front 61 Small segments of DNA synthesized on the lagging strand of DNA are called ___ ___. | back 61 Okazaki fragments |
front 62 DNA polymerase III is a complex of ______ subunit(s) while DNA polymerase I is composed of ______ subunit(s). Multiple choice question. 5 ; 3 3 ; 1 1 ; 5 10 ; 1 10 ; 3 | back 62 10 ; 1 |
front 63 DNA polymerase attaches nucleotides to the newly synthesized strand in the ______. Multiple choice question. 5'-to-3' direction or the 3'-to-5' direction 3'-to-5' direction only 5'-to-3' direction only | back 63 5'-to-3' direction only |
front 64 The enzyme that catalyzes the formation of a covalent phosphodiester bond between adjacent Okazaki fragments is called DNA | back 64 ligase |
front 65 List the events of DNA synthesis at the replication fork in the correct sequence. DNA strands separate at the origin, creating two replication forks. DNA polymerase I removes the primers and adds DNA. DNA ligase catalyzes the phosphodiester bond between adjacent Okazaki fragments. RNA primers are added to both the leading and lagging strand. DNA polymerase III adds nucleotides to the 3' end continuously on the leading strand, and discontinuously on the lagging strand. | back 65  Answer in the picture. |
front 66 Select all that apply Which components are needed to make up the complex called a primosome? Multiple select question. DNA polymerase III primase topoisomerase II DNA polymerase I DNA ligase DNA helicase | back 66 primase DNA helicase |
front 67 Small segments of DNA, called Okazaki fragments, are synthesized on the ____ ____. | back 67 Lagging strand |
front 68 What is a replisome? Multiple choice question. A primosome physically associated with two DNA polymerase holoenzymes A complex of two DNA polymerase molecules A primase complexed with DNA helicase DNA ligase associated with an Okazaki fragment | back 68 A primosome physically associated with two DNA polymerase holoenzymes |
front 69 Which DNA polymerase involved in E. coli DNA replication consists of 10 subunits? Multiple choice question. DNA polymerase III DNA polymerase IV DNA polymerase II DNA polymerase I | back 69 DNA polymerase III |
front 70 In dimeric DNA polymerase, two molecules of DNA polymerase _____ act together to replicate the leading and lagging strands of DNA. Multiple choice question. IV III I II V | back 70 III |
front 71 Which enzyme catalyzes the formation of a covalent bond between adjacent Okazaki fragments? Multiple choice question. DNA gyrase DNA polymerase I RNA primase DNA ligase Helicase | back 71 DNA ligase |
front 72 Identify the protein that binds to the ter sequence to terminate DNA replication. Multiple choice question. oriC DnaA Tus DnaB | back 72 Tus |
front 73 A complex consisting of DNA helicase and primase is called a ____. | back 73 primosome |
front 74 Two transiently intertwined molecules of DNA are called a ____. | back 74 catenanes |
front 75 A primosome physically associated with two DNA polymerase holoenzymes is called a ____. | back 75 replisome |
front 76 A temperature-sensitive mutant is an example of a ____ mutant. | back 76 conditional |
front 77 A complex of two DNA polymerase holoenzymes that move as a unit during DNA replication is described as ______ DNA polymerase. Multiple choice question. conjoined duplex dimeric paired | back 77 dimeric |
front 78 The energy used to fuel the endergonic reaction of DNA replication is supplied from the exergonic cleavage of ______. Multiple choice question. the primosome adenosine triphosphate (ATP) DNA polymerase the replisome a deoxyribnucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) | back 78 a deoxyribnucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) |
front 79 The area of DNA where Tus binds to stop the movement of the replication fork is called a ____ ____.termin | back 79 termination sequence |
front 80 DNA polymerase III does not dissociate from the DNA template strand after it has catalyzed the joining of two adjacent nucleotides so it is described as a ____ enzyme. | back 80 processive |
front 81 What are catenanes? Multiple choice question. Promoter sequences where initiation factors bind Transiently intertwined DNA molecules formed during DNA replication Termination sequences that prevent the movement of the replisome | back 81  Transiently intertwined DNA molecules formed during DNA replication |
front 82 Which molecule, when bound to DNA polymerase III forming a holoenzyme, dramatically increases the processivity of the enzyme? Multiple choice question. dNTP DnaB DnaA β subunit | back 82 β subunit |
front 83 A mutation that only blocks DNA replication when specific environmental conditions are present is called a ____ mutant. | back 83 conditional or ts |
front 84 For E. coli, the protein that promotes dimerization of two DNA polymerase III proteins at the replication fork is encoded by which gene? Multiple choice question. dnaX dnaG dnaB dnaC dnaE | back 84 dnaX |
front 85 True or false: The formation of covalent bonds between adjacent nucleotides during DNA replication requires energy input. True false question.TrueFalse | back 85 True |
front 86 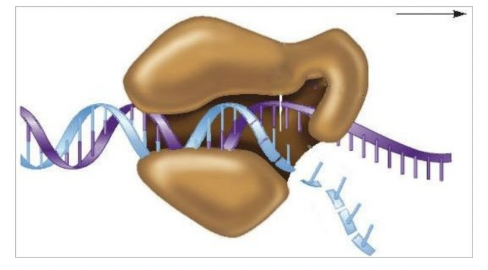 DNA polymerase III is described as a(n) ____ enzyme since, as shown in the diagram, it remains clamped to the DNA template and slides along the template as it catalyzes the synthesis of the daughter strand. | back 86 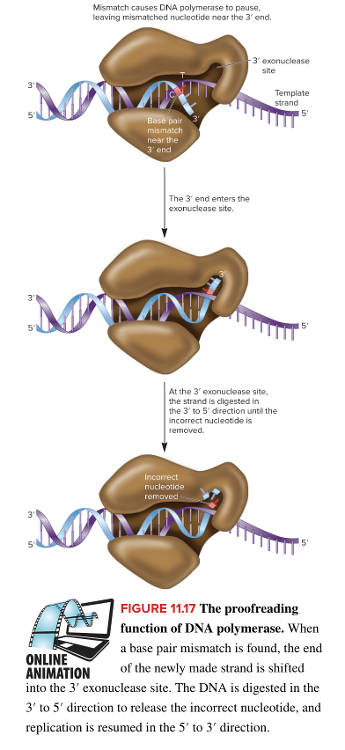 processive |
front 87 The speed of DNA replication depends on the ability of DNA polymerase III to remain attached to the template strand after catalyzing covalent bonds between adjacent nucleotides. For this reason, it is called a(n) ______ enzyme. Multiple choice question. progressive processive adhering binding catalyzing | back 87 processive |
front 88 Select all that apply Identify the three mechanisms that ensure the fidelity of DNA replication. Multiple select question. DNA polymerase active site structure DNA proofreading The ter sequence Stability of base pairing Processivity induced by binding of the β clamp | back 88 DNA polymerase active site structure DNA proofreading Stability of base pairing |
front 89 In E. coli, the DNA polymerase III holoenzyme, which includes the β subunit, can add nucleotides at a rate of ______ nucleotides per second. Multiple choice question. about 750 only 20 about 2,000 more than 10,000 | back 89 about 750 |
front 90 Select all that apply Select all of these that are similar in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Multiple select question. Linear chromosomes Chromatin compacted within nucleosomes DNA ligases DNA helicases Primases | back 90 DNA ligases DNA helicases Primases |
front 91 For E. coli, the protein that recruits DNA helicase to the origin of replication is encoded by which gene? Multiple choice question. dnaX dnaC dnaB dnaG dnaE | back 91 dnaC |
front 92 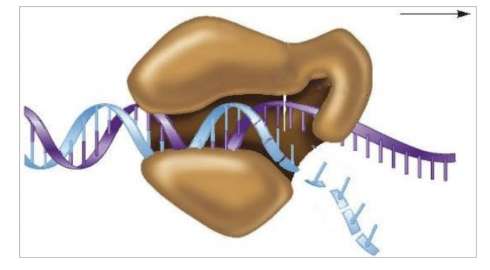 In the diagram, DNA polymerase III surrounds the DNA molecule like a curled hand. This structural arrangement allows DNA synthesis to proceed rapidly due to the ______ of the enzyme. Multiple choice question. accuracy processivity precision reactivity | back 92  processivity |
front 93 Which type of cell has chromosomes with multiple origins of replication? Multiple choice question. Eukaryote Prokaryote | back 93 Eukaryote |
front 94 The three mechanisms that ensure the fidelity of DNA replication are the stability of ____ ____, the active site structure of DNA ____ and the process of DNA ____. | back 94 Stability of base pairing |
front 95 In eukaryotes, DNA replication occurs ______ from multiple origins of replication. Multiple choice question. unidirectionally bidirectionally | back 95 bidirectionally |
front 96 Which molecule, when bound to DNA polymerase III forming a holoenzyme, dramatically increases the processivity of the enzyme? Multiple choice question. dNTP β subunit DnaA DnaB | back 96 β subunit |
front 97 Autonomously replicating sequences (ARS) are required to initiate DNA replication in ______. Multiple choice question. prokaryotes eukaryotes | back 97 eukaryotes |
front 98 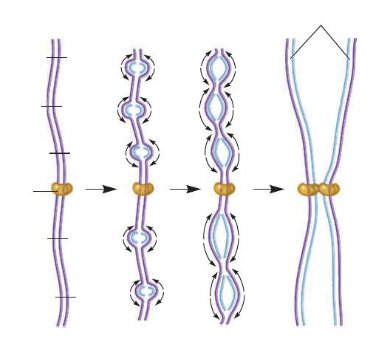 Replication of the chromosome in the diagram is representative of that in a(n) ______. Multiple choice question. eukaryote. prokaryote. | back 98 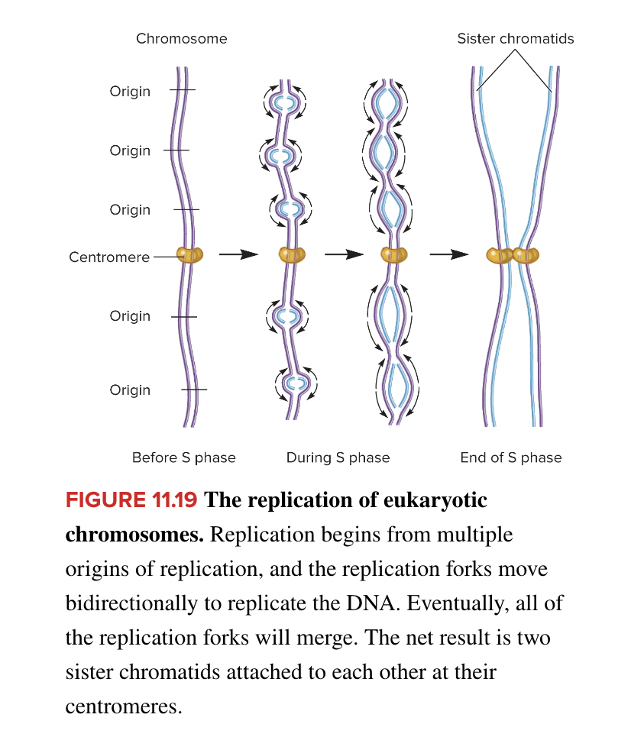 eukaryote |
front 99 In eukaryotes, DNA replication begins with the ______. Multiple choice question. binding of MCM gyrase assembly of a preRC binding of MCM helicase binding of DnaA | back 99 assembly of a preRC |
front 100 True or false: Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have multiple origins of replication. True false question.TrueFalse | back 100 False |
front 101 DNA replication licensing allows DNA synthesis to begin after which protein binds to the origin of replication? Multiple choice question. primase DNA polymerase α DNA gyrase MCM helicase origin recognition complex (ORC) | back 101 MCM helicase |
front 102 True or false: DNA replication in eukaryotes occurs unidirectionally from multiple origins of replication. True false question.TrueFalse | back 102 False |
front 103 In eukaryotes DNA polymerase ε synthesizes DNA on the ____ strand and DNA polymerase δ synthesizes DNA on the ____ strand. | back 103 leading; lagging |
front 104 What consensus sequence is found in ARS elements? Multiple choice question. ATTATTATTATTATTATT GCGCGCGCGCGCGC ATTTAT (A or G) TTTA AGCAGCAG (C or A) AA | back 104 ATTTAT (A or G) TTTA |
front 105 A polymerase switch occurs when the complex of primase with DNA polymerase _____ is exchanged for DNA polymerase ______ on the leading strand and DNA polymerase ______ on the lagging strand. Multiple choice question. α; ε; δ ε; α; δ ε; δ; α α; δ; ε δ; ε; α | back 105 α; ε; δ |
front 106 List the steps of eukaryotic DNA replication initiation in the correct sequence. MCM helicases bind to the origin of replication ORC binds to the origin of replication DNA synthesis begins | back 106
|
front 107 What is the function of the complex of primase and DNA polymerase α? Multiple choice question. Unwind the DNA at the replication fork Synthesize a short RNA-DNA primer Synthesize DNA using the lagging strand as a template Relax supercoils that form ahead of the replication fork Synthesize DNA using the leading strand as a template | back 107 Synthesize a short RNA-DNA primer |
front 108 A type of DNA polymerase that is attracted to damaged DNA and can synthsize a complementary strand over the abnormal region is called a - polymerase. | back 108 translesion replicating |
front 109 In a process known as DNA replication ____, the binding of MCM helicase allows DNA replication to begin at an origin of replication in eukaryotic cells. | back 109 licensing |
front 110 True or false: In both eukaryotes and prokaryotes RNA primers are removed by DNA polymerase I. | back 110 False |
front 111 Match each eukaryotic DNA polymerase with the correct function. α ε δ γ Replication of the leading strand Initiate DNA replication Replication of mitochondrial DNA Replication of the lagging strand | back 111 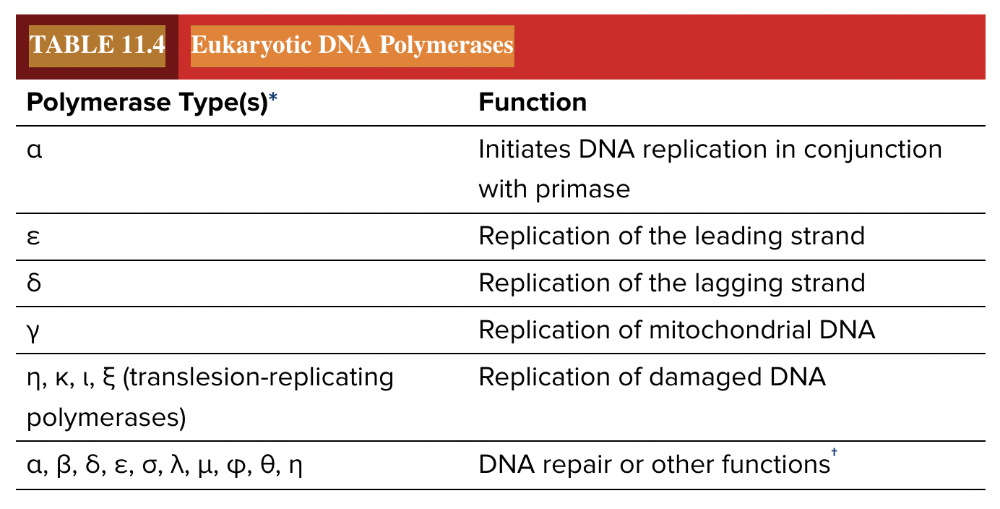
|
front 112 The tandemly repeated DNA sequences located at the both ends of eukaryotic chromosomes, as shown in the image, comprise the ______. Multiple choice question. nucleosome kinetochore centromere telomere | back 112 telomere |
front 113 A ____ ____ is the exchange that occurs when a DNA polymerase α/primase complex dissociates from the replication fork and is replaced by DNA polymerase ε or δ. | back 113 polymerase switch |
front 114 DNA polymerase cannot replicate the 3' end of a DNA strand because a ____ cannot be made upstream from this point. | back 114 primer |
front 115 Select all that apply A complex that synthesizes a short RNA-DNA complex used as a primer in eukaryotic DNA replication is made from which components? Multiple select question. DNA polymerase α DNA polymerase ε DNA polymerase δ helicase primase DNA gyrase | back 115 DNA polymerase α primase |
front 116 The enzyme that synthesizes the short repetitive sequences at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes is called ____. | back 116 telomerase |
front 117 An enzyme that can replicate DNA in a damaged region is ______. Multiple choice question. DNA polymerase ε a template repair enzyme DNA polymerase α a translesion-replicating polymerase DNA polymerase δ | back 117 a translesion-replicating polymerase |
front 118 During telomere synthesis the enzyme ____ binds to the 3' overhang region and synthesizes many 6-____ repeats. | back 118 telomerase; nucleotide |
front 119 In eukaryotes, the enzyme ______ removes the RNA primers. Multiple choice question. DNA gyrase MCM helicase DNA polymerase I DNA ligase flap endonuclease | back 119 flap endonuclease |
front 120 Select all that apply The enzyme telomerase consists of which of the following? Multiple select question. RNA Fatty acids DNA Protein subunit ATP | back 120 RNA Protein subunit |
front 121 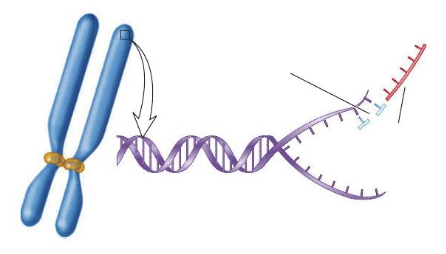 The name for the end of a linear, eukaryotic chromosome is the ____. | back 121 telomere |
front 122 The component of telomerase that enables the enzyme to bind to the telomeric repeat sequence is composed of _____. Multiple choice question. DNA RNA protein | back 122 RNA |
front 123 Select all that apply Which characteristics of DNA polymerase prevent the enzyme from replicating the 3' ends of DNA strands? Multiple select question. DNA polymerase can only elongate an existing nucleotide strand. DNA polymerase wraps around the DNA template like a curled hand. DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA only in a 3' to 5' direction. DNA polymerase can only catalyze the formation of phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides. DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA only in a 5' to 3' direction. | back 123 DNA polymerase can only elongate an existing nucleotide strand. DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA only in a 5' to 3' direction. |
front 124 Telomerase reverse transcriptase is an enzyme that uses a(n) _____ template to produce a(n) ______ strand. Multiple choice question. RNA; DNA RNA; RNA DNA; RNA DNA; DNA | back 124 RNA; DNA |
front 125 What is the role of telomerase? Multiple choice question. Remove RNA primer flaps created by RNA polymerase I Prevent the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes from extending Prevent DNA replication of the centromere region Prevent the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes from shortening | back 125 Prevent the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes from shortening |
front 126 List the events of telomere synthesis in the correct sequence, putting the first event on top. Telomerase binds to the 3' overhang region Telomerase synthesizes a 6-nucleotide repeat Telomerase shifts and synthesizes many more 6-nucleotide repeats The complementary strand is made by primase, DNA polymerase, and ligase | back 126 1) telomerase binds to the 3' overhang region |
front 127 The enzyme telomerase consists of protein subunits and ____, which is complementary to the DNA sequence in the telomeric repeat. | back 127 RNA |
front 128 True or false: Telomeres remain the same length throughout the lifespan of a cell. | back 128 False |
front 129 Telomerase RNA component ______. Multiple choice question. polymerizes DNA to lengthen the telomeres synthesizes a strand of DNA that is complementary to the lengthened telomeric strand contains a sequence complementary to the telomeric repeat sequence | back 129 contains a sequence complementary to the telomeric repeat sequence |
front 130 As telomeres of a somatic cell shorten, the cell may become ______, losing the ability to divide. Multiple choice question. mature senescent unresponsive quiescent | back 130 senescent |
front 131 The subunits of the enzyme telomerase that are responsible for lengthening the ends of the chromosomes are called telomerase ____ ____. | back 131 reverse transcriptase |
front 132 The ability of cancer cells to continue to divide indefinitely is due to an increase in the activity of the enzyme ______. Multiple choice question. DNA ligase telomerase DNA gyrase DNA polymerase α | back 132 telomerase |
front 133 The enzyme that synthesizes the short repetitive sequences at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes is called ____. | back 133 telomerase |
front 134 In actively dividing cells, telomeres tend to ______ with age. Multiple choice question. remain the same shorten lengthen | back 134 shorten |
front 135 In somatic cells, telomeres tend to shorten with age. When telomeres are too short, the cells become ____, meaning that they lose their ability to ____. | back 135 senescent; divide, duplicate, or reproduce |
front 136 Many types of cancer cells have an increase in the activity of ______. Multiple choice question. telomerase DNA gyrase MCM helicase DNA polymerase α | back 136 telomerase |