Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Pharmacology
front 1 Digoxin (Lanoxin) | back 1 D- dig level 2ng/ml or greater is toxic
|
front 2 Epinephrine | back 2 N- nervousness (undesirable effect)
|
front 3 norepinephrine (levophed) | back 3 S- stim alpha and beta adrenergic receptors
|
front 4 nitroglycerin | back 4 A- avoid alcohol
|
front 5 ACE INHIBITORS | back 5 S- suppresses renin angiotensin aldosterone system
|
front 6 Beta- adrenergic blockers | back 6 end in lol- atenolol (Tenormin)
|
front 7 Calcium channel blocker | back 7 amlodipine (norvasc), diltiazem (cardizem), nifedipine (procardia)
|
front 8 Diuretics | back 8 D- diet; increase K+ for all except aldactone
|
front 9 warfarin (coumadin)
| back 9 prothrombin time is monitored 1.5-2.5 X control is the therapeutic range
|
front 10 warfarin | back 10 C- check vital signs, platelte count, and PT
|
front 11 heparin sodium | back 11 PTT must be monitored 1.5-2.5 X control
|
front 12 Clopidogrel (PLAVIX) | back 12 B- bleeding, brochospasms- undesired effects
|
front 13 HMG CoA inhibitors | back 13 competitive inhibitors of HMG-COA reductase, an enzyme necessary for cholesterol biosynthesis
|
front 14 HMG COA inhib pneumonic | back 14 S- statin is the ending
|
front 15 Antibiotics pneumonic | back 15 M- monitor superinfections
|
front 16 Aminoglycosides | back 16 end in mycin
|
front 17 Allopurinol | back 17 G- gulp 10-12 glasses of fluid daily, GI distress (undesirable effect)
|
front 18 Phenytoin (dilantin) | back 18 G- gingival hyperplasia
|
front 19 Lithium pnuemonic | back 19 L- level therapeutic 0.6-1.2 meq/l
|
front 20 LIDOCAINE pneumonic
| back 20 L- local anasthetic
|
front 21 You have 1 heart and 2 lungs": | back 21 Beta-1 are therefore primarily in the heart.
|
front 22 Anti-Epileptic Side Effect
| back 22 A taxia
|
front 23 Barbiturate Side Effects
| back 23 A taxia
|
front 24 ACE Inhibitor Side Effects
| back 24 C ough
|
front 25 SIDE EFFECTS OF CORTICOSTERIODS;
| back 25 C-cushings syndrome
|
front 26 Drugs for heart failure-
| back 26 Digoxin,
|
front 27 Respiratory Depression Inducing drugs | back 27 STOP breathing":
|
front 28 TB treatment | back 28 If you forget your TB drugs, you'll die and might need a PRIEST":
|
front 29 Drugs to treat viral respiratory infections | back 29 "You'd get a respiratory infection if you shoot an ARO (arrow) laced with viruses into the lungs":
|
front 30 Atropine | back 30 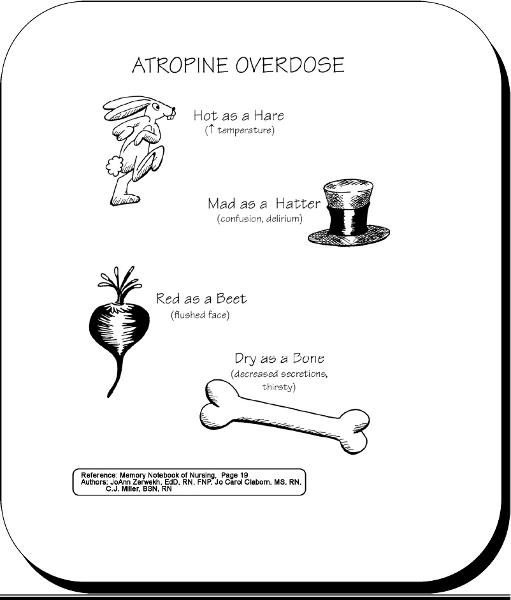 |
front 31 emergency drugs to LEAN on | back 31  |
front 32 Drugs for Bradycardia and decreased BP
| back 32  |
front 33 Cholinergic crisis- SLUD | back 33 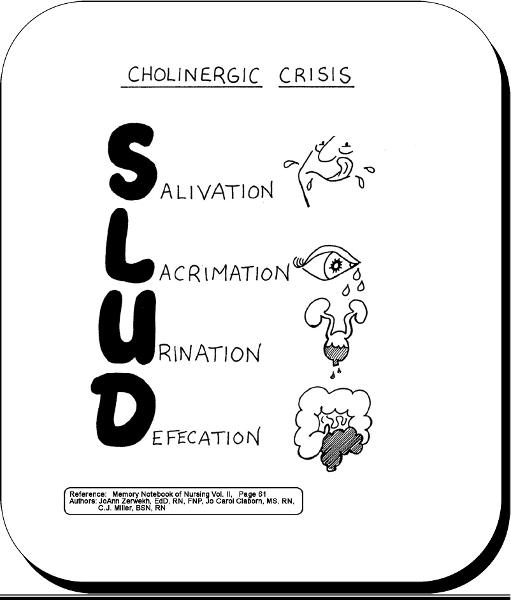 |
front 34 Beta Blocker Actions | back 34 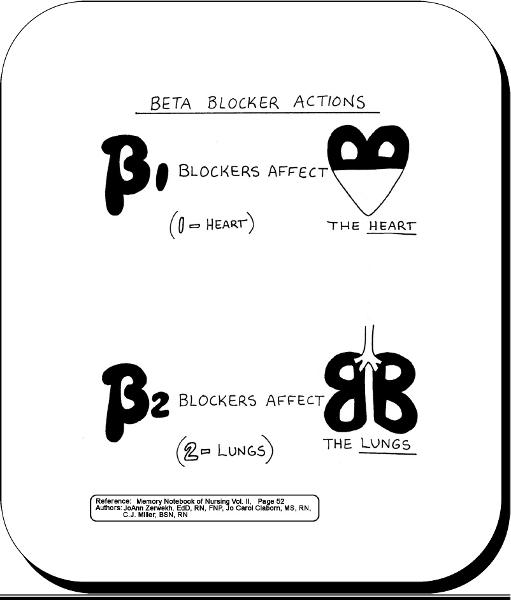 |
front 35 Anticancer drugs | back 35  |
front 36 These drugs can interact (TDCI) | back 36  |
front 37 aminoglycoside toxicity | back 37  |
front 38 Quinalones and Tetracyclines ok in pregnancy??? | back 38  |
front 39 SE of adrenergic antagonists | back 39  |
front 40 Lidocaine Toxicity
| back 40 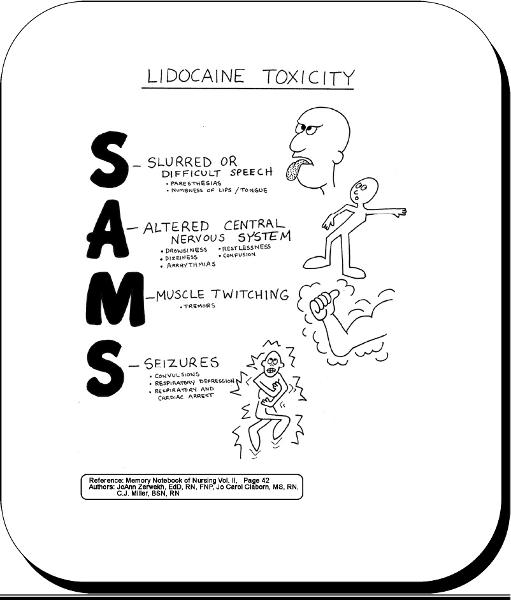 |
front 41 B6 relationship to INH and levadopa? | back 41 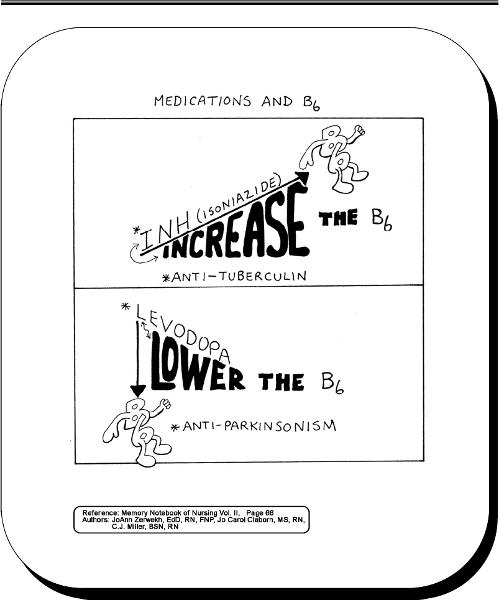 |
front 42 Mixing insulin | back 42 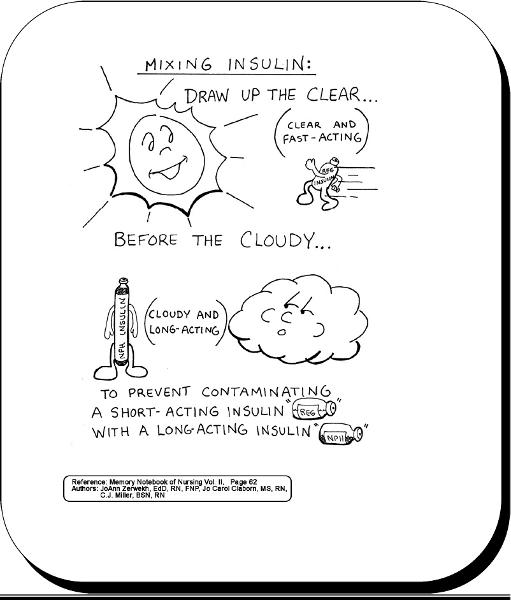 |
front 43 antiinflammatory | back 43  |
front 44 salicylate poisoning | back 44 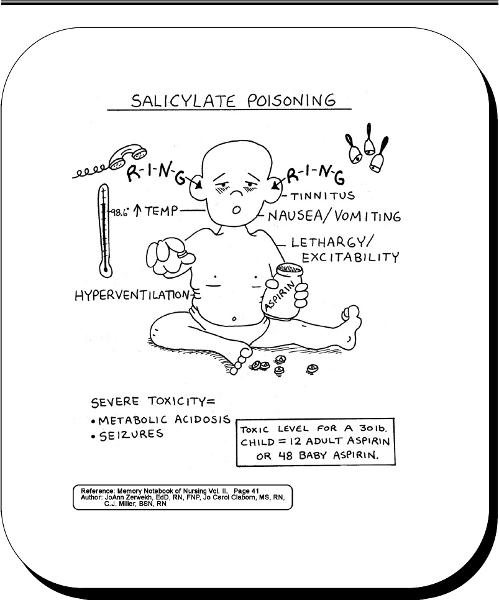 |
front 45 SASH technique | back 45 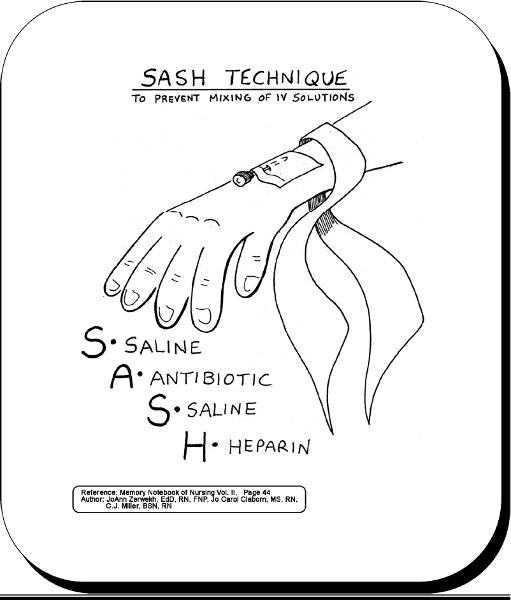 |
front 46 serious complications of oral birth control pills
| back 46 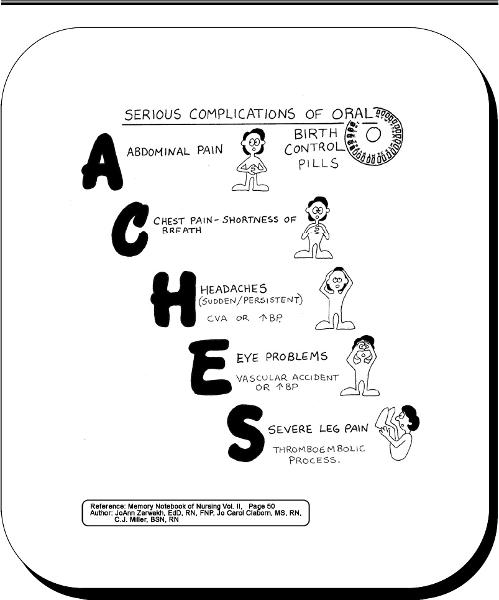 |
front 47 saw palmetto | back 47  stomach problems
|
front 48 ginko | back 48  before couldn't think well.. now can think better! |
front 49 Potassium | back 49 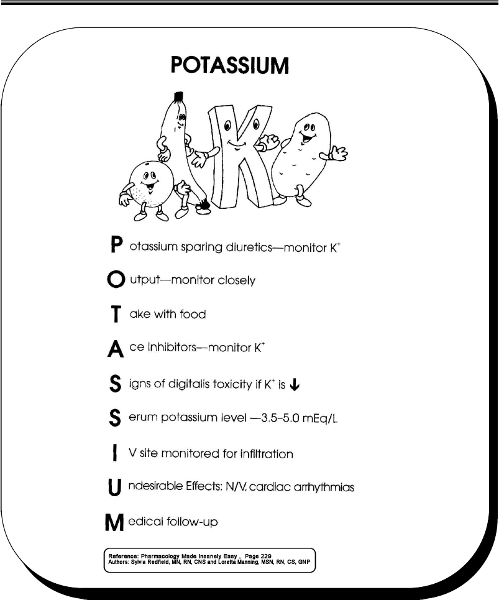 |
front 50 estrogen | back 50 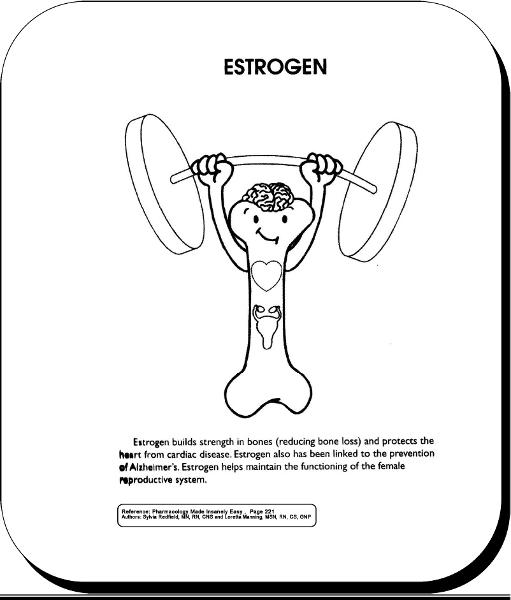 |
front 51 Bipolar clown image | back 51  |
front 52 Buspar | back 52 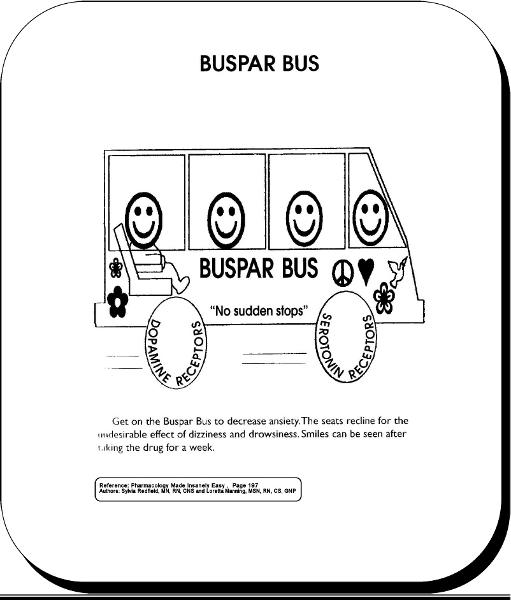 |
front 53 Dueteronomy | back 53 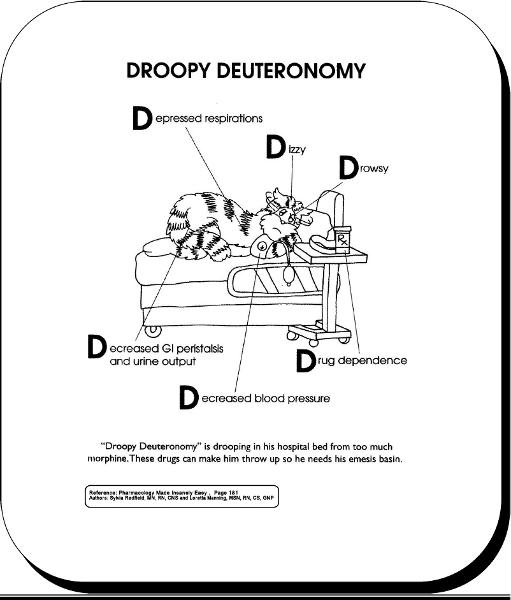 |
front 54 miotics | back 54 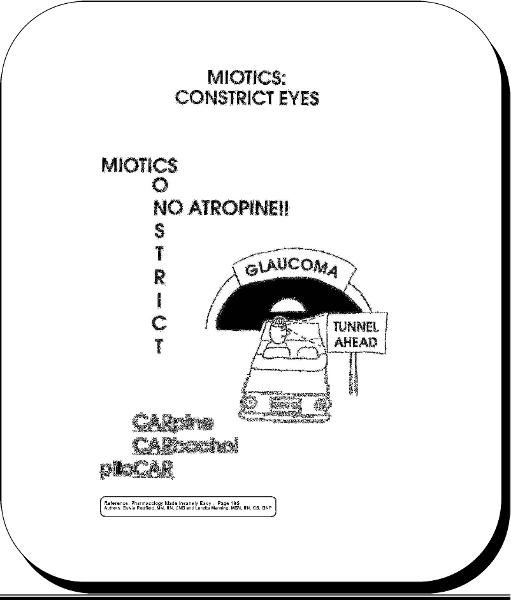 |
front 55 insulins and onset | back 55 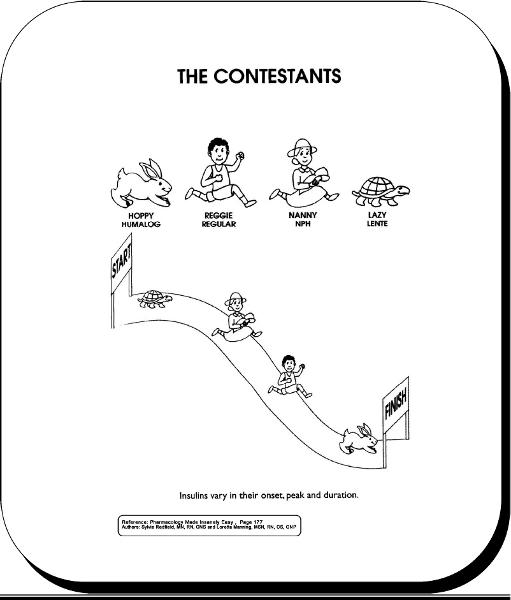 |
front 56 metformin | back 56 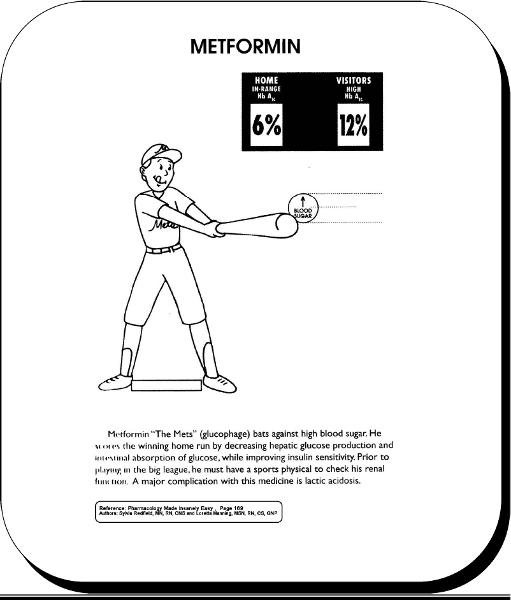 a major complication with this medicine is lactic acidosis |
front 57 cushing | back 57  |
front 58 synthroid | back 58 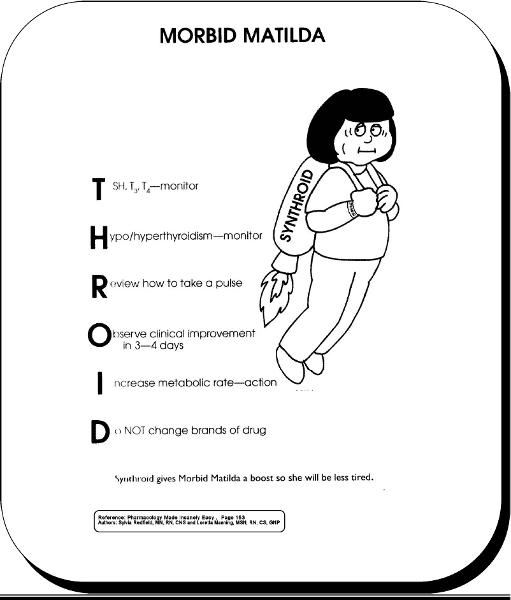 |
front 59 PTU | back 59  |
front 60 tuberculin syringe has the capacity of? | back 60 0.5 ml |
front 61 Drug label should be read? | back 61 3 times |
front 62 patch testing | back 62 identify sensitivity to contact materials such as soap, pollen, and dyes.. allergen on patch is placed in contact with back, arms, or thighs. Patch is left in place for 48 hours. Site is aired for 15 min, then read. Wheal is the definitive reaction measured from 1+ to 4+. Emergency equipment must be available in case of anaphylaxis. |
front 63 after applying eye drops how long do you hold pressure to the inner corner of eyelid? | back 63 1-2 min |
front 64 how to put in ear drops for child younger than 3 | back 64 down and back
|
front 65 MDI meds should be shaken? | back 65 vigorously 5-6 times prior to use. The client may position her mouth around the device or 2-4 cm in front of mouth |
front 66 DPI (dry powder inhalers) | back 66 not to be shaken, and the client should place the mouthpiece between lips.
|
front 67 why might a spacer be attached to an MDI | back 67 the spacer keeps the med in the device longer and thereby facilitates delivery of the med to the lungs and decreases the amount of med deposited in the oropharynx. This is beneficial for the delivery of glucocorticoids |
front 68 after applying ear drops apply pressure to the? | back 68 tragus of the ear with finger |
front 69 how are suppositories stored? | back 69 refrigerated! Remove foil wrapper and lubricate supposiory if needed. Instruct client to retain med and not expel it. Rectal suppositories are insterted beyond the internal sphincter and vaginal suppositories are inserted with an applicator. |
front 70 Intramuscular route | back 70 used for irritating meds, solutions in oils, and aqueous suspensions.
|
front 71 volume injected IM route | back 71 1-3 ml. If a greater amount is required it should be divided into 2 syringes and two different sites should be used. |
front 72 z-track | back 72 prevents medication from leaking back into subcutaneous tissue
|
front 73 Intradermal | back 73 tuberculin testing or checking med/allergy sensitivities
|
front 74 Time release capsules crushed? | back 74 They should not be crushed or diluted as med will be absorbed at a faster rate than recommended. |
front 75 When should a breastfeeding mother take medication to ensure the least amount is recieved by the infant? | back 75 immediately after breastfeeding so this will minimize med concentration in the next feeding |
front 76 Instilling vag meds | back 76 pt in lithotomy position, elevate hips with pillow
|
front 77 antimicrobials | back 77 treat bacterial, viral, and fungal infections |
front 78 narrow spectrum antibiotics | back 78 are effective against a few species of microorganisms such as gram positive cocci, gram positive bacilli, and gram neg aerobes |
front 79 broad spectrum antibiotics | back 79 effective against a wide variety of microorganisms |
front 80 what should be collected prior to antimicrobial therapy | back 80 specimens for a culture and sensitivity test |
front 81 prescribed antimicrobial meds should be taken with what freq? | back 81 around the clock to maintain therapeutic blood levels |
front 82 adverse reactions to antimicrobials | back 82 rash
|
front 83 how do penicillins destroy bacteria | back 83 weaken the bacterial cell wall |
front 84 penicillins are the choice for? | back 84 gram + cocci such as streptococcus pneumonia (pnuemonia and meningitis)infectious endocarditis, streptococcus pyogenes (pharyngitis) |
front 85 penicillins are also med of 1st choice for | back 85 meningitis - gram neg cocci and for treatment of syphillus |
front 86 should penicillin and aminoglycosides be mixed in same intravenous solution | back 86 no, b/c penicillin inactivates aminoglycosides when mixed in same IV solution |
front 87 nurse gives penicillin, what should nurse watch for? | back 87 observe client 30 min following admin of parenteral penicillin
|
front 88 ________ are beta lactam antibiotics sim to penicillins that destroy bacterial cell walls causing destruction of the micro-organism | back 88 cephalosporins, grouped into 4 generations. they are broad spectrum with a high therapeutic index that treat UTI, post op infections, pelvic infections, and meningitis |
front 89 clients should take oral cephalosporins with? | back 89 food, oral cephalosporin suspensions should be stored in the refrigerator. |
front 90 bacteriostatic | back 90 prevent bacteria from reproduction |
front 91 carbapenems | back 91 meropenem, beta lactam antibiotics that destroy bacterial cell wall
|
front 92 monobactams- vancomycin | back 92 beta lactam antibiotics destroy bacterial cell wall
|
front 93 vancomycin peak blood levels should be collected? | back 93 1-2 hrs after completion of IV infusion. Appropriate peak levels are between 30-40 mg/ml |
front 94 how do we evaluate vancomycins effectiveness? | back 94 clear breath sounds, wound healing, improvement of sx of antibiotic associated pseudo colitis symptoms such as resolution of diarrhea and negative stool cultures for c-diff. |
front 95 Tetracyclines (sumycin) | back 95 other meds- doxycycline. Broad spectrum antibiotics that inhibit microorganism growth by preventing protein synthesis (bacteriostatic). Tx acne. 1st line med for rickettsia (rocky mountain spotted fever, typhus fever, infections of urethra or cervix caused by chlamydia, lyme disease, anthrax, GI infections caused by h.pylori and periodontal disease. |
front 96 avoid giving tetracycline to? | back 96 children under 8, yellow/brown tooth discoloration
|
front 97 taking tetracycline with milk/calcium/mag/antacids | back 97 should take tetracyclines at least 1 hr before and 2 hr after taking food and supplements containing calcium and mag |
front 98 Tetracyclines should not be given with food except for? | back 98 doxycycline and minocycline |
front 99 Bacteriostatic inhibitors | back 99 erythromycin, clindamycin, axithromycin, etc
|
front 100 bacteriostatic inhibitors are used to? | back 100 treat infection in clients with a penicillin allergy. ex) diptheria, whoop cough, chlamydia. |
front 101 medication interactions with erythromycin? | back 101 antihistamines, theophyline (asthma med), carbamazepine (anticonvulsant), and warfarin (anticoagulant). result in toxicity |
front 102 aminoglycosides- gentamicin | back 102 bactericidal antibiotics disrupt protein synthesis. med of choice against aerobic gram neg bacilli |
front 103 aminoglycosides adverse effects | back 103 ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity |
front 104 peak levels of aminoglycosides should be obtained? | back 104 30 min after admin IM or IV. |
front 105 sulfa | back 105 TMP- bactrim. inhibit bacterial growth by inhibiting synthesis of folic acid. folic acid is essential for production of DNA, RNA, and proteins. |
front 106 Bactrim drug of choice | back 106 for uti caused by e.coli and other infections (otitis media, bronchitis, shigellosis, pneumonia) |
front 107 Bactrim is contraindicated in? | back 107 clients with a folate deficiency, b/c it increases the risk of megaloblastic anemia. Avoid use in pregnancy and lactation risk of kernicterus increases. Do not use if creatinine clearance is less than 15 ml/min |
front 108 how should bactrim be taken? | back 108 on an empty stomach with a full glass of water |
front 109 antimycobaterial (antituberculosis) | back 109 isoniazid INH, streptomycin, ethambutol, pyranzinamide |
front 110 INH | back 110 highly specific for mycobacteria. Inhibits growth of mycobacteria by preventing sysnthesis of mycolic acid in cell wall. Indicated for active and latent use.
|
front 111 Stop INH if? | back 111 Liver function tests are elevated |
front 112 pt on INH develops peripheral neuropathy | back 112 admin 50-20 mg of vit b6 daily |
front 113 How should patient take INH? | back 113 on an empty stomach 1 hr before meals or 2 hrs after. Can taken INH with meals if GI upset occurs. |
front 114 Antiviral (acyclovir) | back 114 prevents reproduction of viral DNA
|
front 115 ganciclovir | back 115 tx of choice for CMV retinitis in immunocompromised clients with HIV, transplant clients at risk for CMV infection. Med of choice for CMV (cytomegalovirus). |
front 116 pt on ganciclovir, if neutrophil count is below 500? | back 116 stop treatment. Cell counts improve within 3-5 days. |
front 117 gancyclovir and pregnancy? | back 117 it is tetratogenic, women should avoid pregnancy during course of therapy and for 90 days after the end of therapy. males should be informed about sterility. |
front 118 never admin acyclovir by? | back 118 IV bolus, it should be administered by IV infusion slowly over 1 hr or longer. Clients should understand than acyclovir diminishes symptoms but does not cure the virus. For topical admin advise client to put on rubber gloves to avoid transfer of virus to other areas of body. |
front 119 Fluoroquinolones | back 119 ciproflaxacin (cipro), levaquin, floxin
|
front 120 ciproflaxacin should not be administered to children less than 18 years of age due to? | back 120 risk of achilles tendon rupture |
front 121 common s/e of quinolones | back 121 N, V, diarrhea, discomfort, dizzy, light headed |
front 122 used to treat soft tissue infections | back 122 quinolones.. contraindicated in children, pregnancy
|
front 123 for inhalation anthrax infection ciproflaxacin is administered every? | back 123 12 hours for 60 days |
front 124 treat UTI and otitis media, used prophylactically in pts susceptible to streptococcal infection or rheumatic fever when penicillin is contraindicated | back 124 sulfanomides |
front 125 antiprotozoals | back 125 metronidazole (flagyl)
|
front 126 s/e of flagyl | back 126 GI discomfort, dry mouth, metallic taste, dark urine (harmless effect of med), CNS symptoms (stop med) |
front 127 flagyl is effective when | back 127 no more bloody muscoid diarrhea,
|
front 128 Streptogramins | back 128 synercid
|
front 129 Antitubercular agent
| back 129 Alter cellular RNA synthesis and phosphate metabolism
|
front 130 why is vit B6 admin with INH? | back 130 decrease neurologic side effects |
front 131 Antitubercular Agent
| back 131 prevent RNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA dependent RNA polymerase
|
front 132 antifungals
| back 132 acts on fungal cell membranes to increase cell permeability which results in leakage of intracellular cations leading to cell death. These agents can be fungistatic (slow growth) or fungicidal (destroys fungus). |
front 133 topical antifungal agents | back 133 clotrimazole, miconazole, ketoconazole, nystatin, |
front 134 amphotericin B | back 134 tx systemic life threatening fungal infections. Administration of amphotericin B should be infused slowly over 2-4 hr by IV route. Renal dammage can be lessened with administration of 1L saline solution on the day of amphotericin B infusion. |
front 135 Ketoconazole | back 135 antifungal used to tx superficial fungal infections; dermatophytic infections, tinea pedis, tinea cruiris. |
front 136 amphotericin B- infusion reactions | back 136 fever, chills, rigors, h/a 1-3 hr after innitiation. Pretreat with diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and aspirin. Meperidine or dantrolene may be given for rigors
|
front 137 Griseofulvin | back 137 stop cell division and new growth
|
front 138 B lymphocytes or B cells | back 138 produce antibodies IgA, IgD, IgG, IgE, or IgM |
front 139 Helper T lymphocytes or CD 4 cells | back 139 activate B cells and are responsible for teh delayed hypersensitivity reaction |
front 140 CD 8 cells | back 140 destroy target cells directly causing death of the microorganism |
front 141 hep B immunization | back 141 dosese at birth, 1-2 months and 6-18 months |
front 142 Diptheria and tetanus toxoids and pertussis vaccine DTAP | back 142 doses at 2, 4, 6, 15 to 18 months, and at 4-6 yrs |
front 143 TDAP | back 143 11-12 years |
front 144 TD booster | back 144 every 10 years following DTAP |
front 145 HIB | back 145 dose at 2, 4, 6, and at 12-15 months |
front 146 innactivated polio virus vaccine | back 146 dose at 2, 4, 6 to 18 months, and at 4-6 yrs |
front 147 MMR measles, mumps, and rubella | back 147 12- 15 months and at 4-6 years |
front 148 caricella vaccine | back 148 single dose at 12-18 months or 2 doses administered 4 weeks apart if administered after age 13 |
front 149 Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) | back 149 dose at 2,4,6, and 12-15 months |
front 150 hep A | back 150 2 doses 6 months apart after age 12 |
front 151 influenza vacinne | back 151 begin at age 6 months (october through november) |
front 152 meningococcal vaccine MCV4 | back 152 a dose at age 11-12 years |
front 153 MMR is contraindicated in? | back 153 pregnant women and children who are allergic to eggs, gelatin, and neomycin
|
front 154 DTAP is contraindicated in? | back 154 severe febrile illness
|
front 155 Hep B is contraindicated in? | back 155 prior hx of anaphylactic reaction
|
front 156 if you have a hypersensitivity to eggs can you get the influenza vaccine? | back 156 no, vaccine is grown in eggs and may contain small amount of egg proteins. conduct a skin test prior to administration |
front 157 adult influenza vaccine | back 157 annually after age 50, earlier if specific risk factors |
front 158 PPV adult | back 158 one dose at age 65 and revaccinate every 6-8 years after initial vaccination |
front 159 Immune globulins provide what immunity | back 159 passive immunity and provide gamma globulin antibodies
|
front 160 Immune globulins given- | back 160 within 6 days of measles exposure, 7 days of hep B exposure, and within 14 days of hep A exposure |
front 161 Interferon Alfa- Interleukin 2 | back 161 immunostimulant enhance host immune response and reduce proliferation of cancer cells |
front 162 Interleuken-2 is used to tx | back 162 hairy cell leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, malignant melanoma, AIDS |
front 163 S/E interleuken 2 | back 163 flu like sx, bone marrow suppression, alopecia, cardiotoxicty, neurotoxicity, hypotension |
front 164 meds to avoid while on interleuken 2 | back 164 antihypertensives, retrovir ( increase risk of neutropenia), theophylline |
front 165 storage and admin of interleuken 2 | back 165 store med in refrigerator and do not freeze. Administer at room temp. Do not shake vial. Admin subcutaneously or IM as prescribed. |
front 166 Immunosuppressants | back 166 cyclosporine, glucocorticoid, prednisone, cytotoxics, imuran, prograf, rehumatrex |
front 167 immunosupressants act- | back 167 suppression of the proliferation of b cells and t cells.
|
front 168 antiviral | back 168 famvir, inhibit viral replication, tx recurrent infections of genital herpes and acute herpes zoster |
front 169 zidovudine (AZT) retrovir | back 169 hiv inhib viral replication. Used in combin with other antiviral agents to HIV-1. |
front 170 antihistamine actions is on- | back 170 H1 receptors which results in blocking histamine release in the small blood vessels, capilaries, and nerves during an allergic reaction. |
front 171 antihistamines/pregnancy | back 171 contraindicated during the third trimester of pregnancy for mothers who are breastfeeding and for newborns. Newborns are sensitive to the sedation effects of this med |
front 172 Chemotherapy agents | back 172 cytoxan, methotrexate, rheumatrex,
|
front 173 s/e of chemo agents | back 173 bone marrow suppression
|
front 174 dosage for chemo agents should be | back 174 individualized |
front 175 when should a pt preparing for chemo select a hairpiece? | back 175 before the occurence of hair loss |
front 176 patient who has recieved immune globulins, whole blood, serum, and specific immune globulins, when should MMR vaccine be scheduled? | back 176 postponed 3-6 months. |
front 177 does tylenol have an antiinflammatory effect? | back 177 no, but it has analgesic and antipyretic effects |
front 178 salicylism | back 178 tinnitus, sweating, headache and dizziness, respiratory alkalosis |
front 179 when should aspirin be stopped before a scheduled surgery | back 179 1 week |
front 180 take aspirin with? | back 180 food, milk, water to reduce gastric discomfort |
front 181 Ketorolac | back 181 provides analgesia w/o anti-inflammatory. Ketorolac should ne used no more than 5 days. Usually started as a parenteral administration and then progresses to oral doses. |
front 182 not to exceed ___ g tylenol a day | back 182 4 g |
front 183 antidote of tylenol- | back 183 mucomyst |
front 184 pt on tylenol and coumadin- | back 184 places client at risk for bleeding, watch for bruising, petechia, hematuria, |
front 185 opiod agonist- morphine sulfate
| back 185 act on the mu receptors, produces analgesia, respiratory depression, euphoria, and sedation,
|
front 186 stop opiods if the clients RR is less than | back 186 12 bpm |
front 187 avoid use of opiods with? | back 187 CNS depressants (barbituates, benzo's, and consumption of alcohol) |
front 188 pt on morphine assess the clients bladder? | back 188 for distention by palpating the lower abdomen area every 4-6 hr |
front 189 morphine is contraindicated in | back 189 premature infants and after biliary tract surgery |
front 190 meperidine dosing | back 190 do not administer more than 600 mg/24 hr and limit its use to less than 48 hrs |
front 191 opiods/antihypertensives | back 191 don't, it can further lower BP... |
front 192 administer opiods | back 192 intravenously slowly over a period of 4-5 min, have narcan and resuscitation equipment available. |
front 193 administer opiods to client with cancer | back 193 on a fixed schedule around the clock, not when necessary |
front 194 fentanyl is 100 times more potent than | back 194 morphine |
front 195 agonist-antagonist | back 195 stadol and talwin
|
front 196 abstinenece syndrome- | back 196 cramping, htn, vomitting, may be precipitated when given to clients who are physically dependent on opiod agonsits. |
front 197 opiod antagonist- narcan | back 197 tx of opiod overdose
|
front 198 route to admin nalaxone | back 198 IV,IM, or SC. Do not administer orally. |
front 199 Adjuvant meds for pain | back 199 tricyclic antidepressants- elavil
|