Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 3 - Movement into and out of cells
front 1 Look at the definition of diffusion in the Key words box. Explain
what each of these words in the definition means: | back 1 a. net movement – the overall result of some
particles moving one way, but more |
front 2 When substances diffuse into and out of cells, which part of the cell must they move through? | back 2 cell membrane |
front 3 Describe three examples of diffusion in organisms. For each example, state whether the substance that is diffusing is a gas or a solute. | back 3 Any three from (or other correct examples):
|
front 4 Where does the energy for diffusion come from? | back 4 the kinetic energy of the particles |
front 5 Using what you know about how diffusion happens, explain each | back 5 a. At higher temperatures, particles have more kinetic energy and move faster. b. The greater the diffusion gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion. (Some learners may be able to explain this in terms of the larger number of moving particles in the area of high concentration, resulting in a greater net movement towards the area of low concentration.) c. Many small tubes have a larger surface area than a single large tube, which speeds up diffusion. d. This decreases the distance across which the particles have to travel, to get from the blood into the dialysis fluid, so it takes them less time. |
front 6 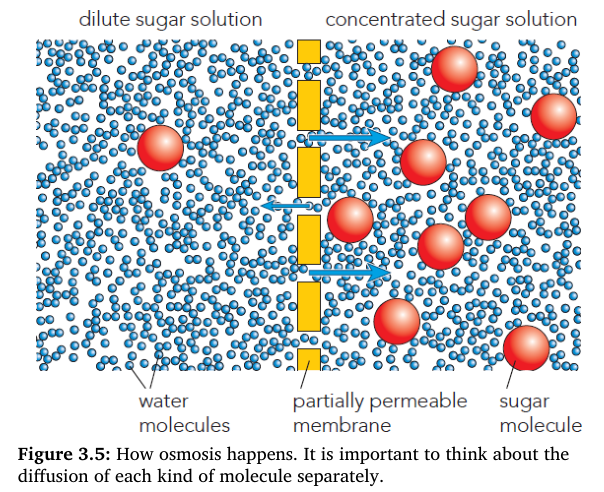 These questions are about the diagram in Figure 3.5. What is the solvent in the sugar solution? What is the solute? | back 6 Water is the solvent, and sugar is the solute. |
front 7  These questions are about the diagram in Figure 3.5. Explain why water molecules can move from one side of the membrane to the other, but sugar molecules cannot. | back 7 The water molecules are small enough to get through the holes in the membrane, but the sugar molecules are too big. |
front 8  These questions are about the diagram in Figure 3.5. In which direction is the net movement of water molecules? | back 8 From the dilute solution to the concentrated solution. |
front 9  These questions are about the diagram in Figure 3.5. Where does the energy come from, to cause this movement of water molecules? | back 9 The kinetic energy of the water molecules. |
front 10  In Figure 3.5, which solution has the higher water potential? Explain your answer. | back 10 The dilute solution has the higher water potential, because it
contains more water |
front 11 Copy and complete this sentence: When an animal cell is placed in pure water, water ____________________ the cell by ____________________ through the partially permeable cell ____________________. | back 11 When an animal cell is placed in pure water, water enters the cell by osmosis through the partially permeable cell membrane. |
front 12 Animal cells burst if they are placed in pure water, but plant cells do not. Explain why. | back 12 Plant cells have a strong cell wall surrounding the cell membrane, which stops the cell bursting. |
front 13 Here are some descriptions of what happens to a plant cell when it is placed in a concentrated solution. They are in the wrong order. Write the descriptions in the correct order.
| back 13
|
front 14 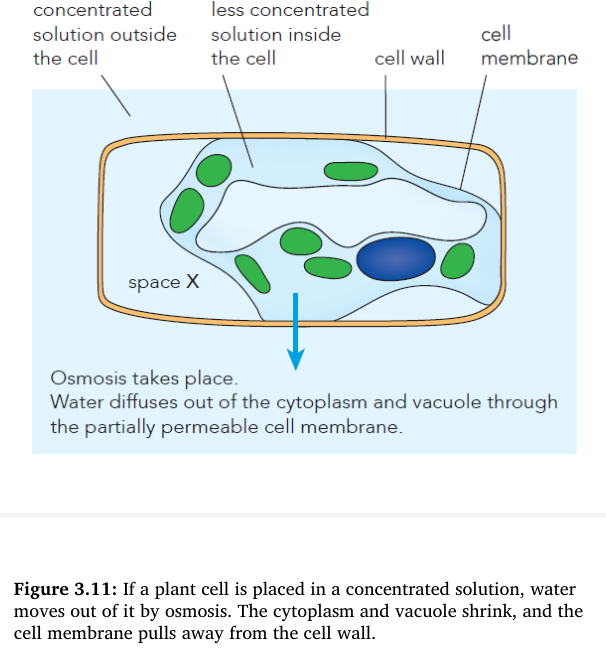 Look at Figure 3.11. What fills space X? Explain your answer. | back 14 The same solution that the cell is immersed in. The only thing between the external solution and space X is the cell wall, which is fully permeable. |
front 15 A group of plant cells has been placed in a concentrated solution, and the cells are plasmolysed. Predict what will happen if the cells are now placed in pure water. Explain your answer, using the term water potential. | back 15
|