Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 10 Practice Questions
front 1 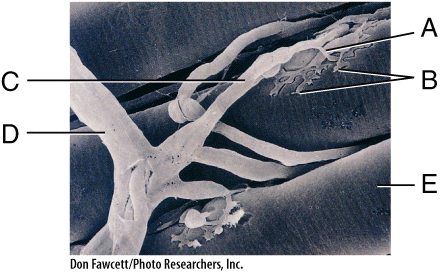 In the diagram, calcium ions will rush into this area. | back 1 B |
front 2 Which type of muscle tissue contracts when excited by their own autorhythmic muscle fibers? | back 2 cardiac muscle |
front 3 Which age group would be most susceptible to an increase in slow oxidative muscle fibers? | back 3 30+ years |
front 4 Which of the regions of a sarcomere contain titin? | back 4 from M line to Z disc |
front 5 What is the result of acetylcholine attaching to the ligand gates of the motor end plate? | back 5 The sarcolemma increases permeability to sodium |
front 6 Smooth muscle tone is maintained by the prolonged presence of [_____] in the muscle cell’s cytosol? | back 6 calcium ions |
front 7 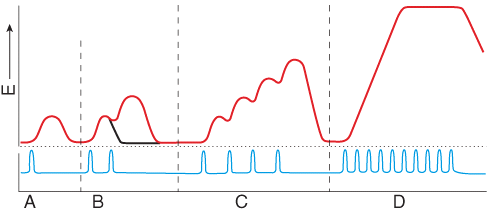 All of the muscle fibers within the muscle are fully contracted and are in sustained contraction with no individual twitches detected due to high frequency of stimulation. | back 7 D |
front 8 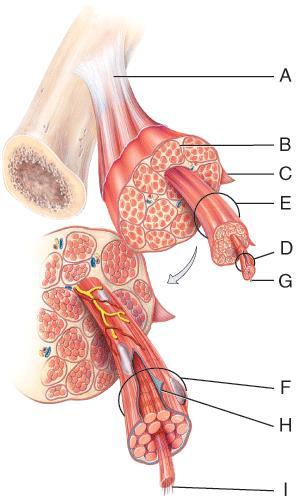 Which of the following structures are made of dense regular connective tissue? | back 8 A |
front 9 Which region of a sarcomere contain thin filaments? | back 9 Both I band and A band. |
front 10 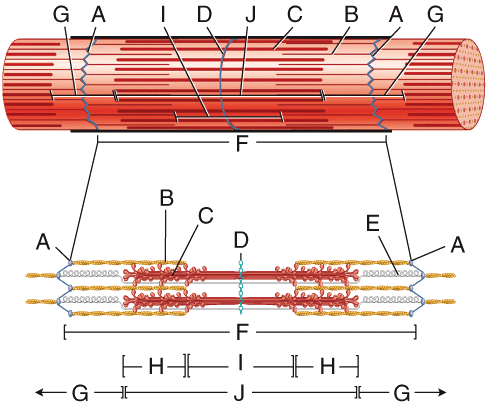 In the diagram, which structure(s) moves towards the center of the sarcomere (closer together) when the fiber contracts? | back 10 A |
front 11 At the neuromuscular junction, _______must enter the synaptic end bulb to stimulate the release of ____________, which binds to ligand gates so ________can enter the muscle fiber. | back 11 calcium ions; ACh, sodium ions |
front 12 When athletes is preparing to perform a pull up, they hang from the bar. At this point, they are performing what type of contractions? | back 12 Isometric |
front 13 For the muscle to contract and relax, what must be present (choose all that apply)? | back 13 ATP Calcium ions ACh |
front 14 Writer's cramp can occur in Anatomy and Physiology lecture class. What factor would most likely contribute to the muscles not being able to relax? | back 14 a deficit of ATP keeping myosin from detaching |
front 15 Which type of muscle tissue is capable of undergoing the stress-relaxation response when stretched? | back 15 single-unit smooth muscle fibers |
front 16 Muscle damage can be indicated by… | back 16 myoglobin found in blood. |
front 17 Which term describes a somatic motor neuron and all the skeletal muscle fibers it stimulates? | back 17 motor unit |
front 18 The relaxation phase of a muscle contraction is often prolonged in a fatigued muscle, raising the likelihood of fused summation of action potentials causing painful disturbances to a skeletal muscle. What disturbance is being described? | back 18 Cramp |
front 19 Which microscopic structure is found only in the cardiac muscle tissue? | back 19 intercalated discs |
front 20 Myofibrils contain what type of proteins? Select all that apply. | back 20 contractile proteins regulatory proteins structural proteins. |
front 21 Place the muscle tissue type in order from least to most ability to regenerate. | back 21 skeletal, cardiac, smooth |
front 22 What energizes the myosin head? | back 22 ATP hydrolysis reaction |
front 23 Motor unit recruitment occurs when there is _______ in the number of active motor units within a skeletal muscle. | back 23 Increase |
front 24 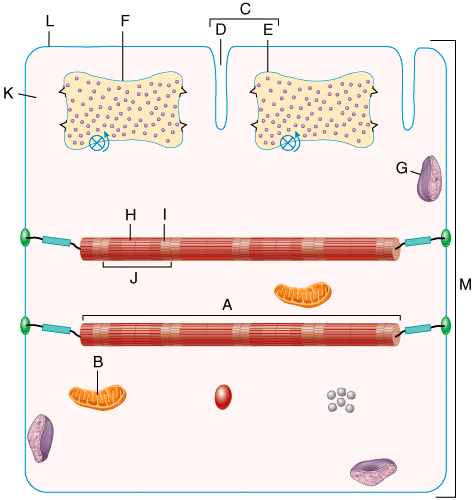 In the diagram, where would you find stored Ca2+? | back 24 F |
front 25 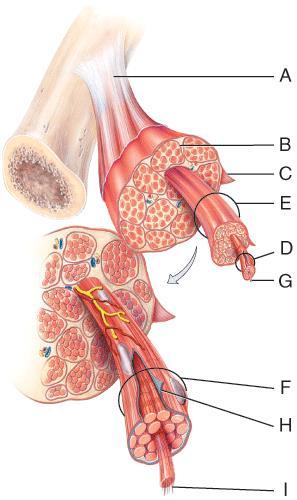 On the diagram, which layer is composed of dense irregular connective tissue and surrounds the entire muscle.? | back 25 C |
front 26 Which statement explains the sarcomere appearance change during a muscle contraction? | back 26 The light A bands remain at a constant length. |
front 27 During muscle contractions , thin filaments are pulled towards the | back 27 M line |
front 28 What proteins are found in thin filaments of skeletal muscle fibers? Select all that apply | back 28 tropomyosin myosin actin nebulin |
front 29 Strength training would result in | back 29 hypertrophy of fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers |
front 30 Which characteristics describe both skeletal and cardiac muscle? | back 30 Striations |
front 31 The outermost layer of connective tissue surrounding a skeletal muscle is the | back 31 Epimysium |
front 32 A brief contraction of all muscle fibers in a motor unit in response to a single action potential moving down the somatic motor neuron is known as | back 32 twitch contraction. |
front 33 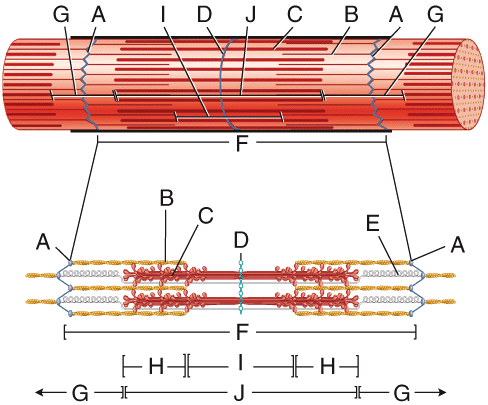 In the diagram, what structure contains motor proteins that convert the energy in ATP into mechanical movements? | back 33 C |
front 34 In skeletal muscles, the combined amounts of creatine phosphate and ATP provide enough energy for the muscle to contract maximally for approximately | back 34 15 seconds |
front 35 After prolonged strenuous exercise has stopped, heavy breathing will often continue for several minutes in order to provide the oxygen needed to | back 35 all of these choices are correct |
front 36 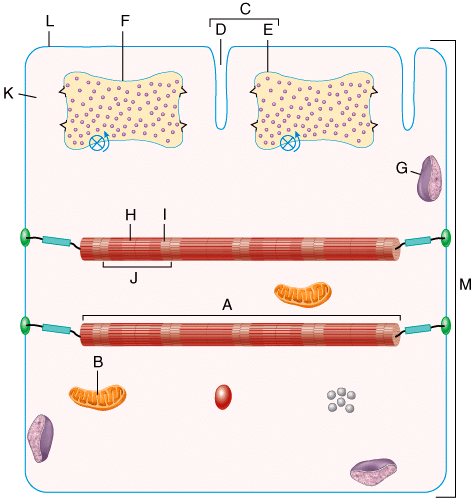 In the diagram, how do action potentials penetrate the outside of the muscle fiber? . | back 36 D |
front 37 Which correctly lists the sequence of structures that action potentials must move through to excite skeletal muscle contraction? | back 37 axon of neuron, sarcolemma, T tubules |
front 38 Which regions of the sarcomere contain thick filaments? Select all that apply. | back 38 zone of overlap A band H zone |
front 39 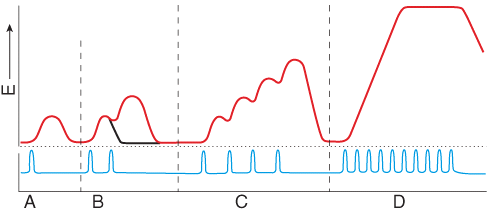 Which portion of this myogram shows a single twitch of the muscle? | back 39 A |
front 40 The zone of overlap increases during the | back 40 contraction period |
front 41  On the diagram, a tendon is formed by the merging of which structures? | back 41 C, D, and H |
front 42 Myasthenia Gravis is an autoimmune disorder that targets the ACh receptors at the NMJ and ultimately reduces the number of available receptors. Predict what happens if you treat the patient with a drug that inhibits the activity of acetylcholinesterase? | back 42 The drug will increase contraction. |
front 43 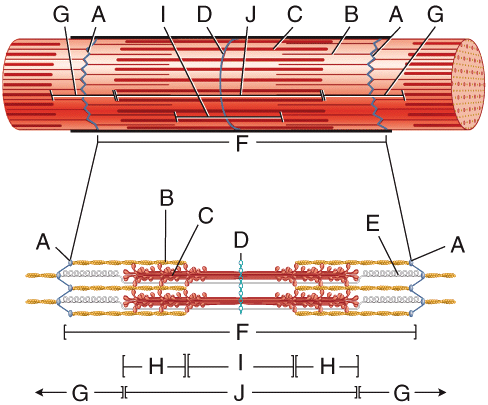 In the diagram, where are troponin, tropomyosin and nebulin located? | back 43 B |
front 44 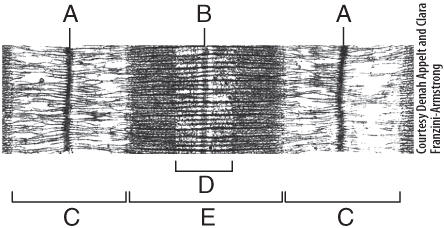 In the diagram, what area is composed of only thick filaments? | back 44 D |
front 45 Leg muscles are predominantly composed of which type of muscle fiber? | back 45 fast oxidative-glycolytic |
front 46 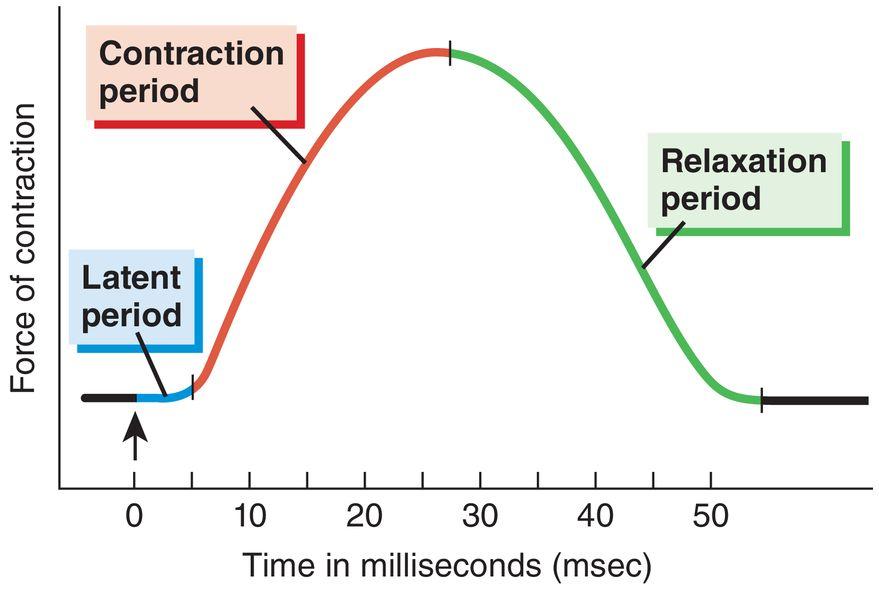 Diltiazem is a calcium channel blocker, reducing free intracellular calcium. What stage of the myogram would be affected immediately? | back 46 Latent period |
front 47 Which function do all three muscles perform? | back 47 Moving and storing material throughout the body |
front 48 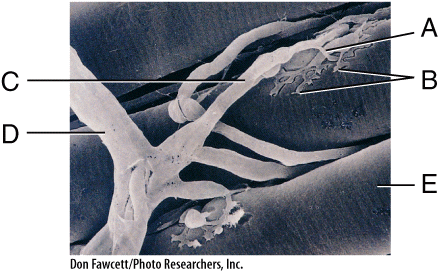 In the diagram, acetylcholine is released from ____ and diffuses to _____. | back 48 B; E |
front 49 Which functions as a motor protein in all three types of muscle tissue? | back 49 Myosin |
front 50 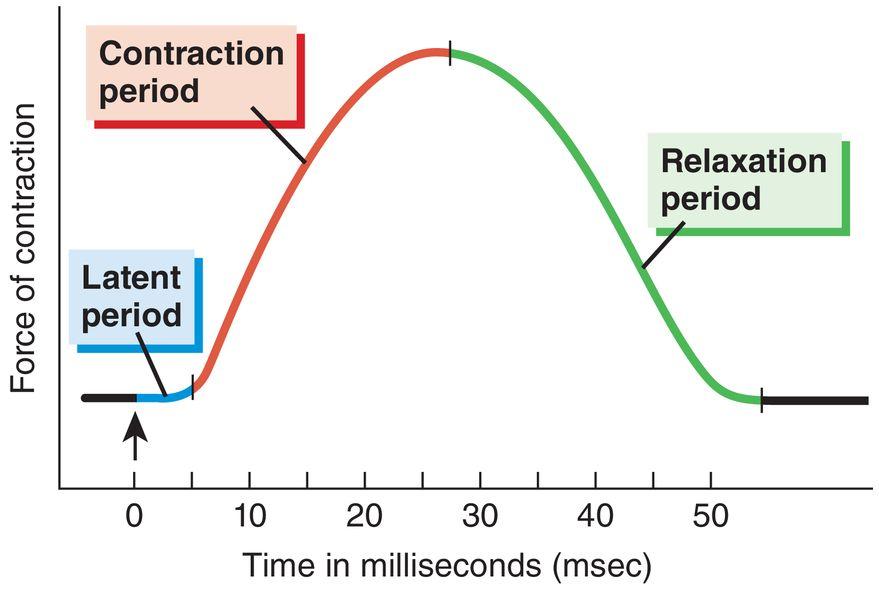 Thapsigargin is a potent calcium ATPase pump inhibitors. What state of the myogram would be affected immediately? | back 50 Relaxation period |
front 51 Why would cardiac muscles have longer refractory periods than skeletal muscles. Choose the best answer? | back 51 to preserve the normal rhythm of the heart and prevent fatigue |
front 52  In the diagram, which structure helps return a stretched sarcomere to its resting length? | back 52 E |
front 53 Which disorder occurs when little to no proteins are produced to support the sarcolemma? | back 53 muscular dystrophy |
front 54 When an athlete performs a pull up (raising their chin to a bar while their body hangs), the process of pulling the body up so the chin can touch the bar is | back 54 Concentric |
front 55 Contraction of myofibrils within a muscle fiber begins when | back 55 calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum |
front 56 In a neuromuscular junction, the effect of acetylcholine (ACh) binding to receptors on the motor end plate lasts only briefly due to | back 56 rapid destruction of ACh in the synaptic cleft by acetylcholinesterase. |
front 57 . Skeletal muscle contraction is triggered to begin when calcium is released from | back 57 terminal cisterns of sarcoplasmic reticulum |
front 58 Which ATP production would be sufficient to run in place for one minute? | back 58 anaerobic cellular respiration |
front 59 After the fusion of myoblasts, the muscle fiber loses its ability to | back 59 go through mitosis |
front 60 When an athlete performs a pull up (raising their chin to a bar while their body hangs), the process of lowering the body down is | back 60 Eccentric |
front 61 Mitochondrial activity in skeletal muscle cells are usually efficient, but can have limited ATP production if | back 61 there is limited O2 availability |
front 62 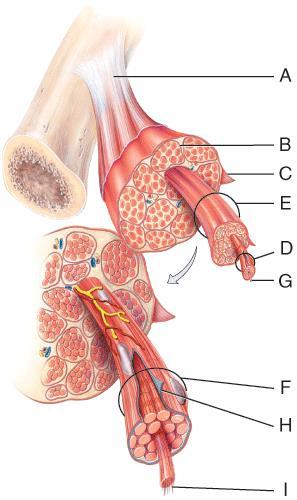 On the diagram, what structure is composed of the three connective tissue layers that extend past the muscle? | back 62 A |
front 63 Which protein is used to reinforce the sarcolemma and help transmit the tension generated by the sarcomeres to the tendons? | back 63 dystrophin |
front 64 Why will an individual who lifts weights build larger muscles? | back 64 skeletal muscles increase number of myofibrils but not number of cells |
front 65 Which property of muscle gives it the ability to stretch without damage? | back 65 Extensibility |
front 66 Cross bridges are formed during muscle contraction when _____ binds to _____. | back 66 myosin; actin |
front 67 The opening of ligand gates on the sarcolemma is directly caused by | back 67 all choices are correct |
front 68  In the diagram, what area contains both thick and thin filaments? | back 68 H |
front 69 For crossbridges to occur, what events must happen? Select all that apply. | back 69 ATPase breaks down ATP Calcium ions be present in the sarcoplasm Myosin binding sites be exposed. |
front 70 World class shot-putters will have a higher percentage of ______in their arm muscles. | back 70 fast glycolytic fibers |