Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Exercise 7
front 1 SKIN STRUCTURE | back 1 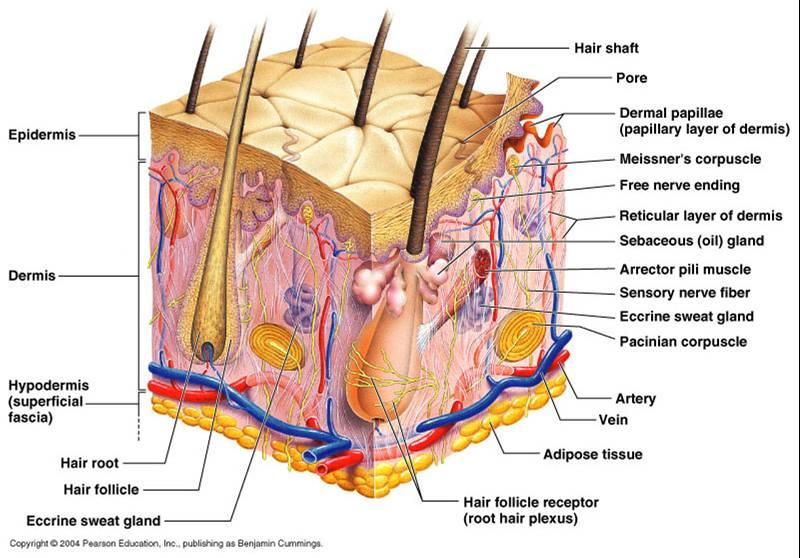 |
front 2 The main structural features in epidermis of the skin | back 2 |
front 3 The dense irregular connective tissue making up the dermis is made of two principle layers | back 3 1. Papillary Layer
|
front 4 More superficial dermal region composed of Areolar CT.
| back 4 Papillary Layer |
front 5 The deepest skin layer. Composed of dense irregular connective tissue and contains many arteries and veins, sweat and sebaceous glands, and pressure receptors (Pacinian Corpuscles) | back 5 Reticular Layer |
front 6 Bed sores (decubitus ulcers) | back 6 Occur in bedridden patients that are not turned regularly enough. The weight of the body exerts pressure on the skin, especially over bony projections, which leads to restrictions of the blood supply and tissue death. |
front 7 Decubitus Ulcers | back 7 in patients with, diabetes (Type II) or burns |
front 8 When in newborns a chemical called bilirubin rises high | back 8 Jaundice |
front 9 STRUCTURE OF THE NAIL | back 9 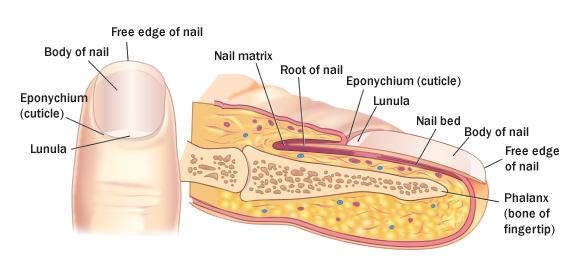 |
front 10 A single row of cells immediately adjacent to the dermis. Alternate name is Stratum germinativum, 10% to 25% are melanocytes, which thread their processes through this and the adjacent layers of keratinocytes. Also has Tactile cells in this layer. | back 10 Stratum Basale (Basal Layer) |
front 11 Several cell layers immediately superficial to the basal layer. cells in this layer appear spiky. | back 11 Stratum Spinosum (Spiky Layer) |
front 12 Contains granules of two types:
| back 12 Stratum Granulosum (Granular layer) |
front 13 Thin translucent band of flattened dead keratinocytes. This layer is found in the palm of hands and soles of the feet. | back 13 Stratum Lucidum (Clear Layer) |
front 14 Consists of 20-30 layers and accounts for the bulk of the epidermal thickness. This is the layer where you would find keratinized cells. | back 14 Stratum Corneum (Horny Layer) |
front 15 The external body covering, protects, insulates, cushions, regulates body temperature, metabolic duties | back 15 SKIN, OR INTEGUMENT |
front 16 Cells of the Epidermis | back 16 Keratinocytes, Melanocytes, Epeidermal dendritic cells (Langerhan's Cells), Tactile Cells |
front 17 Skin Color | back 17 melanin, brown pigment
|
front 18 Jaundice | back 18 tissue becomes yellowed, is almost always diagnostic for liver disease. |
front 19 Addison's Disease | back 19 bronzing of the skin hints that a person's adreanl cortex is hypoactive. |
front 20 Parts of the Nail | back 20 Body: The visible attached portions.
|
front 21 Parts of the Nail | back 21 Nail Bed: Extension of the stratum basale beneath the nail.
|
front 22 Small bands of smooth muscle cells connect each hair follicle to the papillary layer of the dermis.
| back 22 Arrector Pili Muscle |
front 23 A small nipple of dermal tissue that protrudes into the hair bulb from the connective tissue sheath and provides nutrition to the growing hair. | back 23 Papilla |
front 24 Eccrine Glands (merocrine sweat glands) | back 24 distributed all over the body.
|
front 25 Appocrine Glands | back 25 found predominately in the axillary and genital areas, these glands secrete a milky protein- and a fat- rich substance excellent nutrient medium for bacterium. and sex glands, secretes pheromones for some animals. |
front 26 Cutaneous Glands | back 26 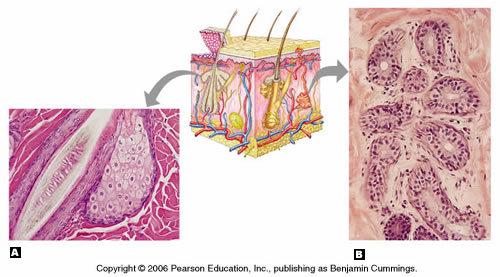 |
front 27 Blackheads | back 27 are accumulations of dried sebum, bacteria, and melanin from epithelial cells in the oil duct. |
front 28 Acne | back 28 is an active infection of the sebaceous glands. |