Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Bio 112: Chapter 54
front 1 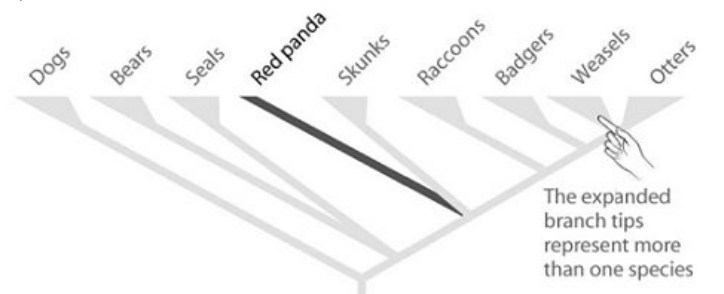 According to the accompanying figure, which of the following explains why the red panda is an important species to preserve? A) Red pandas are a symbol of conservation efforts. B) Red pandas live in areas that are critically endangered. C) Seals are more important to preserve than the red panda because the ocean environment is critically endangered. D) Phylogenetically distinct species are high-priority species to target for conservation. | back 1 D. Phylogenetically distinct are high priority species to target for conservation |
front 2 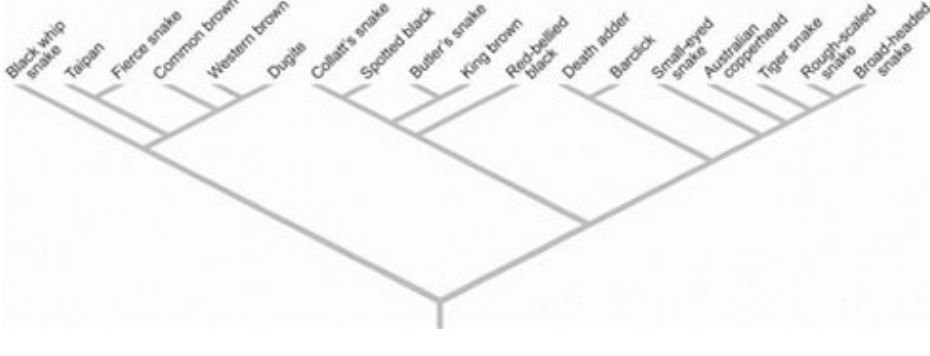 By knowing the interrelatedness of various snake species, the appropriate antivenom can be chosen. Based on the accompanying figure, which snake antivenom would you administer to a person bitten by an Australian copperhead, if antivenom to the Australian copperhead were not available? A) taipan B) common brown snake C) red-bellied black snake D) death adder E) tiger snake | back 2 E. tiger snake |
front 3  Based on the accompanying figure, what snake antivenom would you administer to a person bitten by a king brown snake if king brown snake antivenom were not available? A) taipan B) common brown snake C) red-bellied black snake D) death adder E) tiger snake | back 3 C. red-bellied black snake |
front 4 Philippe Bouchet and colleagues conducted a massive survey of marine mollusks on the west coast of New Caledonia. Twenty percent of the species found had only a single specimen collected. What does that suggest about the diversity of mollusks in this area? A) The west coast of New Caledonia is not an appropriate habitat for mollusks. B) They did not spend enough time sampling in the area. C) Many of the species from this 20 percent are probably rare. D) They were not sampling uniformly throughout the area. E) Many of the species from this 20 percent are most likely just dispersing through the area. | back 4 C) Many of the species from this 20 percent are probably rare. |
front 5 Which one of the following is LEAST likely to be a hot spot for birds? A) Amazon River basin B) East Africa C) Southwest China D) Greenland | back 5 D) Greenland |
front 6 If all individuals in the last remaining population of a particular bird species were all highly related, which type of diversity would be of greatest concern when planning to keep the species from going extinct? I. genetic diversity II. species diversity III. ecosystem diversity A) only I B) only II C) only III D) only II and III E) I, II, and III | back 6 A) only I |
front 7 What is the biological significance of genetic diversity between populations? A) Genes for traits conferring an advantage to local conditions make evolution possible. B) The population that is most fit would survive by competitive exclusion. C) Genetic diversity allows for species stability by preventing speciation. D) Isolated populations become more fit. E) Diseases and parasites are not spread between separated populations. | back 7 A) Genes for traits conferring an advantage to local conditions make evolution possible. |
front 8 Which of the following is a TRUE statement regarding species diversity and taxonomic diversity? A) Species diversity measures the relative frequency of all alleles present in a species. B) In taxonomic diversity, the number of species in a lineage is important. C) In species diversity, the number of animals in a particular lineage is important. D) The variety of species in a given area represents taxonomic diversity. | back 8 B) In taxonomic diversity, the number of species in a lineage is important. |
front 9 With regard to the destruction of tropical forests, the focus is often on biodiversity and the impact on these ecosystems. What is a direct benefit to humans that helps explain why these forests need to be preserved? A) This diversity could contain undocumented insect species. B) Natural and undisturbed areas are important wildlife habitats. C) The diversity could contain novel drugs for consumers. D) The plant diversity provides shade, which reduces the impact of global warming. | back 9 C) The diversity could contain novel drugs for consumers. |
front 10 Which of the following terms includes all of the others? A) species diversity B) biodiversity C) genetic diversity D) ecosystem diversity E) species richness | back 10 B) biodiversity |
front 11 During the inventory of bacterial genes present in the Sargasso Sea in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean, a research team concluded that at least 1800 bacterial species were discovered. Based on what you know about this area, what would you expect to see in coral reef waters? A) slightly greater genetic diversity B) slightly smaller genetic diversity C) equal genetic diversity D) markedly greater genetic diversity E) markedly smaller genetic diversity | back 11 D) markedly greater genetic diversity |
front 12 Which of the following ecological locations has the greatest species diversity? A) tundra B) deciduous forests C) tropical rain forest D) grasslands E) islands | back 12 C) tropical rain forest |
front 13 Erwin and Scott used an insecticidal fog to knock down insects from the top of a L. seemannii tree. The researchers identified over 900 species of beetles among the individuals that fell. Erwin also projected that this entire tree is host to about 600 arthropod species unique to this tree species. There are approximately 50,000 species of tropical trees. Although it could not be entirely accurate, what would be the best way to estimate the total number of arthropod species? A) Estimate the species density and then multiply by 50,000. B) Multiply 900 by 50,000. C) Multiply 600 by 50,000. D) Divide 900 by 600 and then multiply by 50,000 | back 13 C) Multiply 600 by 50,000. |
front 14 Relatively small geographic areas with high concentrations of endemic species and a large number of endangered and threatened species are known as ________. A) endemic sinks B) critical communities C) biodiversity hot spots D) endemic metapopulations E) bottlenecks | back 14 C) biodiversity hot spots |
front 15 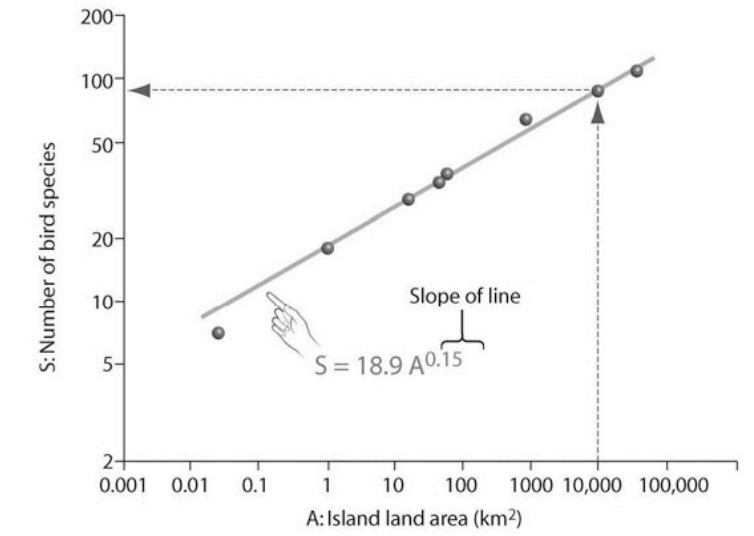 In looking at the species—area plot in the accompanying figure, what can be concluded? A) The number of bird species increases linearly with island area. B) The number of bird species remains the same on these various islands. C) Diversity is independent from island area. D) The number of bird species increases exponentially with island area | back 15 A) The number of bird species increases linearly with island area |
front 16 Based on the species—area plot in the accompanying figure, if habitable area on an island were reduced from 10,000 km2 (square kilometers) to 1000 km2, roughly what percentage of the species would disappear? A) 0.3 percent B) 3 percent C) 30 percent D) 60 percent | back 16 C) 30 percent |
front 17 Which of the following statements regarding extinction is (are) correct? I. Only a small percentage of species is immune from extinction. II. Extinction occurs whether humans interfere or not. III. Extinctions can be caused indirectly by humans. A) only I B) only II C) only III D) only II and II | back 17 D) only II and II |
front 18 Which of the following criteria have to be met for a species to qualify as invasive? A) endemic to the area, spreads rapidly, and displaces foreign species B) introduced to a new area, spreads rapidly, and displaces native species C) introduced to a new area, spreads rapidly, and displaces other invasive species D) endemic to the area, spreads slowly, and displaces native species | back 18 B) introduced to a new area, spreads rapidly, and displaces native species |
front 19 A land developer and several ecologists are discussing how a parcel of private land should be developed while saving 20 hectares as natural habitat. The land developer suggests that the 20 hectares be divided into twenty separate 1-hectare areas. The ecologists suggest that it would be better to have one intact parcel of 20 hectares. What is the significance of these different arrangements of the 20 hectares? A) There really is no difference; they should both work equally well. B) The isolated hectare plots increase the ability of individuals to disperse from one habitat to another. C) The isolated plots are more vulnerable to edge effects. D) The large plot will create more inbreeding in many species | back 19 C) The isolated plots are more vulnerable to edge effects. |
front 20 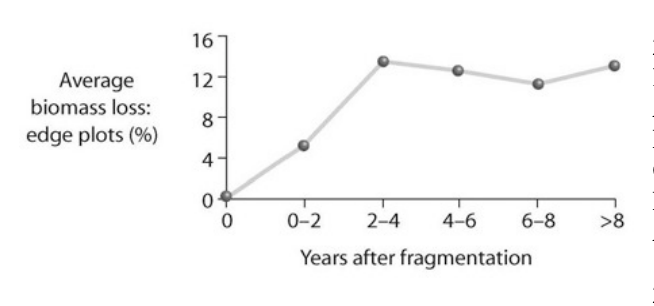 Looking at the accompanying figure, what can be said about edge effects? A) Biomass declines along edges of forest fragments. B) Biomass increases along the edges of forest fragments. C) Species diversity decreases along the edges of forest fragments. D) Fragmentation does not affect biomass. | back 20 A) Biomass declines along edges of forest fragments. |
front 21 The main factor that leads to the loss of biodiversity is ________. A) habitat fragmentation B) habitat destruction C) industrialization D) transportation | back 21 B) habitat destruction |
front 22 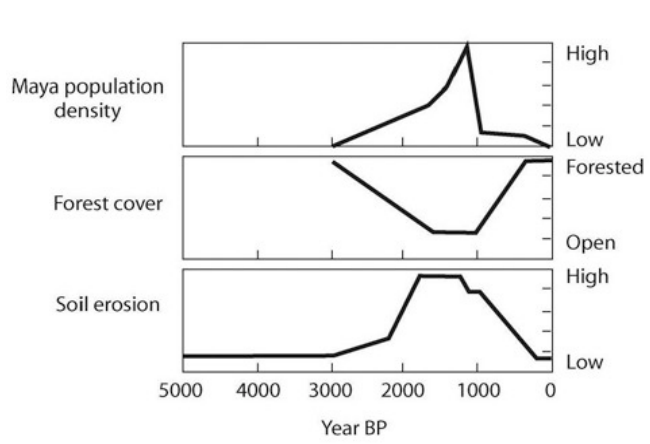 Based on the accompanying figure, what can you conclude about the history of land use in the southern Yucatán? A) Massive soil erosion caused the Mayan population to crash. B) Reduction in forest cover caused the Mayan population to crash. C) As Mayan population increased, deforestation increased, probably leading to increased soil erosion. D) This Mayan population practiced sustainable developmen | back 22 C) As Mayan population increased, deforestation increased, probably leading to increased soil erosion. |
front 23 Although extinction is a natural process, current extinctions are of concern to environmentalists because ________. A) more animals than ever before are going extinct B) most current extinctions are caused by introduced species C) the rate of extinction is higher than background extinction rates D) current extinction is primarily affecting plant diversity | back 23 C) the rate of extinction is higher than background extinction rates |
front 24 According to most conservation biologists, the single greatest threat to global biodiversity is ________. A) chemical pollution of water and air B) stratospheric ozone depletion C) overexploitation of certain species D) alteration or destruction of the physical habitat | back 24 D) alteration or destruction of the physical habitat |
front 25 The introduction of the Burmese python by pet owners in Florida has resulted in ________. A) eradication of nonnative rats and other undesirable/pest species B) the threatening of many native species C) a good lesson in biological control D) a new species of hybrids from crossbreeding with a native snake species E) its failure to compete with native species and its quick elimination | back 25 B) the threatening of many native species |
front 26 Approximately what percentage of bird species are on the IUCN Red List? A) 0 percent B) 13 percent C) 23 percent D) 33 percent E) 53 percent | back 26 B) 13 percent |
front 27 What type of ecosystem is most harmed by pollution? A) freshwater B) ocean C) tropical rain forest D) temperate forest | back 27 A) freshwater |
front 28 ) The most serious consequence to humans of a decrease in global biodiversity would be the ________. A) increase in global warming and thinning of the ozone layer B) potential loss of ecosystem services on which people depend C) increase in the abundance and diversity of edge-adapted species D) loss of sources of genetic diversity to preserve endangered species E) loss of species for use as crops | back 28 B) potential loss of ecosystem services on which people depend |
front 29 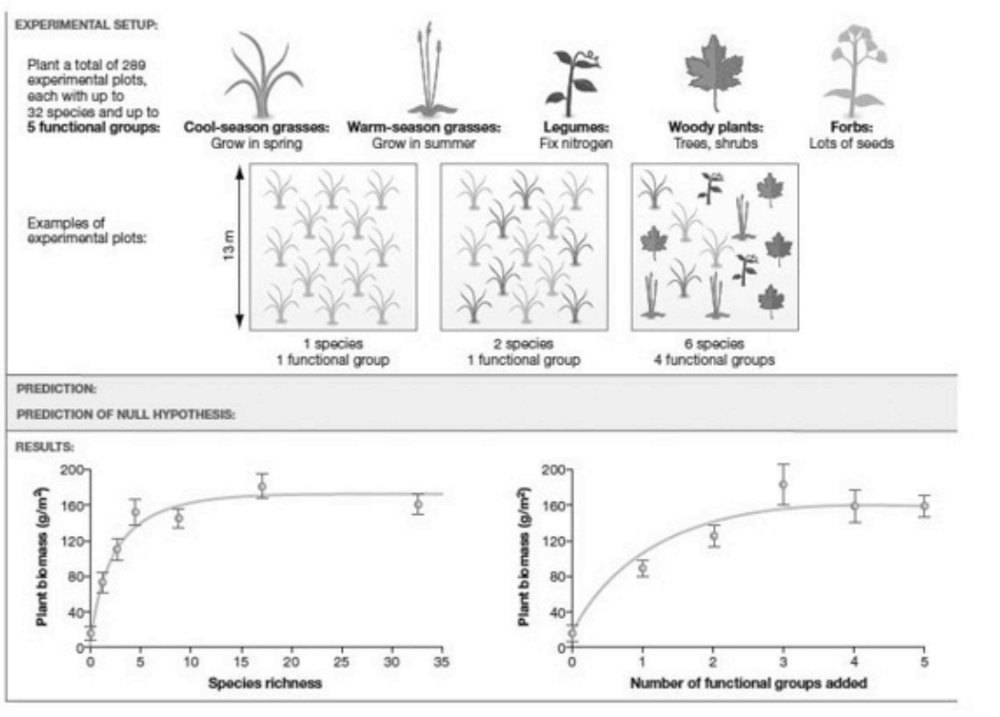 Use the accompanying figure to answer this question: What two variables were manipulated? A) plant biomass and species richness B) plant biomass and number of functional groups C) number of functional groups and species richness D) plot size and plant biomass | back 29 C) number of functional groups and species richness |
front 30  Use the accompanying figure to answer this question: What factors have a positive effect on plant biomass, based on the data presented? A) plot number and species richness B) No factors have a positive effect on plant biomass. C) number of functional groups and species richness D) plot size and type of plants in plot | back 30 C) number of functional groups and species richness |
front 31 Net primary productivity is important because ________. A) it is the source of chemical energy used by a species throughout a food web B) It is not important because of the inefficiency of energy flow through food webs. C) it leads to lower biodiversity within small areas D) it can lead to the expiration of more CO2 into the atmosphere by plants | back 31 A) it is the source of chemical energy used by a species throughout a food web |
front 32 In prairies, the presence of plants in the onion family may discourage herbivores within the prairie. This is an example of ________. A) facilitation B) resource use efficiency C) competition D) predation | back 32 A) facilitation |
front 33 Community stability refers to ________. A) the ability of a community to maintain productivity and other aspects of ecosystem function as conditions change over time and to recover to former levels of productivity or species richness after a disturbance B) the extent to which a community remains unchanged during a disturbance C) how quickly a community recovers following a disturbance D) how many species are in the community | back 33 A) the ability of a community to maintain productivity and other aspects of ecosystem function as conditions change over time and to recover to former levels of productivity or species richness after a disturbance |
front 34 Community resistance refers to ________. A) the ability of a community to maintain productivity and other aspects of ecosystem function as conditions change over time and to recover to former levels of productivity or species richness after a disturbance B) the extent to which a community remains unchanged during a disturbance C) how quickly a community recovers following a disturbance D) how many species are in the community | back 34 B) the extent to which a community remains unchanged during a disturbance |
front 35 Community resilience refers to ________. A) the ability of a community to maintain productivity and other aspects of ecosystem function as conditions change over time and to recover to former levels of productivity or species richness after a disturbance B) the extent to which a community remains unchanged during a disturbance C) how quickly a community recovers following a disturbance D) how many species are in the community | back 35 C) how quickly a community recovers following a disturbance |
front 36 Which of the following is a regulating service of ecosystems? A) soil formation B) recreation C) nutrient cycling D) providing genetic resources E) education | back 36 A) soil formation |
front 37 Which of the following is a provisioning service of ecosystems? A) soil formation B) recreation C) nutrient cycling D) providing genetic resources E) education | back 37 D) providing genetic resources |
front 38 Which of the following is a cultural service of ecosystems? A) soil formation B) climate moderation C) nutrient cycling D) providing genetic resources E) education | back 38 E) education |
front 39 Which of the following have an impact on decisions about humans mitigating the extinctions and damages to ecosystem services? I. Moral issues II. Economic problems III. Biological problems A) I and II only B) II and III only C) III only D) I, II, and III | back 39 D) I, II, and III |
front 40 What is TRUE concerning the high consumption of fossil fuels? A) It has no effect on biodiversity. B) It affects biodiversity by directly harming species. C) It affects biodiversity indirectly via climate change. D) It affects biodiversity both directly and indirectly via climate change. E) It affects biodiversity indirectly via decreases in CO2 emissions. | back 40 D) It affects biodiversity both directly and indirectly via climate change. |